Abstract
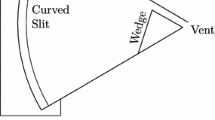
A study to determine the general gas dynamic behaviour associated with the impact of a shock wave on a porous wedge has been undertaken. A number of interesting features are noted. The pattern of wave reflection is shown to be significantly affected by the inflow of gas into the wedge. This has the effect of reducing the triple point trajectory angle for cases of Mach reflection and for strongly reducing the reflection angle in regular reflection. The permeability of the wedge has a significant effect on the strength of the reflected wave and in some cases this wave can be attenuated to the extent that it is almost eradicated. Pressure measurements taken under the wedge are characterized by oscillations which are of similar shape, for a given wedge, over a range of shock wave Mach numbers. It is shown that the wave transmitted into the wedge is attenuated to varying degrees depending on the material properties, and that for weak incident waves the mean propagation velocity can be less than the sound speed in the pore fluid. Photographs taken using a specially constructed wedge which allows the transmitted wave to be visualised, show that the transmitted wave is nearly plane.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi T, Kobayashi S, and Suzuki T (1992) An experimental analysis of oblique shock reflection over a two-dimensional multi-guttered wedge. Fluid Dynamics Research 9: 119–132.
Baer MR (1992) A numerical study of shock wave reflections on low density foam. Shock Waves 2: 121–124.
Beavers GS and Matta RK. (1972) Reflection of weak shock waves from permeable materials. AIAA J 10: 959–961.
Ben-Dor G, Mazor G, Takayama K, and Igra O (1987) Influence of surface roughness on the transition from regular to Mach reflection in pseudosteady flows. J. Fluid Mech. 176: 333–356.
Bray R M. (1984) Reflexion of weak shock waves from acoustically absorbent materials. M.Sc. Thesis. College of Aeronautics, Cranfield Institute of Technology.
Clarke JF (1984) The reflection of weak shock waves from absorbent surfaces. Proc. Roy. Soc. Lond. A396: 365–382.
Cloutier M, Devereux F, Doyon P, Fitchett A, Heckman D, Moir L, and Tardif L (1971) Reflections of weak shock waves from acoustic materials. J Acoust. Soc. Amer. 50: 1393–1396.
Guy TB (1973) Attenuation of reflecting shock waves in a duct with absorbent lining. J Sound Vib. 29: 501–503.
Hornung HG and Taylor JR (1982) Transition from regular to Mach reflection of shock waves. Part I, The effect of viscosity in the pseudosteady case. J. Fluid Mech. 123: 143–153.
Kobayashi S, Adachi T, and Suzuki T. (1993) Regular reflection of a shock wave over porous layer: theory and experiment. 19th International Symposium on Shock Waves, Universite de Provence, Marseille, France.
Levy A, Ben-Dor G, Skews BW, and Sorek S. (1993) Head-on collision of normal shock waves with rigid porous materials. Experiments in Fluids 15: 183–190.
Onodera H and Takayama K (1990) Interaction of a plane shock wave with slitted wedges. Experiments in Fluids 10: 109–115.
Reichenbach H (1985) Roughness and heated layer effects on shock wave propagation and reflection — Experimental results. Ernst Mach Institut Rep E25/85.
Skews BW (1992) Oblique reflection of shock waves from rigid porous materials. 10th Mach Reflection Symposium, University of Denver, Denver, U.S.A.
Skews BW (1993) Shock wave impact on porous materials. 19th International Symposium on Shock Waves. Universite de Provence, Marseille.
Skews BW, Atkins MD, and Seitz (1993) The impact of a shock wave on porous compressible foams. J. Fluid Mech. 253: 245–265.
Smith L G (1945) Photographic investigation of the reflection of plane shocks in air. OSRD Rept 6271.
Suzuki T, Adachi T, and Kobayashi S (1990) An experimental analysis on shock reflection over the two-dimensional model of a dust layer. AIP Conf. Proc. 208: 776–781.
van der Grinten J G M, van Dongen M E H, and van der Kogel H (1985) A shock-tube technique for studying pore-pressure propagation in a dry and water-saturated porous medium. J. Appl. Phys. 58: 2937–2942.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This article was processed using Springer-Verlag TEX Shock Waves macro package 1.0 and the AMS fonts, developed by the American Mathematical Society.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Skews, B.W. Oblique reflection of shock waves from rigid porous materials. Shock Waves 4, 145–154 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01417430
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01417430