Summary
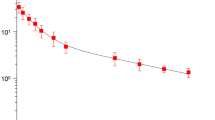
The results of two kinetic studies examining soft tissue, cartilage and bone after uptake of oral ofloxacin [administered as 200 mg twice daily (study I/nose) or 400 mg once daily (study II/ear)] show that antibiotic concentrations lie within the therapeutic range. Findings demonstrate that 400 mg ofloxacin daily is a compliance-enhacing and effective approach to the treatment of ENT-related infections, in particular those caused by problem organisms such asPseudomonas aeruginosa.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baba S (1986) Clinical efficacy of ofloxacin in the treatment of orthorhinolaryngological infections. Infection 14 [Suppl 4]: S327-S331
Bernabel L, Piccini A, Benedetti M, Fostini R (1989) Treatment of bacterial ear nose and throat infections with ofloxacin. Clin Trials J 26: 120–126
Brand KG, Sprinkle PM, Veltrie RW, Paparella MM, Shumrick DA (eds) (1980) Otolaryngology, vol I, 2nd edn. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 574–599
Federspil F (1987) Moderne HNO-Therapie. Ecomed, Landsberg
Gehanno P, Moisy N, Depondt J (1989) Chronic otitis and chronic sinusitis. Bacteriological data—use of ofloxacin—multicenter study. 4th European Congress on Clinical Microbiology, Nice, April 1989. The European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, Book of Abstracts 22 abs 33/PP3
Geyer G (1988) Ofloxacin-Therapie bei chronischen Mittelohrentzündungen. Med Welt 39:1551–1553
Klein JO (1980) Microbiology of otitis media. Microbiology 3 [Suppl 68]:98–101
Lenarz T (1986) Ofloxacin in der konservativen Therapie der akuten und chronischen Otitis media—ein, vorläufiger klinischer Erfahrungsbericht. Infection 14 [Suppl 1]:87–88
Lenarz T (1986) Ofloxacin in oral chromtherapy of acute and chronic otitis media. Infection 14 [Suppl 4]:S324-S326
Lenarz T (1987) Chemotherapy of otitis media with ofloxacin (with discussion). Drugs 34 [Suppl 1]:139–143
Oberascher G, Karas C (1988) Ofloxacin zur Behandlung von Pyocyaneusinfektionen des Ohres. HNO 36:230–233
Thorn V (1987) Tissue concentrations of ofloxacin in the middle ear. Clin Ther 9:523–527
Thorn V, Stange G (1988) Konzentration of Ofloxacin in Schleimhaut und Knochen des Mittelohres. Therapiewoche 38:2179–2182
Tolsdorff P (1989) Tissue levels of ofloxacin (Tarivid) in serum nasal mucosa septum cartilage and the bone of os chonchale (poster). 4th European Congress of Clinical Microbiology, Nice, April 1989. The European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, Book of Abstracts 21 abs 30/PP3
Tolsdorff P (1991) Levels of ofloxacin (Tarivid) in serum mastoid (corticalis and spongiosa) mucosa of the tympanum, malleus and incus, choncha cartilage and cholesteatoma after 400 mg once daily (poster). 5th European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, Book of Abstracts 189–1735
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tolsdorff, P. Concentrations of ofloxacin in ear and nasal tissues. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 250 (Suppl 1), S7–S11 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02540109
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02540109