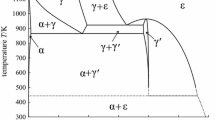
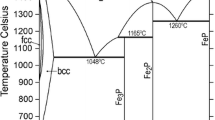
Abstract
In this work, a thermodynamic analysis of the Al-C-Fe system is carried out covering a wide tem-perature range. The sublattice model of Hillert for the solution phases and the Redlich-Kister-Mug-gianu formalism for the interaction parameters are used. The binary and ternary interaction parameters and the Gibbs energies of formation of the carbides are obtained by optimization of the thermochemical and the phase diagram data. The results include a liquidus projection, details of the four-phase invariant reactions, a reaction table, and eight isothermal sections covering the tempera-ture range from 2000 °C to 800 ’C.
Similar content being viewed by others
Cited References
J.R. Lee, “Liquidus-Solidus Relations in the System Iron-Aluminum,”J. Iron and Steel lnst., 194,222–224(1960). (#)
S.V. Radcliffe, B.L. Averbach, and M. Cohen, “Relative Thermodynamic Properties of Solid Iron-Aluminum Alloys,”Acta Metall., 9,169–176(1961).
J. Eldrige and K.L. Komarek, “Thermodynamic Properties of Solid Iron-Aluminum Alloys,”Trans. Metall. Soc. AIME, 230, 226–233(1964).
L. Rimlinger, A. Pianelli, and R. Faivre, “Transformations in Solid Fe-Al Alloys in the Composition Range of 20–40 at% Al,”Compt. Rend., 260,148–151 (1965) in French. (#)
A.N. Sinha and L.J. Balasundaram, “Curie Temperature of Iron-Aluminum and Iron-Silicon Alloys,”Trans. Indian Inst. Met., 20(3), 21–24(1967).
K. Nishida, “A Study of Fe-Al-C Alloys,”Hokkaido Diagaku Kogakubu Kenkyu Hokoku,(48),71-108(1968)inJapanese.(#)
M. Hillert and L.I. Staffansson, “The Regular Solution Model for Stoichiometric Phases and Ionic Melts,”Acta Chem. Scand., 24, 3618–3626(1970).
L. Kaufman and H. Bernstein,Computer Calculation of Phase Diagrams, Academic Press,New York, 184–185(1970).
G.I. Batalin, E.A. Beloborodova, VA. Stukalo, and L.V. Goncharuk, “Thennodynamic Properties of Liquid Aluminum-Iron Alloys,”Zh. Fis. Khim., 45(8), 2007–2009 (1971) in Russian; TR:Russ.J. Phys. Chem, 45(8), 1139-1140(1971).
P. Rocquet, J.C. Petit, and G. Urbain, “The γ-loop of the Fe-Al System,”.Iron and Steel lnst., 209,69–70(1971). (#)
V.G. Dyubanov, A.Ya. Stomakhin, and A.F. Filippov, “Enthalpies of Formation of Iron, Cobalt and Nickel Based Dilute Solutions,”Izv. V.U.Z. ChemayaMeta.lt, (3),5-7(1975)inRussian.
U.V. Choudary and G.R. Belton, “Activities in Carbon-Saturated Fe-Al Alloys and the Stability of AI4C3 at 1873 K,”Metall Trans. B, 8,531–534(1977).
E. Ichise, T. Yamauchi, and T. Mori, “Knudsen Cell-Mass Spectrometric Study of the Thermodynamics of the Iron-Aluminum Alloys,”Tetsu-to-Hagane, 63(3), 417–424(1977) inJapanese.
K.W. Maring, A.J. Algra, F. Stubbe, and F. Van Der Woude, “Some Aspects of a Study of Dilute FeX Alloys withX the Nontransition Elements Al, Si, Ga, Ge, As, Sn, and Sb,”Physica, 86–88B, 437–438(1977).
M. Hillert and M. Jarl, “A Model for Alloying Effects in Ferromagnetic Metals,”Calphad, 2(3), 227–238 (1978).
K. Motzfeldt and B. Sandberg,Light Metals 1979, S. Peterson, Ed., The Metallurgical Society of AIME, Warrendale, PA, 411–428 (1979). (#)
G.H. Rinehart and R.G. Behrens, “Vaporization Thermodynamics of Aluminum Carbide,”J. Chenu Thermodyn., 12,205–215 (1980).
VS. Sudatsova and G.I. Batalin, “The Activity of Aluminum in Iron-Based Liquid Alloys,”Ukr. Khim. Zk, 46(3), 268–270 (1980) in Ukrainian; TR:Ukr. Chenu J., 46(3), 46–48 (1980).
O. Kubaschewski, “Iron-Aluminum,”Iron-Binary Phase Diagrams, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 5–9 (1982). (#)
A.F. Guillemet and P. Gustafson, “An Assessment of the Thermodynamic Properties and P,T Phase Diagrams of Iron,”High Temp.—HighPress., 16,591–610(1985).
P. Gustafson, “A Thennodynamic Evaluation of the C-Fe System,”Scand J. Metall, 14(5), 259–267 (1985). (#)
P. Gustafson, “An Evaluation of the Thennodynamic Properties andRTPhase Diagram of Carbon,”Carbon, 24,169–176(1986).
E. Schuermann and J. Von Schweinichen, “Study of the Melt Equilibria for Iron-Rich Ternary Fe-C-Xi Alloys with Xi=Al, Cu, Ni, andCr,”Giessereiforschung, 38(4),,125–132(1986) in German.(#)
P.D. Desai, “Thennodynamic Properties of Selected Binary Aluminum Alloy Systems,”J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data, 16(1), 109–124 (1987).
J.L. Murray, A.J. McAlister, R. J. Schaefer, L.A. Bendersky, F.S. Biancaniello, and D.L. Moffatt, “Stable and Metastable Phase Equilibria in the Al-MnSystem,”Metall. Trans.A, 18,385–392(1987).
L.L. Oden and R.P. Beyer, “Heat Capacity of 2Al4C3-SiC from 447 to 1447 K and Enthalpy of Peritectic Decomposition of AI4C3, 2Al4C3SiC,and AI4C3SiC,”Thermochim.Acta, 115,11–19(1987).
L.L. Oden and R. A. McCune, “Phase Equilibria in the Al-Si-C System,”Metall. Trans.A, 18,2005–2014(1987). (#)
V. Raghavan, “The Al-C-Fe (Aluminum-Carbon-Iron) System,”Phase Diagrams of Ternary Iron Alloys, Part 1, American Society for Metals, Metals Park, OH, 89–97(1987). (#)
H. Yokokawa, M. Fujishige, S. Ujiie, and M. Dokiya, “Phase Relations Associated with the Aluminum Blast Furnace: Aluminum Oxycarbide Melts and Al-C-X(X = Fe.Si) Liquid Alloys,”Metall Trans. B, 18,433–444 (1987). (#)
L.L. Oden, “Phase Equilibria in the Al-Fe-C System: Isothermal Sections 1550 °C and 2300°C,”Metall Trans. A, 20, 2703–2706 (1989). (#)
CJ. Simensen, “Comments on the Solubility of Carbon in Molten Aluminum,”Metall. Trans. A, 20,191 (1989).
M. Palm, “The Constitution of the Fe-Al-C System,” Doctoral thesis, University Dartmund, 1–72 (1990) in German. (#) indicates presence of a phase diagram.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, K.C.H., Raghavan, V. A Thermodynamic Analysis of the Al-C-Fe System. JPE 12, 275–286 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02649916
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02649916