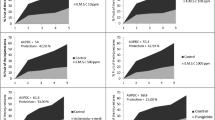
Summary
The addition of small quantity of potassium acetate to the fertilizer applied to tea bushes was an effective method of reducing infestation by the beetle pest,Xyleborus fornicatus. The mechanism of action of potassium acetate is discussed as being due to its conversion to saponins and/or sterol analogues which interfere with pupation of the beetle larvae.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Calnaido, D. 1973 New outlook on the pest management of tea. J. Nat. Sci. Coun. Sri Lanka1, 97–109.
Chu, H.-M., Norris, D. M. and Kok, L. J. 1970 Pupation requirements of the beetle,Xyleborus ferrugineus: Sterols other than cholesterol. J. Insect Physiol.16, 1379–1387.
Clayton, R. B., The utilization of sterols by insects. J. Lipid Res.5, 3–19.
Danthanarayana, W. D. 1973 Host plant-pest relationships of the shot-hole borer of tea (Xyleborus fornicatus) (Coleoptera: Scolytidae). Entomol. Exp. Appl.16, 305–312.
Gadd, C. H. 1961. The life history of the shot-hole borer of tea. Tea Q.14, 5–22.
Hober, E., Leath, K. T., Berrang, B., Marcarian, V. and Hanson, C. H. 1974 Biological activities of saponin components from Dupuits and Lahontan Alfalfa. Entomol. Exp. Appl.17, 410–424.
Judenko, E. 1958 Trials with a method of assessment of infestations caused by shot-hole borer (Xyleborus fornicatus Eichh.) on old tea. Tea Q.29, 51–59.
Matolcsy, G., Varjas, L. and Bordas, B. 1974 Assay of steroid inhibitors for insect antihormone activit. Acta Phytopathol. Acad. Sci. Hung.9, 161–166.
Shany, S., Birk, Y., Gestetner, B. and Bondi, A. 1970 Preparation, characterisation and some properties of saponins from lucerne tops and roots. J. Sci. Food Agric.21, 131–135.
Sivapalan, P., Senaratne, K. A. D. W. and Karunaratne, A. A. C. 1977, Observations on the occurrence and behaviour of live-wood termites (Glyptotermes dilatatus Bugnion and popoff) in low country tea fields. PANS23, 5–12.
Stahl, E. 1969 Thin Layer Chromatography. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1041 p.
Su, H. C. F., Speiers, R. D. and Mahany, P. G. 1972 Toxic effects of soybean saponin and its calcium salt on the rice weevil. J. Econ. Entomol.65, 844–847.
Svoboda, J. A., Thompson, M. J. and Robbins, W. E. 1973 Azasteroids: potent inhibitors of insect molting and metamorphosis. Lipids7, 553–556.
Visser, T. and Kehl, F. H. 1958 Selection and vegetative propogation of tea. Tea Q.29, 76–86.
Wickremasinghe, R. L., Perera, B. P. M. and Perera, K. P. W. C., α-Spinasterol, temperature and moisture content as determining factors in the infestation ofCamellia sinensis byXyleborus fornicatus. Biochem. System. Ecol.4, 103–110.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wickremasinghe, R.L., Thirugnanasuntheram, K. Biochemical approach to the control ofXyleborus fornicatus (Coleoptera: Scolytidae). Plant Soil 55, 9–15 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02149703
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02149703