Abstract
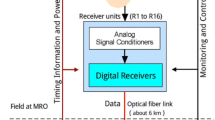
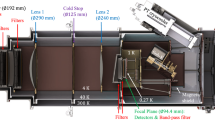
The five antennas of the Plateau de Bure Interferometer have been instrumented with dual-channel receivers in the λ 3 mm and λ 1 mm bands. Polarisation diplexing allows simultaneous observations in the two bands. Each receiver has ambient and cryogenic calibration loads, and one receiver is equipped with a beam switching chopper for total power flux measurements. Typically the receiver noise temperatures are<50 K in both the λ 3 mm band and the λ 1 mm band. Initial observations show that at 115 GHz the sensitivity is doubled compared to the previous receivers, and high quality fringes have been obtained at 230 GHz. Preliminary experiments show that the receiver stability is good enough to correct atmospheric phase variations by monitoring the fluctuations in atmospheric emission at 225 GHz. VLBI fringes have been detected between one 15-m antenna and the IRAM 30-m antenna in Spain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Guilloteau, J. Delannoy, D. Downes, A. Greve, M. Guélin, R. Lucas, D. Morris, S. J. E. Radford, J. Wink, J. Chernicharo, T. Forveille, S. Garcia-Burillo, R. Neri, J. Blondel, A. Perrigouard, D. Plathner, and M. Torres: “The IRAM interferometer on Plateau de Bure,”Astronomy and Astrophys., vol. 262, pp. 624–633, 1992.
B. Lazareff, “Two lens system with λ-independent illumination,”Proc. European Workshop on Low-Noise Quasi-Optics, Bonn 1994
F. Biraud and G. Daigne, “Achromatic doublets for Gaussian beams,”IEEE Trans Antennas Propagat., vol. 39, no. 4, pp. 559–561, Apr. 1991.
P. F. Goldsmith, “Quasioptical techniques at millimeter and submillimeter wavelengths,” inInfrared and Millimeter Waves, vol. 6, K. Button (ed.), New York: Academic, 1982, pp. 277–246.
J. R. Birch, “Systematic errors in dispersive Fourier transform spectroscopy in a non-vacuum environment,”Infrared Phys., vol. 34, no. 1, pp. 89–93, 1993.
Thomas Keating Ltd, Billingshurst, UK.
Marplex Absorber LAO 5, Marplex, Vert le Petit, France.
F. Mattiocco and M. C. Carter, “80–360 GHz very wide band millimeterwave network analyzer,”Int. J. of Infrared and Millimeterwaves, vol. 16, p. 2249, 1995.
P. J. B. Clarricoats and A. D. Olver,Corrugated Horns for Microwave Antennas. London: Peter Peregrinus, 1984.
A. Karpov and J. Blondel,IRAM Report 232/95, 1995
A. Karpov, J. Blondel, B. Lazareff, P. Billon-Pierron, K.-H. Gundlach,Proc. 27th European Microwave Conf., vol. 2, pp. 1415–19, Sep. 1994, Cannes, France.
Radiall, Rosny-sous-Bois, France
Passive Microwave technology, Inc, Camarillo, CA, USA.
J. D. Gallego and M. W. Pospieszalski, “Design and performance of cryogenically-coolable ultra low noise, L-band amplifier,” Electronics Division Internal Report No. 286, NRAO, Charlottesville VA, USA, March 1990.
Centro Astronómico de Yebes, Guadalajara, Spain.
J. E. Carlstrom, R. L. Plambeck and D. D. Thornton, “A continuously tunable 65–115-GHz Gunn oscillator,”IEEE Trans. Microwave Theor. Tech., vol. MTT-33, no. 7, pp. 610–619, Jul. 1985.
J. E. Carlstrom Co., Chicago, IL, USA.
FTT-04, Millitech Corp., South Deerfield, MA, USA.
Pacific Millimeter Products, San Diego, CA, USA.
Model 800A, XL-Microwave, Oakland, CA, USA.
Infrared Laboratories, Inc, Tucson, AZ, USA.
CTi Cryogenics, Orsay, France.
Edwards SA, Gennevilliers, France.
R. Padman, “Reflection and Cross-Polarisation Properties of Grooved Dielectric Panels,”IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat., vol. AP-26, no. 5, pp. 741–743, Sep. 1978.
A. Greve, M. Torres, J. E. Wink, M. Grewing, W. Wild, J. Alcolea, A. Barcia, F. Colomer, P. Vicente, J. Gómez-González, I. López-Fernández, D. A. Graham, T. P. Krichbaum, R. Schwartz, K. J. Standke, A. Witzel, A. Baudry, “215 GHz VLBI observations: Detection of fringes on the 1147 km baseline Pico Veleta—Plateau de Bure,” submitted toAstron. Astrophys.
M. Bremer, S. Guilloteau, and R. Lucas, “Atmospheric phase correction based on Sky emission in the 210–248 GHz Band,”Proc. Workshop on Science with Large Millimetre Arrays, ESO, Garching, Dec. 1995.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blondel, J., Carter, M., Karpov, A. et al. Dual-channel sis receivers for the iram Plateau de Bure Interferometer. Int J Infrared Milli Waves 17, 2133–2144 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02069489
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02069489