Summary
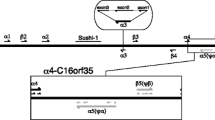
To investigate the evolution of globin genes in the genusXenopus, we have determined the primary structure of the related adult α1- and αII genes ofX. laevis and of the adult α-globin gene ofX. tropicalis, including their 5′-flanking regions. All three genes are comprised of three exons and two introns at homologous positions. The exons are highly conserved and code for 141 amino acids. By contrast, the corresponding introns vary in length and show considerable divergence. Comparison of 900 bp of the 5′-flanking region revealed that theX. tropicalis gene contains a conserved proximal 310-bp promoter sequence, comprised of the canonical TATA and CCAAT motifs at homologous positions, and five conserved elements in the same order and at similar positions as previously shown for the corresponding genes ofX. laevis. We therefore conclude that these conserved upstream elements may represent regulatory sequences for cell-specific regulation of the adultXenopus globin genes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bendig MM, Williams JG (1983) Replication and expression ofXenopus laevis globin genes injected into fertilizedXenopus eggs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:6197–6201
Bisbee CA, Baker MA, Wilson AC, Hadji-Azimi I, Fischberg M (1977) Albumin phylogeny for clawed frogs (Xenopus). Science 195:785–787
Bozzoni I, Tagnoni A, Perandrei-Amaldi P, Beccari E, Buongiorno-Nardelli M, Amaldi F (1982) Isolation and structural analysis of ribosomal protein genes inXenopus laevis. J Mol Biol 161:353–371
Breathnach R, Benoist C, O'Hare K, Gannon F, Chambon P (1978) Ovalbumin gene: evidence for a leader sequence in mRNA and DNA sequences at the exon-intron boundaries. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75:4853–4857
Chien Y-H, Dawid IB (1984) Isolation and characterization of calmodulin genes fromXenopus laevis. Mol Cell Biol 4:507–513
Dodgson JB, Engel JD (1983) The nucleotide sequence of the adult chicken α-globin genes. J Biol Chem 258:4623–4629
Hosbach HA, Wyler T, Weber R (1983) TheXenopus laevis globin gene family: chromosomal arrangement and gene structure. Cell 32:45–53
Jeffreys AJ, Wilson V, Wood D, Simons JP, Kay RM, Williams JG (1980) Linkage of adult α- and β-globin genes inX. laevis and gene duplication by tetraploidization. Cell 21:555–564
Kay RM, Harris R, Patient RK, Williams JG (1983) Complete nucleotide sequence of a cloned cDNA derived from the major adult α-globin mRNA ofX. laevis. Nucleic Acids Res 11: 1537–1542
Knöchel W, Meyerhof W, Hummel S, Grundmann U (1983) Molecular cloning and sequencing of mRNA coding for minor adult globin polypeptides ofXenopus laevis. Nucleic Acids Res 11:1543–1553
Knöchel W, Korge E, Basner A, Meyerhof W (1986) Globin evolution in the genusXenopus: comparative analysis of cDNAs coding for adult globin polypeptides ofXenopus borealis andXenopus tropicalis. J Mol Evol 23:211–223
Liebhaber SA, Goossens MJ, Wai Kan Y (1980) Cloning and complete nucleotide sequence of human 5′-α-globin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:7054–7058
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor NY
Messing J, Vieira J (1982) A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digit restriction fragments. Gene 19:269–276
Meyerhof W, Köster M, Stalder J, Weber R, Knöchel W (1986) Sequence analysis of the larval βII gene ofXenopus laevis. Mol Biol Rep 11:155–161
Michelson AM, Orkin SH (1983) Boundaries of gene conversion within the duplicated human α-globin genes. J Biol Chem 258:15245–15254
Ryffel GU, McCarthy BJ (1975) Complexity of cytoplasmic RNA in different mouse tissues measured by hybridization of polyadenylated RNA to complementary DNA. Biochemistry 14:1379–1385
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR (1977) DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74: 5463–5467
Sege RD, Söll D, Ruddle FH, Queen C (1981) A conversational system for the computer analysis of nucleic acid sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 9:437–444
Stalder J, Meyerhof W, Wirthmüller U, Gruber A, Wyler T, Knöchel W, Weber R (1986) Conserved sequences and cell specific DNase I hypersensitive sites upstream of the coordinately expressed α1- and αII-globin genes ofXenopus laevis. J Mol Biol 188:119–128
Stutz F, Spohr G (1986) Isolation and characterization of sarcomeric actin genes expressed inXenopus laevis embryos. J Mol Biol 187:349–361
Stutz F, Spohr G (1987) A processed gene coding for a sarcomeric actin inXenopus laevis andXenopus tropicalis. EMBO J 6:1989–1995
Thiébaud C-H, Fischberg M (1977) DNA content in the genusXenopus. Chromosoma 59:253–257
Tymowska J, Fischberg M (1982) A comparison of the karyotype, constitutive heterochromatin, and nucleolar organizer regions of the new tetraploid speciesXenopus epitropicalis Fischberg and Picard with those ofXenopus tropicalis Gray (Anura, Pipidae). Cytogenet Cell Genet 34:149–157
Wahli W, Dawid IB (1980) Isolation of two closely related vitellogenin genes, including their flanking regions from aXenopus laevis gene library. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77: 1437–1441
Westley B, Wyler T, Ryffel G, Weber R (1981)Xenopus laevis serum albumins are encoded in two closely related genes. Nucleic Acids Res 9:3557–3574
Widmer HJ, Andres A-C, Niessing J, Hosbach HA, Weber R (1981) Comparative analysis of cloned larval and adult globin cDNA sequences ofXenopus laevis. Dev Biol 88:325–332
Wilson AC, Ochman H, Prager EM (1987) Molecular time scale for evolution. Trends Genetics 3:241–247
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stalder, J., Wirthmüller, U., Beck, J. et al. Primary structure and evolutionary relationship between the adult α-globin genes and their 5′-flanking regions ofXenopus laevis andXenopus tropicalis . J Mol Evol 28, 64–71 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02143498
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02143498