Abstract
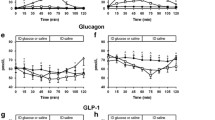
The fact thatH. pylori gastritis results in an increased secretion of basal and meal-stimulated gastrin, which is also a physiologic amplifier of insulin release directed us to investigate whetherH. pylori gastritis may lead to an enhancement of nutrient-stimulated insulin secretion. For this purpose, we have investigated the insulin responses to both oral glucose and a mixed meal in 15 patients withH. pylori gastritis before and one month after the eradication therapy and also in 15H. pylori-negative control subjects. The areas under the curve (AUC) for serum insulin following both oral glucose and a mixed meal in the patients withH. pylori gastritis before the eradication were significantly (P<0.05) higher than those in theH. pylori-negative controls. After the eradication ofH. pylori, the AUC for serum insulin following oral glucose and mixed meal decreased by 9.4% and 13.1%, respectively (P<0.001 in both), and serum basal and meal-stimulated gastrin levels decreased significantly (P<0.001). These results suggest thatH. pylori gastritis enhances glucose and meal-stimulated insulin release probably by increasing gastrin secretion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Warren JR, Marshall B: Unidentified curved bacilli on gastric epithelium in active chronic gastritis. Lancet 1:1273–1275, 1983
Blaser MJ:Helicobacter pylori and the pathogenesis of gastroduodenal inflammation. J Infect Dis 161:626–633, 1990
Marshall BJ, Goodwin CS, Warren JR, Murray R, Blincow ED, Blackbourn SJ, Phillips M, Waters TE, Sanderson CR: Prospective double-blind trial of duodenal ulcer relapse after eradication ofCampylobacter pylori. Lancet 2:1437–1442, 1988
Parsonnet J, Friedman GD, Vandersteen DP, Chang Y, Vogelman JH, Orentreich N, Sibley RK:Helicobacter pylori infection and the risk of gastric carcinoma. N Engl J Med 325:1127–1131, 1991
Isaacson PG, Spencer J: Is gastric lymphoma an infectious disease? Hum Pathol 24:569–570, 1993
Levi S, Beardshall K, Haddad G, Playford R, Ghosh P, Calam J:Campylobacter pylori and duodenal ulcers: The gastrin link. Lancet 1:1167–1168, 1989
Graham DY, Opekun A, Lew GM, Evans DJ Jr, Klein PD, Evans DG: Ablation of exaggerated meal-stimulated gastrin release in duodenal ulcer patients after clearance ofHelicobacter (Campylobacter)pylori infection. Am J Gastroenterol 85:394–398, 1990
Smith JT, Pounder RE, Nwokolo CU, Lanzon-Miller S, Evans DG, Graham DY, Evans DJ Jr: Inappropriate hypergastrinaemia in asymptomatic healthy subjects infected withHelicobacter pylori. Gut 31:522–525, 1990
Mossi S, Meyer-Wyss B, Renner EL, Merki HS, Gamboni G, Beglinger C: Influence ofHelicobacter pylori, sex, and age on serum gastrin and pepsinogen concentrations in subjects without symptoms and patients with duodenal ulcers. Gut 34:752–756, 1993
Dupre J, Curtis JD, Unger RH, Waddell RW, Beck J: Effects of secretin, pancreozymin, gastrin on the response of the endocrine pancreas to administration of glucose or arginine in man. J Clin Invest 48:745–757, 1969
Rehfeld JF, Stadil F: The effect of gastrin on basal and glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in man. J Clin Invest 52:1415–1426, 1973
Ebert R, Creutzfeldt W: Gastrointestinal peptides and insulin secretion. Diabetes Metab Rev 3:1–26, 1987
Unger RH, Eisentraut AM: Entero-insular axis. Arch Intern Med 123:261–266, 1969
Shapiro ET, Tillil H, Miller MA, Frank BH, Galloway JA, Rubenstein AH, Polonsky KS: Insulin secretion and clearance: Comparison after oral and intravenous glucose. Diabetes 36:1365–1371, 1987
Colturi TJ, Unger RH, Feldman M: Role of circulating somatostatin in regulation of gastric acid secretion, gastrin release, and islet cell function. Studies in healthy subjects and duodenal ulcer patients. J Clin Invest 74:417–423, 1984
Gyr K, Beglinger C, Kohler E, Trantzl U, Keller U, Bloom SR: Circulating somatostatin: Physiological regulator of pancreatic function? J Clin Invest 79:1595–1600, 1987
Moss SF, Legon S, Bishop AE, Polak JM, Calam J: Effect ofHelicobacter pylori on gastric somatostatin in duodenal ulcer disease. Lancet 340:930–932, 1992
Kaneko H, Nakada K, Mitsuma T, Uchida K, Furusawa A, Maeda Y, Morise K:Helicobacter pylori infection induces a decrease in immunoreactive-somatostatin concentrations of human stomach. Dig Dis Sci 37:409–416, 1992
Takemura J, Seino Y, Yamamura T, Yoshiya K, Ishikawa Y, Itoh N, Imura H: The evidence for the regulatory role of endogenous GIP as a glucose-dependent insulinotropic hormone in patients with duodenal ulcer. Clin Endocrinol 19:345–353, 1983
Malagelada JR, Larch JR: Gastric emptying in duodenal ulcer. Scand J Gastroenterol 15(suppl 63):115–130, 1980
Williams NS, Grossman MI, Meyer JH: Abnormalities of gastric emptying of liquids in duodenal ulcer disease. Dig Dis Sci 31:943–952, 1986
Kreymann B, Ghatei MA, Williams G, Bloom SR: Glucagon-like peptide-1 7–36: A physiological incretin in man. Lancet 2:1300–1303, 1987
Wegener M, Borsch G, Schaffstein J, Schultz-Flaake C, Mai U: Does gastricCampylobacter pylori colonization cause delay of gastric emptying in non-ulcer dyspepsia? Am J Gastroenterol 38:737–740, 1988
Pieramico O, Didschuneit H, Malfertheiner P: Gastrointestinal motility in patients with non-ulcer dyspepsia: A role forHelicobacter pylori infection? Am J Gastroenterol 88:364–368, 1993
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Açbay, Ö., Çelik, A.F. & Gündoğdu, S. DoesHelicobacter pylori-induced gastritis enhance food-stimulated insulin release?. Digest Dis Sci 41, 1327–1331 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02088555
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02088555