Summary
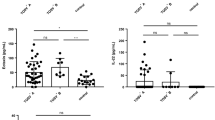
Interferon (IFN) was measured in serum and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of dogs after experimental (intranasal) infection with different strains of virulent canine distemper virus (CDV). Viral strains employed produce neurological changes in dogs that range from acute inflammatory to subacute, delayed demyelinating encephalomyelitis. With few exceptions, first appearance of serum-IFN correlated with the first elevated body temperature 4 days post-infection (p.i.). By 16 days p.i. IFN had disappeared from the serum of all infected dogs. In contrast, IFN was constantly detectable in CSF in dogs with CDV infection of the central nervous system (CNS). It was first detected 5 days p.i., was continuously detectable during the variable preclinical phase and into the period when signs of acute or delayed encephalomyelitis were evident. Dogs from which CDV would be retrieved from CNS tissue at necropsy always had CSF-IFN (up to 56 days p.i.). In contrast, dogs that recovered from infection, substantiated at necropsy by minimal, resolving CNS lesions and non-detectable virus, had IFN in CSF demonstrable for only a brief post-inoculation period. CSF-IFN appears to be a valid marker for CDV persistence in the canine CNS and may have broader applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appel, M. J. G.: Pathogenesis of canine distemper. Amer. J. vet. Res.30, 1167–1182 (1969).
Appel, M. J. G., Gibbs, E. P. J., Martin, S. J., Meulen, V. ter, Rima, B. K., Stephenson, J. R., Taylor, W. P.: Morbillivirus diseases of animals and man. In:Kurstak, E. (ed.), Comparative diagnosis of viral diseases, Vol. IV: Vertebrate animal and related viruses. New York: Academic Press 1981.
Appel, M. J. G., Jones, O. R.: Use of alveolar macrophages for cultivation of canine distemper virus. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. Med.126, 571–574 (1967).
Appel, M. J. G., Robson, D. S.: A microneutralization test for canine distemper virus. Amer. J. vet. Res.34, 1450–1462 (1973).
Campbell, J. J., Cosby, J. K., Scott, J. K., Rima, B. K., Martin, S. J., Appel, M.: A comparison of measles and canine distemper virus polypeptides. J. gen. Virol.48, 149–159 (1980).
Cook, S. D., Dowling, P. C.: Multiple sclerosis and viruses: An overview. Neurology30, 80–91 (1980).
Degre, M., Dahl, H., Vandvik, B.: Interferon in the serum and cerebrospinal fluid in patients with multiple sclerosis and other neurological disorders. Acta Neurol. Scand.53, 152–160 (1976).
Friedman, R. M., Ramseur, J. M.: Inhibition of murine leukemia virus production in chronically infected AKR cells: A novel effect of interferon. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.71, 3542–3544 (1974).
Gresser, I., Naficy, K.: Recovery of an interferon-like substance from cerebrospinal fluid. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. Med.117, 285–289 (1964).
Gresser, I., Tovey, M. G., Bandu, M. T., Maury, C., Brouty-Boye, D.: Role of interferon in the pathogenesis of virus diseases in mice as demonstrated by the use of anti-interferon serum. J. exp. Med.144, 1305–1315 (1976).
Hall, W. W., Lamb, R. A., Choppin, P. W.: The polypeptides of canine distemper virus: Synthesis in infected cells and relatedness to the polypeptides of other morbilliviruses. Virology100, 433–449 (1980).
Hilfenhaus, J., Ackermann, R.: Endogenous interferon in the cerebrospinal fluid of herpes encephalitis patients. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. Med.166, 205–209 (1981).
Jacobs, L., O'Malley, J., Freeman, A., Ekes, R.: Intrathecal interferon reduces exacerbations of multiple sclerosis. Science214, 1026–1028 (1981).
Joncas, J. H., Robillard, L. R., Boudreault, A., Leyritz, M., McLaughlin, B. J. M.: Interferon in serum and cerebrospinal fluid in subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Can. Med. Assoc. J.115, 309 (1976).
Koestner, A.: Animal model — distemper-associated sclerosing panencephalitis. Amer. J. Pathol.78, 361–364 (1975).
Larke, R. P. B.: Interferon in the cerebrospinal fluid in children with central nervous system disorders. Can. Med. Assoc. J.96, 21–32 (1967).
Legasapi, R. C., Gatmaitan, B., Bailey, E. J., Lerner, A. M.: Interferon in biopsy and autopsy specimens of brain. Its presence in herpes simplex virus encephalitis. Arch. Neurol.37, 76–79 (1980).
McCullough, B., Krakowka, S., Koestner, A.: Experimental canine distemper virus-induced demyelination. Lab. Invest.31, 216–222 (1974).
Pitha, P. M., Wivel, N. A., Fernie, B. F., Harper, H. P.: Effects of interferon on murine leukemia virus infection. IV. Formation of non-infectious virus in chronically infected cells. J. gen. Virol.42, 467–480 (1979).
Raine, C. S.: The etiology and pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis: Recent developments. In:Ioachim, H. L. (ed.), Pathobiology Annual, Vol. 7, 347–384. Appleton-Century-Crofts 1977.
Ramseur, J. M., Friedman, R. M.: Prolonged infection of interferon-treated cells by vesicular stomatitis virus: Possible role of temperature sensitive mutants and interferon. J. gen. Virol.37, 523–533 (1977)
Stephenson, J. R., ter Meulen, V.: Antigenic relationships between measles and canine distemper viruses: Comparison of immune response in animals and humans to individual virus-specific polypeptides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.76, 6601–6605 (1979).
Stringfellow, D. A., Kern, E. R., Kelsey, D. G., Glasgow, L. A.: Suppressed response to interferon induction in mice infected with encephalomyelitis virus, Semliki Forest virus, influenza A 2 virus, herpesvirus hominis type 2, or murine cytomegalovirus. J. Inf. Dis.135, 540–551 (1977).
Summers, B. A., Greisen, H. A., Appel, M. J. G.: Possible initiation of viral encephalomyelitis in dogs by migrating lymphocytes infected with distemper virus. Lancetii, 187–190 (1978).
Summers, B. A., Greisen, H. A., Appel, M. J. G.: Early events in canine distemper demyelinating encephalomyelitis. Acta Neuropathol.46, 1–10 (1979).
Tsai, S. C., Appel, M. J.: Interferon induction in dogs. Amer. J. vet. Res.40, 356–361 (1979).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
With 3 Figures
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsai, S.C., Summers, B.A. & Appel, M.J.G. Interferon in cerebrospinal fluid. Archives of Virology 72, 257–265 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01315222
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01315222