Abstract
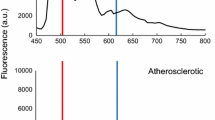
A study of the potential of laser-induced fluorescence for the characterization of human atherosclerotic plaque is reported. Pathologically-characterized specimens from autopsies were investigated using a pulsed nitrogen laser (λ=337 nm) as the excitation source and an optical multichannel analyser for the analysis of the fluorescence. Characteristic spectral features at 395, 420, 450 and 480 nm were utilized in forming different dimensionless contrast functions which were tested for discrimination properties. Plaque from aorta and coronary arteries was examined and could clearly be differentiated from the surrounding, histologically normal vessel wall. Imaging fluorescence measurements, processed for contrast enhancement, are also reported. Implications for spectroscopically guided laser angioplasty are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Isner JM, Clarke RH. The current status of lasers in treatment of cardiovascular disease.IEEE J Quant Electr 1984,QE-20:1406–20
Prince MR, Deutsch TF, Mathews-Roth MM et al. Preferential light absorption in atheromas in vitro.J Clin Invest 1986,78:295–302
Kittrell C, Willett RL, de los Santos-Pacheo C et al. Diagnosis of fibrous arterial atherosclerosis using fluorescence.Appl Opt 1985,24:2280–1
Cothren RM, Hayes GB, Kramer JR et al. A multifiber catheter with an optical shield for laser angiosurgery.Lasers Life Sci 1986, 1:1–12
Kato H, Cortese DA. Early detection of lung cancer by means of hematoporphyrin derivative fluorescence and laser photoradiation.Clin Chest Med 1985,6:237–53
Ankerst J, Montán S, Svanberg K, Svanberg S. Laser-induced fluorescence studies of hematoporphyrin derivative (HPD) in normal and malignant tissue of rat.Appl Spectr 1984,38:890–6
Svanberg K, Kjellén E, Ankerst J et al. Fluorescence studies of hematoporphyrin derivative in normal and malignant rat tissue.Cancer Res 1986,46:3803–8
Montán S, Svanberg K, Svanberg S. Multicolor imaging and contrast enhancement in cancer-tumor localization using laser-induced fluorescence in hematoporphyrin-derivative-bearing tissue.Opt Lett 1985,10:56–8
Andersson PS, Montán S, Svanberg S. Multi-spectral system for medical fluorescence imaging.IEEE J Quant Electr 1987,QE-23 (10)
Andersson PS, Kjellén E, Montán S et al. Autofluorescence of rodent tissues and some human skin samples.Lasers Med Sci 1987,2:41–9
Andersson PS, Ankerst J, Kjellén E et al. Tissue diagnostics using laser-induced fluorescence techniques. Proceedings of the International Laser Science Conference, Seattle, 1986
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andersson, P.S., Gustafson, A., Stenram, U. et al. Diagnosis of arterial atherosclerosis using laser-induced fluorescence. Laser Med Sci 2, 261–266 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02594170
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02594170