Summary
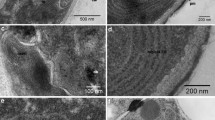
Ultrastructural observations on the principal endomembranes (endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus) of synchronously growing of wild type and mutant (CW 2, CW 15) strains ofChlamydomonas reinhardii have been carried out. The dictyosomes of the Golgi apparatus in all three cases are highly polar in morphology but lack intercisternal filaments. A clear spatial relationship between dictyosomes and endoplasmic reticulum is seen and a transfer of vesicles from the latter to the former is easily visualized. Coated vesicles invariably appear to be restricted to the trans-pole of the dictyosomes. The endoplasmic reticulum adjacent to the cis pole of dictyosomes is considerably hypertrophied in the case of the wild type, only partially so in the mutant CW 2 but not at all in the mutant CW 15. In the wild type this swelling is most extreme during the period of wall deposition and for several hours afterwards. The results are discussed in relation to the biosynthesis and intracellular transport of, particularly O-glycosidically linked, glycoproteins.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberts B, Bray D, Lewis J, Raff M, Roberts K, Watson JD (1983) Molecular biology of the cell. Garland Publishing Inc, New York London
Amrhein N, Filner P (1973) Adenosine 3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate inChlamydomonas reinhardii. Isolation and characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 70: 1099–1107
Bloom W, Fawcett DW (1975) Textbook of histology. 10th edn. Saunders WB. Philadelphia London Toronto
Dodge JD (1973) The fine structure of algal cells. Academic Press, New York
Farquhar MG (1985) Progress in unraveling pathways of Golgi traffic. Ann Rev Cell Biol 1: 447–488
—,Palade GE (1981) The Golgi apparatus (complex)—(1954–1981)-from artifact to center stage. J Cell Biol 91: 775–1035
Griffiths G, Pfeiffer S, Simons K, Matlin K (1985) Exit of newly synthesized membrane proteins from the trans cisterna of the Golgi complex to the plasma membrane. J Cell Biol 101: 949–964
Hyams J, Davies DR (1972) The induction and characterization of cell wall mutants ofChlamydomonas reinhardii. Mutation Res 14: 381–389
Jaenicke L, Waffenschmidt S (1981) Literation of reproduction units inVolvox andChlamydomonas: proteolytic processes. Ber dt bot Ges 94: 375–386
Johnson UG, Porter K (1968) Fine structure of cell division inChlamydomonas reinhardii. Basal bodies and microtubules. J Cell Biol 38: 403–425
Kristen U (1980) Endoplasmic reticulum-dictyosome interconnections in ligula cells ofIsoetes lacustris. Eur J Cell Biol 23: 16–21
Lang NJ (1963) Electron microscopy of theVolvocaccae andAstrephomenaceae. Am J Bot 50: 280–300
Lang W, Chrispeels MJ (1976) Biosynthesis and release of cell walllike glycoproteins during the vegetative cell cycle ofChlamydomonas reinhardii. Planta 129: 183–189
Lockhausen J,Kristen U (1986) Dictyosome-endoplasmic reticulum associations in gland cells ofVeronica beccabunga. Eur J Cell Biol (in press)
Matsuda Y, Yamazaki Y, Saito T, Yamaguchi T (1984) Purification and characterization of cell wall lytic enzyme released by mating types ofChlamydomonas reinhardii. FEBS Lett 166: 293–297
Melkonian M (1984) Flagellar root-mediated interactions between the flagellar apparatus and cell organelles in green algae. In:Wiessner W, Robinson DG (eds) Compartments in algal cells and their interaction. Springer, Heidelberg New York, pp 96–108
Mihara S, Hase (1971) Studies on the vegetative life cycle ofChlamydomonas reinhardii Dangeard in synchronous culture. I. Some characteristics of the cell cycle. Plant and Cell Physiol 12: 225–236
Mollenhauer HH.Morré DJ (1978) Structural differences contrast higher plant and animal Golgi apparatus. J Cell Sci 32: 357–362
— —,Totten C (1973) Intercisternal substances of the Golgi apparatus, unstacking of plant dictyosomes using chaotropic agents. Protoplasma 78: 443–459
Orci L, Ravazzola M, Amherdt M, Louvard D, Perrelet A (1985) Clathrin-immunoreactive sites in the Golgi apparatus are concentrated at the trans pole in polypeptide hormone-secreting cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 42: 5385–5389
Palade GW (1975) Intracellular aspects of the process of protein secretion. Science 189: 347–358
Pickett-Heaps JD, Fowke LC (1969) Cell division inOedogonium. I. Mitosis, cytokinesis and cell elongation. Austr J Biol Sci 22: 857–894
Pickett-Heaps JD, Fowke LC (1970) Cell division inOedogonium. II. Nuclear division inO. cardiacum. Austr J Biol Sci 23: 71–92
—(1971) Reproduction by zoospores inOedogonium. I. Zoosporogenesis. Protoplasma 72: 275–314
—Staehelin LA (1975) The ultrastructure ofScenedesmus (Chlorophyceae). II. Cell division and colony formation. J Phycol 11: 186–202
Pohlmann R, Waheed A, Hasilik A, Figura K von (1982) Synthesis of phosphorylated recognition marker in lyosomal enzymes is located in the cis part of Golgi apparatus. J Biol Chem 257: 5323–5325
Roberts K (1974) Crystalline glycoprotein cell walls of algae: their structure, composition and assembly. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B 268: 129–146
— (1982) The structure of algal cell walls. In:Harris JR (ed) Electron microscopy of proteins, vol III. Academic Press, London, pp 1–40
Robinson DG (1980) Dictyosome-endoplasmic reticulum associations in higher plant cells? A serial-section analysis. Eur J Cell Biol 23: 22–36
—Kristen U (1982) Membrane flow via the Golgi apparatus of higher plant cells. Int Rev Cytol 77: 89–127
— (1985) Plant Membranes: endoand plasma membranes of plant cells. In:Bittar EE (ed) Cell Biology Monographs, vol 3. Wiley, New York
Schlösser UG (1966) Enzymatisch gesteuerte Freisetzung von Zoosporen beiChlamydomonas reinhardii Dangeard in Synchronkultur. Arch Mikrobiol 54: 129–159
Schnepf E, Deichgräber G, Herth W (1982) Development of cell wall appendages inAcanthosphaera zachariasi (Chlorococcales): kinetics, site of cellulose synthesis and of microfibril assembly, and barb formation. Protoplasma 110: 203–214
Schötz F, Barthelt H, Arnold C-G, Schimmer O (1972) Die Architektur und Organisation der Chlamydomonas-Zelle. Ergebnisse der Elektronenmikroskopie von Serienschnitten und der daraus resultierenden dreidimensionalen Rekonstruktion. Protoplasma 75: 229–254
Tartakoff AM (1983) The confined function model of the Golgi complex: center for ordered processing of biosynthetic products of the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Int Rev Cytol 85: 221–252
Turner FR, Whaley WG (1965) Intercisternal elements of the Golgi apparatus. Science 147: 1303–1304
Zhang Yu-Hua, Robinson DG (1987) On the fixation ofChlamydomonas reinhardii. Ber dt Bot Ges (in press)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, YH., Robinson, D.G. The Endomembranes ofchlamydomonas reinhardii: A comparison of the wildtype with the wall mutants CW 2 and CW 15. Protoplasma 133, 186–194 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01304634
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01304634