Abstract
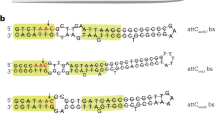
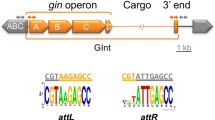
Integrons are unusual DNA elements which include a gene encoding a site-specific DNA recombinase, a DNA integrase, and an adjacent site at which a wide variety of antibiotic resistance and other genes are found as inserts. One or more genes can be found in the insert region, but each gene is part of an independent gene cassette. The inserted genes are expressed from a promoter in the conserved sequences located 5′ to the genes, and integrons are thus natural expression vectors. A model for gene insertion in which circular gene cassettes are inserted individually via a single site-specific recombination event has been proposed and verified experimentally. The gene cassettes include a gene coding region and, at the 3′ end of the gene an imperfect inverted repeat, a 59-base element. The 59-base elements are a diverse family of elements which function as sites recognized by the DNA integrase. Site-specific insertion of individual genes thus represents a further mechanism which contributes to the evolution of the genomes of Gram-negative bacteria and their plasmids and transposons.
Members of the most studied class of integrons, which include thesulI gene in the conserved sequences, are believed to be mobile DNA elements on the basis that they are found in many independent locations, and a discrete boundary is found at the outer end of the 5′-conserved segment. However, the length of the 3′-conserved segment is variable in the integrons examined to date, and it is likely that this variability has arisen as the result of insertion and deletion events. Though the true extent of the 3′-conserved segment remains to be determined, it seems likely that these integrons are mobile DNA elements. The second known class of integrons comprises members of the Tn7 transposon family.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bissonnette, L. & P.H. Roy, 1992. Characterization of In0 of Pseudomonas aeruginosa plasmid pVS1, an ancestor of integrons of multiresistance plasmids and transposons of Gram-negative bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 174: 1248–1257.
Brown, N.L., T.K. Misra, J.N. Winnie, A. Schmidt, M. Seiff & S. Silver, 1986. The nucleotide sequence of the mercuric resistance operons of plasmid R100 and transposon Tn501: further evidence former genes which enhance the activity of the mercuric ion detoxification system. Mol. Gen. Genet. 202: 143–151.
Cameron, F.H., D.J. Groot Obbink, V.P. Ackerman & R.M. Hall, 1986. Nucleotide sequence of the AAD(2′) aminoglycoside adenylyltransferase determinantaadB. Evolutionary relationship of this region with those surroundingaadA in R538-1 anddhfrII in R388. Nucleic Acids Res. 14: 8625–8635.
Collis, C.M. & R.M. Hall, 1992a. Site-specific deletion and rearrangement of integron insert genes catalysed by the integron DNA integrase. J. Bacteriol. 174: 1574–1585.
Collis, C.M. & R.M. Hall, 1992b. Gene cassettes from the insert region of integrons are excised as covalently closed circles. Mol. Microbiol., 6: 2875–2885.
Collis, C.M., G. Grammaticopoulos, J. Briton & R.M. Hall, 1993. Site-specific insertion of gene cassettes into integrons. Mol. Microbiol. 9.
Diver, W.P., J. Grinsted, D.C. Fritzinger, N.L. Brown, J. Altenbuchner, P. Rogowsky & R. Schmitt 1983. DNA sequences of and complementation by the tnpR genes of Tn21, Tn501 and Tn1721. Mol. Gen. Genet. 191: 189–193.
Fling, M.E., J. Kopf & C. Richards, 1985. Nucleotide sequence of the transposon Tn7 gene encoding an aminoglycosidemodifying enzyme, 3′(9)-O-nucleotidyl-transferase. Nucleic Acids Res. 13: 7095–7106.
Guerineau, F., L. Brooks & P. Mullineaux, P., 1990. Expression of the sulfonamide resistance gene from plasmid R46. Plasmid 23: 35–41.
Hall, R.M. & C. Vockler, 1987. The region of the IncN plasmid R46 coding for resistance to β-lactam antibiotics, streptomycin/spectinomycin and sulphonamides is closely related to antibiotic resistance segments found in IncW plasmids and in Tn21-like transposons. Nucleic Acids Res. 15: 7491–7501.
Hall, R.M. & H.W. Stokes, 1990. The structure of a partial duplication in the integron of plasmid pDGO100. Plasmid 23: 76–79.
Hall, R.M., D.E. Brookes & H.W. Stokes, 1991. Site-specific insertion of genes into integrons: role of the 59-base element and determination of the recombination crossover point. Mol. Microbiol. 5: 1941–1959.
Hall, R.M., D.E. Brookes & H.W. Stokes. Integrons found in different locations have identical 5′ ends, but variable 3′ ends. Submitted.
Hyde, D.R. & C.-P.D. Tu, 1985. tnpM: a novel regulatory gene that enhances Tn21 transposition and suppresses cointegrate resolution. Cell 42: 629–638.
Ireland Valentine, C.R., 1985. One-kilobase direct repeats of plasmid pSa. Plasmid 14: 167–170.
Littlejohn, T.G., D. Diberardino, L.J. Messorotti, S.J. Spiers & R.A. Skurray, 1990. Structure and evolution of a family of genes encoding antiseptic and disinfectant resistance inStaphylococcus aureus. Gene 101: 59–66.
Martinez, E. & F. de la Cruz, 1988. Transposon Tn21 encodes a RecA-independent site-specific integration system. Mol. Gen. Genet. 211: 320–325.
Martinez, E. & F. de la Cruz, 1990. Genetic elements involved in Tn21 site-specific integration, a novel mechanism for the dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes. EMBO J. 9: 1275–1281.
Mercier, J., J. Lachapelle, F. Couture, M. Lafond, G. Vezina, M. Boissinot & R.C. Levesque, 1990. Structural and functional characterization oftnpI, a recombinase locus in Tn21 and related β-lactamase transposons. J. Bacteriol. 172: 3745–3757.
Meyer, J.F., B.A. Nies, J. Kratz & B. Wiedemann, 1985. Evolution of Tn21-related transposons: isolation of Tn2425, which harbours IS161. J. Gen. Microbiol. 131: 1123–1130.
Nies, B.A., J.F. Meyer, J. Kratz & B. Wiedemann, 1985. R1767, an example of the evolution of resistance plasmids. Plasmid 13: 163–172.
Ouellette, M., L. Bissonnette & P.H. Roy, 1987. Precise insertion of antibiotic resistance determinants into Tn21-like transposons: nucleotide sequence of the OXA-1 β-lactamase gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84: 7378–7382.
Ouellette, M. & P.H. Roy, 1987. Homology of ORFs from Tn2603 and from R46 to site-specific recombinases. Nucleic Acids Res. 15: 10055.
Parsons, Y., R.M. Hall & H.W. Stokes, 1991. A new trimethoprim resistance gene,dhfrX, in the In7 integron of plasmid pDG0100. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 35: 2436–2439.
Paulsen, I.T., T.G. Littlejohn, P. Rådström, L. Sundström, O. Sköld, G. Swedberg & R.A. Skurray, 1993. The 3′ conserved segment of integrons contains a gene associated with multidrug resistance to antiseptics and disinfectants. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 37: 761–768.
Recchia, G.D., H.W. Stokes & R.M. Hall, Characterization of the 5′-conserved segment site of integrons. In preparation.
Schmidt, F., 1984. The role of insertions, deletions, and substitutions in the evolution of R6 related plasmids encoding aminoglycoside transferase ANT-(2′). Mol. Gen. Genet. 194: 248–259.
Schmidt, F. & I. Klopfer-Kaul, 1984. Evolutionary relationship between Tn21-like elements and pBP201, a plasmid fromKlebsiella pneumoniae mediating resistance to gentamicin and eight other drugs. Mol. Gen. Genet. 197: 109–119.
Schmidt, F.R.J., E.J. Nücken & R.B. Henschke, 1988. Nucleotide sequence analysis of 2′-aminoglycoside nucleotidyltransferase ANT(2′) from Tn4000: its relationship with AAD(3′) and impact on Tn21 evolution. Mol. Microbiol. 2: 709–717.
Shaw, K.J., C.A. Cramer, M. Rizzo, R. Mierzwa, K. Gewain, G.H. Miller & R.S. Hare, R.S., 1989. Isolation, characterization, and DNA sequence analysis of an AAC(6′)-II gene fromPseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 33: 2052–2062.
Simonsen, C.C., E.Y. Chen & A.D. Levinson, 1983. Identification of the type I trimethoprim-resistant dihydrofolate reductase specified by theEscherichia coli R-plasmid R483: comparison with procaryotic and eucaryotic dihydrofolate reductases. J. Bacteriol. 155: 1001–1008.
Stokes, H.W. & R.M. Hall, 1989. A novel family of potentially mobile DNA elements encoding site-specific gene-integration functions: integrons. Mol. Microbiol. 3: 1669–1683.
Stokes, H.W. & R.M. Hall, 1991. Sequence analysis of the inducible chloramphenicol resistance determinant in the Tn1696 integron suggests regulation by translational attenuation. Plasmid 26: 10–19.
Stokes, H.W. & R.M. Hall, 1992. The integron In1 in plasmid R46 includes two copies of theoxa2 gene cassette. Plasmid, In press.
Stokes, H.W., Y. Parsons, C. Tomaras & R.M. Hall, 1993. The partial 3′-conserved segment duplications in the integrons In6 from pSa and In7 from pDGO100 have a common origin. Plasmid. 30: 39–50.
Sundström, L., P. Radström, G. Swedberg & O. Sköld, 1988. Site-specific recombination promotes linkage between trimethoprim and sulfonamide resistance genes. Sequence characterization ofdhfrV andsulI and a recombination active locus of Tn21. Mol. Gen. Genet. 213: 191–201.
Sundström, L. & O. Sköld, 1990. ThedhfrI trimethoprim resistance gene of Tn7 can be found at specific sites in other genetic surroundings. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 34: 642–650.
Swift, G., B.J. McCarthy & F. Heffron, 1981. DNA sequence of a plasmid-encoded dihydrofolate reductase. Mol. Gen. Genet. 181: 441–447.
Tait, R.C., H. Rempel, R.L. Rodriguez & C.I. Kado, 1985. The aminoglycoside-resistance operon of the plasmid pSa: nucleotide sequence of the streptomycin-spectinomycin resistance gene. Gene 36: 97–104.
Tanaka, M., T. Yamamoto & T. Sawai, 1983. Evolution of complex resistance transposons from an ancestral mercury transposon. J. Bacteriol. 153: 1432–1438.
Tenover, F.C., K.L. Phillips, T. Gilbert, P. Lockhart, P.J. O'Hara & J.J. Plorde, 1989. Development of a DNA probe from the deoxyribonucleotide sequence of a 3-N-aminoglycoside acetyltransferase [AAC(3)-I] resistance gene. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 33: 551–559.
Tietze, E., J. Brevet & H. Tschape, 1987. Relationships among the streptothricin resistance transposons Tn1825 and Tn1826 and the trimethoprim resistance transposon Tn7. Plasmid 18: 246–249.
Wiedemann, B., J.F. Meyer & M.T. Zuhlsdorf, 1987. Insertions of resistance genes into Tn21-like transposons. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 18: 85–92.
Wohlleben, W., W. Arnold, L. Bissonnette, A. Pelletier, A. Tanguay, P.H. Roy, G.C. Gamboa, G.F. Barry, E. Aubert, J. Davies & S.A. Kagan, 1989. On the evolution of the Tn21-like multiresistance transposons: sequence analysis of the gene (aacC1) for gentamicin acetyltransferase-3-I(AAC(3)-I), another member of the Tn21-based expression cassette. Mol. Gen. Genet. 217: 202–208.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hall, R.M., Stokes, H.W. Integrons: Novel DNA elements which capture genes by site-specific recombination. Genetica 90, 115–132 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01435034
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01435034