Abstract
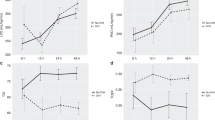
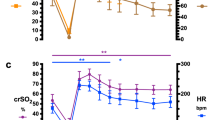
The objectives of this study were to evaluate the effect of repeated indomethacin administration on cerebral oxygenation in relation to changes in cerebral blood flow velocity (CBFV) and other relevant physiological variables. Fourteen preterm infants with patent ductus arteriosus were studied during three subsequent indomethacin bolus administrations with intervals of 12 and 24 h. Changes in concentration of oxyhaemoglobin (cO2Hb), deoxyhaemoglobin (cHHb) and oxidized cytochrome aa3 (cCyt.aa3) in cerebral tissue and changes in cerebral blood volume (CBV) were measured by near infrared spectrophotometry; changes in mean CBFV in the internal carotid artery were measured by pulsed Doppler ultrasound. Simultaneously heart rate, transcutaneouspO2 andpCO2, arterial O2 saturation and blood pressure were measured. All variables were continuously recorded until 60 min after indomethacin administration. Within 5 min after each indomethacin administration, significant decreases in CBFV, CBV and cO2Hb and cCyt.aa3 were observed which persisted for at least 60 min, while cHHb increased or did not change at all. There were no changes in the other variables recorded. These data demonstrate that indomethacin administration is accompanied by a reduction in cerebral tissue oxygenation due to decreased cerebral blood flow. Therefore, low arterial oxygen content, either caused by low arterial O2 saturation or by low haemoglobin concentration, may be a contraindication for indomethacin treatment in preterm infants.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CBF :
-
cerebral blood flow
- CBFV :
-
cerebral blood flow velocity
- CBV :
-
cerebral blood volume
- cCyt.aa 3 :
-
oxidized cytochrome aa3 concentration
- cHHb :
-
deoxyhaemoglobin concentration1
- cO 2 Hb :
-
oxyhaemoglobin concentration1
- ctHb :
-
total haemoglobin concentration1
- NIRS :
-
near infrared spectrophotometry
- PDA :
-
patent ductus arteriosus
References
Brun NC, Greisen G (1992) Measuring cerebral blood volume in newborn infants using near-infrared spectrophotometry: corroboration and sources of error. Biol Neonate 62:303
Chemtob S, Beharry K, Barna T, Varma DR, Aranda JV (1991) Differences in the effects in the newborn piglets of various nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs on cerebral blood flow but not on cerebrovascular prostaglandins. Pediatr Res 30:106–111
Cowan F (1986) Indomethacin, patent ductus arteriosus, and cerebral blood flow. J Pediatr 109:341–344
Dahlgren N, Siesjö BK (1981) Effects of indomethacin on cerebral blood flow and oxygen consumption in barbiturate-anesthetized normocapnic and hypercapnic rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1:109–115
Dahlgren N, Nilsson B, Sakabe T, Siesjö BK (1981) The effect of indomethacin on cerebral blood flow and oxygen consumption in the rat at normal and increased carbon dioxide tensions. Acta Physiol Scand 111:475–485
Edvinsson L, MacKenzie ET, McCulloch J (1993) Cerebral blood flow and metabolism. Raven Press, New York
Edwards AD, Wyatt JS, Richardson C, Potter A, Cope M, Delpy DT, Reynolds EOR (1990) Effects of indomethacin on cerebral haemodynamics in very preterm infants. Lancet 335:1491–1495
Edwards AD, Brown GC, Cope M, Wyatt JS, McCormick DC, Roth SC, Delpy DT, Reynolds EOR (1991) Quantification of concentration changes in neonatal human cerebral oxidized cytochrome oxidase. J Appl Physiol 71:1907–1913
Gersony WM, Peckham GJ, Ellison RC, Miettinen OS, Nadas AS (1983) Effects of indomethacin in premature infants with patent ductus arteriosus: results of a national collaborative study. J Pediatr 102:895–906
Hohimer AR, Richardson BS, Bissonnette JM, Machida CM (1985) The effect of indomethacin on breathing movements and cerebral blood flow and metabolism in fetal sheep. J Dev Physiol 7:217–228
Jöbsis FF (1977) Noninvasive infrared monitoring of cerebral and myocardial oxygen sufficiency and circulatory parameters. Science 198:1264–1267
Jöbsis-Vandervliet FF (1991) Near infrared monitoring of cerebral cytochromec oxidase: past and present (and future?). In: Lafeber HN, Aarnoudse JG, Jongsma HW (eds) Fetal and neonatal physiological measurements. Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Fetal and Neonatal Physiological Measurements. Elsevier Science Publishers, Amsterdam, pp 41–55
Lammertsma AA, Brooks DJ, Beaney RP (1984) In vivo measurement of regional cerebral haematocrit using positron emission tomography. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 4:317–322
Laudignon N, Chemtob, Bard H, Aranda JV (1988) Effects of indomethacin on cerebral blood flow velocity of premature newborns. Biol Neonate 54:254–262
Leffler CW, Busija DW, Fletcher AM, Beasley DG, Hessler JR, Green RS (1985) Effects of indomethacin upon cerebral hemodynamics of newborn pigs. Pediatr Res 19:1160–1164
Liem KD, Oeseburg B, Hopman JCW (1992) Method for the fixation of optrodes in near infrared spectrophotometry. Med Biol Eng Comput 30:120–121
McCormick DC, Edwards AD, Brown GC, Wyatt JS, Potter A, Cope M, Delpy DT, Reynolds EOR (1993) Effect of indomethacin on cerebral oxidised cytochrome oxidase in preterm infants. Pediatr Res 33:603–608
Mirro R, Leffler CW, Armstead W, Beasley DG, Busija DW (1988) Indomethacin restricts cerebral blood flow during pressure ventilation in newborn pigs. Pediatr Res 24:59–62
Pryds O, Greisen G, Johansen H (1988) Indomethacin and cerebral blood flow in premature infants treated for patent ductus arteriosus. Eur J Pediatr 147:315–316
Pryds O, Greisen G, Skov LL, Friis-Hansen B (1990) Carbon dioxide-related changes in cerebral blood volume and cerebral blood flow in mechanically ventilated preterm neonates: comparison of near infrared spectrophotometry and133Xenon clearance. Pediatr Res 27:445–449
Siesjö BK (1984) Cerebral circulation and metabolism. J Neurosurg 60:883–908
Thalji AA, Carr I, Yeh TF, Raval D, Luken JA, Pildes RS (1980) Pharmacokinetics of intravenously administered indomethacin in premature infants. J Pediatr 6:995–1000
Thorniley MS, Livera LN, Wickramasinghe YABD, Spencer SA, Rolfe P (1990) The non-invasive monitoring of cerebral tissue oxygenation. Adv Exp Med Biol 277:323–334
Van Bel F, Van De Bor M, Stijnen T, Baan J, Ruys JH (1989) Cerebral blood flow velocity changes in preterm infants after a single dose of indomethacin: duration of its effect. Pediatrics 84:802–807
Vert P, Bianchetti G, Marchal F, Monin P, Morselli PL (1980) Effectiveness and pharmacokinetics of indomethacin in premature newborns with patent ductus arteriosus. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 18:83–88
Wennmalm A, Eriksson S, Wahren J (1981) Effect of indomethacin on basal and carbon dioxide stimulated cerebral blood flow in man. Clin Physiol 1:227–234
Wyatt JS, Cope M, Delpy DT, Wray S, Reynolds EOR (1986) Quantification of cerebral oxygenation and haemodynamics in sick newborn infants by near infrared spectrophotometry. Lancet II:1063–1066
Wyatt JS, Cope M, Delpy DT (1990) Measurement of optical pathlength for cerebral near-infrared spectroscopy in newborn infants. Dev Neurosci 12:140–144
Wyatt JS, Cope M, Delpy DT, Richardson CE, Edwards AD, Wray S, Reynolds EOR (1990) Quantitation of cerebral blood volume in newborn human infants by near infrared spectroscopy. J Appl Physiol 68:1086–1091
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liem, K.D., Hopman, J.C.W., Kollée, L.A.A. et al. Effects of repeated indomethacin administration on cerebral oxygenation and haemodynamics in preterm infants: Combined near infrared spectrophotometry and Doppler ultrasound study. Eur J Pediatr 153, 504–509 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01957006
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01957006