Abstract
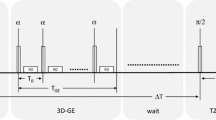
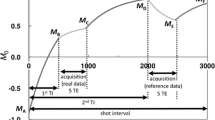
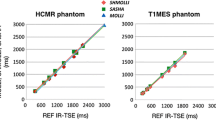
Increasing the contrast between atheromatous plaque components is a major issue in cardiovascular MRI research. It would allow one to identify unstable plaque by differentiating the lipid core associated with vulnerability, from the fibrous cap, considered as a factor of stability. T2 and diffusion-weighted imaging have already provided satisfying results. Magnetization transfer (MT) between restricted protons Hr and free-water protons Hf could achieve a different contrast related to collagen and lipoprotein macromolecules present in the fibrous cap and lipid core, respectively. The purpose of this work was to evaluate in vitro the MT effect produced by adapted T2-selective 1-3-3-1 binomial pulses on isolated samples of atheromatous arteries at 3 T. A method based on simulation was used in order to improve the MT specificity: it is shown that 50% 1-3-3-1 pulses (the percentage indicating the level of Hr saturation) allow an estimation of T2r, the Hr T2. Using this technique, magnetization transfer was observed for the first time in atherosclerotic plaque components, an effect more pronounced for the fibrous cap and media than for the lipid core and advantitia. The T2r estimation gave values ranging from 20 to 25 μs for the four samples. This preliminary study provides a basis for establishing an MT imaging sequence of atheromatous arteries, by using 50% 1-3-3-1 pulses calibrated for saturating protons with a 20 μs T2. This MT protocol should be further compared to T2 and diffusion-weighted imaging.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Falk E, Shah P, Fuster V. Coronary plaque disruption. Circulation 1995;92:657–71.
Libby P. Molecular bases of the acute coronary syndromes. Circulation 1995;91:2844–50.
Toussaint JF, Southern JF, Fuster V, Kantor HL. T2-weighted contrast for NMR characterization of Human Atherosclerosis. Arterioscl Thromb Vasc Biol 1995;15:1533–42.
Toussaint JF, LaMuraglia GM, Southern JF, Fuster V, Kantor HL. Magnetic resonance images lipid, fibrous, calcified, hemorrhagic, and thrombotic components of human atherosclerosis in vivo. Circulation 1996;1994:932–8.
Toussaint JF, Southern JF, Fuster V, Kantor HL. Diffusion properties of human atherosclerosis and thrombosis measured by pulse field gradient NMR. Arterioscl Thromb Vasc Biol 1997;17:542–6.
Wolff SD, Balaban RS. Magnetization transfer contrast (MTC) and tissue water proton relaxation in vivo. Magn Reson Med 1989;10:135–44.
Gray ML, Burstein D, Lesperance LM, Gehrke L. Magnetization transfer in cartilage and its constituent macromolecules. Magn Reson Med 1995;34:319–25.
Kim DK, Ceckler TL, Hascall VC, Calabro A, Balaban RS. Analysis of water macromolecule proton magnetization transfer in articular cartilage. Magn Reson Med 1993;29:211–215.
Seo GS, Aoki JA, Moriya H, Kaharida O, Sone S, Hidaka H, Katsuyama T. Hyaline cartilage: in vivo and in vitro assessment with magnetization transfer imaging. Radiology 1996;201:525–30.
Kucharczyk W, Macdonald PM, Stanisz GJ, Henkelman RM. Relaxivity and magnetization transfer of white matter lipids at MR imaging: importance of cerebrosides and pH. Radiology 1994;192:521–9.
Pachot-Clouard M, Darrasse L. Optimization of T2-selective binomial pulses for magnetization transfer. Magn Reson Med 1995;34:462–9.
Hu BS, Conolly SM, Wright GA, Nishimura DG, Macovski A. Pulsed saturation transfer contrast. Magn Reson Med 1992;26:231–40.
Yeung HN. Transient responses of heterogenous spin system to binomial pulse saturation. J Magn Reson A 1993;102:8–15.
Morris GA, Chilvers PB. General analytical solutions of the Bloch equations. J Magn Reson A 1994;107:236–8.
Brooks D, Kuwata K, Schleich T. Determination of proton magnetization transfer rate constants in heterogeneous, biological systems. Magn Reson Med 1994;31:331–6.
Tessier JJ, Dillon N, Carpenter TA, Hall LD. Interpretation of magnetization transfer and proton cross-relaxation spectra of biological tissues. J Magn Reson 1995;B107:138–44.
Morrison C, Henkelman RM. A model for magnetization transfer in tissues. Magn Reson Med 1995;33:475–82.
Wolff SD, Balaban RS. Magnetization transfer imaging: practical aspects and clinical applications. Radiology 1994;192:593–9.
Listerud J. Off-resonance pulsed magnetization transfer in clinical MR imaging: optimization by an analysis of transients. Magn Reson Med 1997;37:693–705.
Yeung HN, Adler RS, Swanson SD. Transient decay of longitudinal magnetization in heterogeneous spin systems under selective saturation. IV. Reformulation of the spin-bath model equations by the Redfield-Provotorov theory. J Magn Reson A 1994;106:37–45.
Grad J, Bryant RG. Nuclear magnetic cross-relaxation spectroscopy. J Magn Reson 1990;90:1.
Adler RS, Swanson SD, Yeung HN. A three-component model for magnetization transfer. Solution by projection-operator technique, and application to cartilage. J Magn Reson B 1996;110:1–8.
Li JG, Graham SJ, Henkelman RM. A flexible magnetization transfer line shape derived from tissue experimental data. Magn Reson Med 1997;37:866–71.
Henkelman RM, Huang X, Xiang Q, Stanisz GJ, Swanson SD, Bronskill MJ. Quantitative interpretation of magnetization transfer. Magn Reson Med 1993;29:759–66.
Soila K, Nummi P, Ekfors T, Viamonte M, Kormano M. Proton relaxation times in arterial wall and atheromatous lesions in man. Investig radiol 1986;20:411–5.
Zur Y, Wood ML, Neuringer LJ. Spoiling of transverse magnetization in steady state sequences. Magn Reson Med 1991;21:251–63.
Fralix TA, Cekler TL, Wolff SD, et al. Lipid bilayer and water proton magnetization transfer: effect of cholesterol. Magn Reson Med 1991;18:214–23.
Wight TN: The vascular extracellular matrix. In: Fuster V, Ross R, Topol EJ, editors. Atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven, 1996:421–40.
Yurchenco PD, Schittny JC. Molecular architecture of basement membranes. FASEB J 1990;4:1577–90.
Cheng GC, Loree HM, Kamm RD, Fishbein MC, Lee RT. Distribution of circumferential stress in ruptured and stable atherosclerotic lesions. A structural analysis with histopathological correlation. Circulation 1993;87:1179–87.
Jimi S, Sakata N, Matunaga A, Takebayashi S. LDL bind more to type I and III collagens by negative-charge dependent mechanism than to type IV and V. Atherosclerosis 1994;103:1179–87.
Winlove CP, Parker KH, Ewins AR. Some factors influencing the interactions of plasma lipoproteins with arterial elastin. Artery 1988;15:292–303.
Ceckler TL, Wolff SD, Yip V, Simon SA, Balaban R. Dynamic and chemical factors affecting water proton relaxation by macromolecules. J Magn Reson 1992;98:637–45.
Vinée P, Meurer B, Constantinesco A, Kohlberger B, Hauenstein KH, Laubenberger J. In vitro proton NMR study of collagen in human aortic wall. Magn Reson Med 1993;29:292–5.
Pike GB. Pulsed magnetization transfer contrast in gradient echo imaging: a two pool analytic description of signal response. Magn Reson Med 1996;36:95–103.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pachot-Clouard, M., Vaufrey, F., Darrasse, L. et al. Magnetization transfer characteristics in atherosclerotic plaque components assessed by adapted binomial preparation pulses. MAGMA 7, 9–15 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02592251
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02592251