Summary
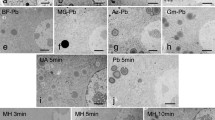
We can divide metachrome mordant staining of nuclei after graded 60°C 1N nitric acid extraction into three groups. The feulgen nucleal reaction and dilute cationic dye staining of nuclei are abolished in about 30 minutes. With one group of metachrome dyes nuclear staining is lost with acid exposures of one hour or less. In a second group nuclear staining is weakened by 30–60 minute extractions, but persists in recognizable grade for 4–6 hours. In the third group nuclear staining remains almost unimpaired for 4–6 hours.
In the first group the nuclear staining seems clearly assignable to the nucleic acids and to DNA in particular. In the second group loss of part of the reactivity on short exposure indicates some participation of DNA in the control staining result, as well as participation of basic nucleoprotein. In the third group staining seems assignable largely to basic nucleoprotein.
The five gallocyanin group dyes, all in group1, all possess a dialkylamino group, probably functioning as an ammonium chloride. Hematoxylin, the fluorone blacks and gallein all present ano-hydroxysemiquinone group which probably acts as a weak acid, in addition to the carboxyl group of gallein which gives the strongest staining of nuclei at the longest acid exposure.
Dexyribonuclease digestion (2 hours, 37°C) separated sharply a class in which nuclear staining failed completely, a class in which nuclear staining was fully equal to that in the control preparations and an intermediate group in which slight, moderate, or severa impairment was present. Generally there was good agreement between the two methods of nucleic acid removal, despite the fixation difference. In each case, however, the extraction procedure was one worked out for the fixation on which it was used.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkinson, W. B.: Differentiation of nucleic acids and acid mucopolysaccharides in histologic sections by selective extraction with acids. Science116, 303–305 (1952)
DiStefano, H. S.: In discussion of Koenig and Stahlecker. Proc. Histochem. Soc., 1951. J. nat. Cancer Inst.12, 238 (1951)
DiStefano, H. S.: Perchloric acid extraction of ribose nucleic acid from cytological preparations. Science115, 316–317 (1952)
Einarson, L.: A method for progressive selective staining of Nissl and nuclear substance in nerve cells. Amer. J. Path8, 295–308 (1932)
Feulgen, R., Rossenbeck, H.: Mikroskopisch-chemischer Nachweis einer Nukleinsäre von Typus der Thymonukleinsäure und die darauf beruhende elektive Färbung von Zellkernen in mikroskopische Präparaten
Feulgen, R., Voit, K.: Über ein weitverbreiteten festen Aldehyd. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.206, 389–410 (1924)
Fisher, E. R.: The destruction of cytoplasmic basophilia with mineral acids. Stain Technol.28, 9–12 (1953)
Fullmer, H. M., Lillie, R. D.: Dilute unmordanted hematoxylin as a stain for basic nuclear protein. J. Histochem. Cytochem.10, 502–503 (1962)
Fyg, W.: Über einige Karminfärbungen. Z. wiss. Mikr.45, 442–452 (1928)
Kasten, F. H.: Loss of RNA and protein and changes in DNA during a 30-hour cold perchloric acid extraction of cultured cells. Stain Technol.40, 127–135 (1965)
Kiefer, G., Zeller, W., Sandritter, W.: Eine Methode zur histochemischen Bestimmung von RNS und DNS an der gleichen Zelle. Histochemie,20, 1–10 (1964)
Koenig, H., Stahlecker, H.: Further studies on the differential extraction of nucleic acids from mammalian nerve cells with perchloric acid. J. nat. Cancer Inst,12, 237–238 (1951)
Lillie, R. D.: Histopathologic technic and practical histochemistry, 2nd ed. New York: Blakiston 1954
Lillie, R. D.: Histopathologic technic and practical histochemistry, 3rd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill 1965
Lillie, R. D., Pizzolato, P., Dessauer, H. C., Donaldson, P. T.: Histochemical reaction at arginine sites with alkaline solutions of β-naphthoquinone-4-sodium sulfonate and othero-quinones and oxidizedo-diphenols. A possible mechanism of the Sakaguchi reaction. J. Histochem. Cytochem.19, 487–497 (1971)
Lillie, R. D., Pizzolato, P., Welsh, R. A., Holmquist, N. D., Donaldson, P. T., Berger, C.: A consideration of substitutes for alum hematoxylin in routine histologica and cytologic diagnostic procedures. Amer. J. clin. Path.60, 817–819 (1973)
Lillie, R. D., Pizzolato, P., Donaldson, P. T.: The Clara hematoxylin reaction. Acta Histochem.49, 204–219 (1974a)
Lillie, R. D., Pizzolato, P., Donaldson, P. T.: Hemtoxylin substitutes: Gallein as a biological stain. Stain Technol.49, 339–346 (1974b)
Lillie, R. D., Pizzolato, P., Donaldson, P. T.: Hematoxylin substitutes: Fluorone black and methyl fluorone balck (9-phenyl-and 9-methyl-2,3,7-trihydroxy-6-fluorone) as metachrome iron alum mordant dyes. Stain Technol.50, 127–131 (1975a)
Lillie, R. D., Pizzolato, P., Donaldson, P. T.: Hematoxylin substitutes: A study of phenocyanin TC and the use of afterchrome mordanting in histology. Amer. J. clin. Path.65, 876–885 (1975b)
Lillie, R. D., Pizzolato, P., Donaldson, P. T.: Hematoxylin substitutes: A survey of the mordant dyes tested and consideration of the relation of their structure to performance as nuclear stains. Stain Technol.50 (1975 c or 1976), in press
Lillie, R. D., Donaldson, P. T., Jirge, S. K., Pizzolato, P.: Iron and aluminum lakes of gallo blue E as nuclear and metachromatic mucin stains. Stain Technol.51 (1976), in press
Love, R., Rabotti, G.: Studies of the cytochemistry of nucleoproteins. III Demonstration of deoxyribonucleic-ribonucleic acid complexes in mammalian cells. J. Histochem. Cytochem.11, 605–612 (1963)
Mallory, R. B.: Pathological Technique. Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders Co. 1938
Meloan, S. N., Puchtler, H.: Iron alizarin blue S stain for nuclei. Stain Technol.49, 301–304 (1974)
Neumeyer, G.: Hämatoxylin-Ersatz durch Anthracenblau. Zbl. allg. Path.84, 109–110 (1938)
Ogur, M., Rosen, G.: Extraction and estimation of desoxypentose nucleic acid (DNA) and pentose nucleic acid (PNA) from plant tissues. Fed. Proc.8, 234 (1949)
Proescher, F., Arkush, A. S.: Metallic lakes of the oxazines (Gallamin blue, Gallocyanin and Celestin blue) as nuclear stain substitutes for hematoxylin. Stain Technol.3, 28–40 (1928)
Sandritte, W., Kiefer, G., Rick, W.: Über die Stochiometrie von Gallocyaninchromalaun mit Desoxyribonukleinsäure. Histochemie3, 315–340 (1963)
Seschacher, B. R., Flick, E. W.: Application of perchloric acid technique to protozoa. Science110, 659 (1949)
Sulkin, N. M., Kuntz, A.: Histochemical determination of ribose nucleic acid in vertebrate tissues following extraction with perchloric acid. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N. Y.)73, 413–415 (1950)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Assisted by National Cancer Institute Contract No. NO 1 CB43912.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lillie, R.D., Donaldson, P.T. & Pizzolato, P. The effect of graded 60°C 1N nitric acid extraction and of deoxyribonuclease digestion on nuclear staining by metachrome mordant dye metal salt mixtures. Histochemistry 46, 297–306 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02464419
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02464419