Summary
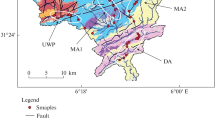
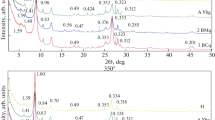
Results of extensive investigations carried out by the authors on the microstructures of genetic types of clay soils differing in composition, age and degree of compaction are presented. Clays of marine, lacustrine, alluvial, glacial, glacial-lacustrine and eluvial origin have been studied. Investigations were carried out with the help of scanning electron microscopy and the X-ray method. The data obtained have made it possible to ascertain that each genetic type of clay-soil has its characteristic microstructure, which confirms the close interrelation of the microfabric of clay sediments with the conditions of their formation and their subsequent transformation in the course of compaction.
Résumé
Les auteurs présentent les résultats de plusieurs années de recherches concernant les microstructures de roches argileuses de divers types génétiques différant par leur composition, leur âge et leur degré de compaction. Des argiles d’origine marine, lacustre, alluviale, glaciaire, lacustro-glaciaire et éluviale ont été étudiées. Les recherches furent réalisées à l’aide du microscope électronique à balayage et par la méthode des rayons X. Les données obtenues ont permis d’établir qu’à chaque type génétique de roches argileuses correspondent des particularités défines de leurs microstructures ce qui confirme une corrélation étroite de la microstructure des sédiments argileux avec les conditions de leur formation et de leur transformation ultérieure au cours de leur compaction.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
AYLMORE L.A. — QUIRK J.P. (1960): Domain or Turbostratic Structure of Clays. Nature, 187.
BARDEN L. — SIDES G. (1971): Sample Disturbance in the Investigation of Clay Structure. Geotechnique, 21, 3.
CASAGRANDE A. (1932): The Structure of Clay and its Importance in Foundation Engineering. J. Boston Soc. Civil Eng., 19.
GILLOT J.E. (1969): Study of the Fabric of Fine-grained Sediments with the Scanning Electron Microscopy. J. Sedim. Petrology, 39, 1.
GORKOVA I.M. (1966): Theoretical Fundaments for the Evaluation of Sedimentary Rocks for Engineering Geological Purposes (in Russ.). Moscow, “Nauka” Publ.
KOTLOV V.F. (1976): Estimation of the Microfabrics of Clay Soils from the Data of Diffractometric Analysis (in Russ.) Cand. thesis. Moscow, MGU.
OSIPOV V.I. (1976): Physico-chemical Nature of the Strength and Deformation Properties of Clay Soils (in Russ.). Doctoral thesis. Moscow, MGU.
OSIPOV V.I. — SOKOLOV V.N. (1976): Preparation of Clay Samples for Microstructure Studies (in Russ.). Proc. XI All-Union Conf. on Studies and Utilization of Clays and Clay Minerals. Moscow, pp. 211–212.
PUSCH R. (1971) : Microstructural Features of Pre-Quaternary Clays. Acta Universitatis Stockholmiensis, Stockholm Cont. in Geol., v. 24, 2.
SERGEYEV YE.M. — GRABOWSKA-OLSZEWSKA B. — OSIPOV V.I.—SOKOLOV V.N. (1978) : Types of the Microstructures of Clayey Soils. Proc. III Intern. Conf. of Eng. Geology. Madrid.
TERZAGHI K. (1925) : Erdbaumechanik auf bodenphysikalischer Grundlage. (in German.) Franz. Deutsche Presse, Leipzig und Wien.
TOVEY N.K.—JAN W.K. (1973) : The Preparation of Soils and Other Geological Materials for the SEM. Proc. Intern. Symp. on Soil Structure, Gothenburg.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Osipov, V.I., Sokolov, V.N. Relation between the microfabric of clay soils and their origin and degree of compaction. Bulletin of the International Association of Engineering Geology 18, 73–81 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02635351
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02635351