Summary
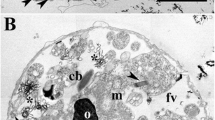
The differentiation of resting cysts of the algaPolytomella agilis was examined by electron microscopy. During encystment the free-swimming, quadriflagellate unicells lose their flagella, sink to the bottom of the culture, and form a thick cell wall. Populations of cells at various stages of encystment were collected on microscope slides placed at the bottom of the culture flasks. The mature cyst wall consists of four layers which are laid down sequentially next to the plasma membrane. Freeze-etching has shown that the first layer of wall deposited consists of fibrils which are formed partly embedded within the plasma membrane. A proliferation of rough endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi bodies is seen in early stages of encystment followed by a reduction in size or number of these organelles and of plastids in the maturing cyst. Microtubular structures, including the basal bodies, dedifferentiate and are not observed in the later stages of encystment. The redifferentiation of the swimming cell during excystment is described in the companion paper.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bibby, B. T., andJ. D. Dodge, 1972: The encystment of a freshwater dinoflagellate: a light and electron-microscopical study. Brit. Phycol. J.7, 85–100.
Bloodgood, R. A., 1974: Resorption of organelles containing microtubules. Cytobios9, 143–161.
Branton, D.,et al., 1975: Freeze-etching nomenclature. Science190, 54–56.
Brown, D. L., A. Massalski, andR. Patenaude, 1976: Organization of the flagellar apparatus and associated microtubules in the quadriflagellate algaPolytomella agilis. J. Cell Biol.69, 106–125.
Brown, D. L., A. Massalski, andG. G. Leppard, 1976: Fine structure of excystment of the quadriflagellate algaPolytomella agilis. Protoplasma90, 155–171.
Colvin, J. R., and G. G.Leppard, 1976: The biosynthesis of cellulose byAcetobacter xylinum andAcetobacter acetigenum (in press).
- L. C.Sowden, and G. G.Leppard, 1976: The structure of the cellulose-producing bacteria,Acetobacter xylinum andAcetobacter acetigenum (in press).
Corliss, J. O., andS. C. Esser, 1974: Comments on the role of the cyst in the life cycle and survival of free-living protozoa. Trans. amer. micros. Soc.93, 578–593.
Gittleson, S. M., R. E. Alper, andS. F. Conti, 1969: Ultrastructure of trophic and encystedPolytomella agilis. Life Sci.8, 591–599.
Grimes, G. W., 1973: Morphological discontinuity of kinetosomes during the life cycle ofOxytricha fallax. J. Cell Biol.57, 229–232.
Hearth, W., A. Kuppel, andW. W. Franke, 1975: Cellulose inAcetabularia cyst walls. J. Ultrastruct. Res.50, 289–292.
Kahn, W. C., andJ. Moore, 1971: Excystment inPolytomella agilis. J. Protozool.18, 19–20 (abstr.).
Kater, J., 1925: Morphology and life history ofPolytomella citri sp. nov. Biol. Bull.49, 213–236.
—, andR. D. Burroughs, 1926: The cause and nature of encystment inPolytomella citri, Biol. Bull.50, 38–55.
Kink, J., 1973: The organization of fibrillar structures in the trophic and encystedDileptus visscheri (Ciliata, Rhabdophorina). Acta Protozool.12, 173–194.
Leppard, G. G., L. C. Sowden, andJ. R. Colvin, 1975: Nascent stage of cellulose biosynthesis. Science189, 1094–1095.
Lewis, E., G. Munger, R. Watson, andD. Wise, 1974: Life cycle ofPolytomella caeca (Phytomonadida, Polyblepharidae). J. Protozool.21, 647–649.
Moor, H., 1971: Recent progress in the freeze-etching technique. Trans. Roy. Soc. (London), Ser. B261, 121–131.
Moore, J., M. H. Cantor, P. Sheeler, andW. Kahn, 1970: The ultrastructure ofPolytomella agilis. J. Protozool.17, 671–676.
Neff, R. J., S. A. Ray, W. F. Benton, andM. Wilborn, 1964: Induction of synchronous encystment (differentiation) inAcanthamoeba sp. In: Methods in cell physiology (D. M. Prescott, ed.),1, pp. 55–83. New York: Academic Press Inc.
Potter, J. L., andR. A. Weisman, 1972: Correlation of cellulose synthesisin vivo andin vitro during the encystment ofAcanthamoeba. Dev. Biol.28, 472–479.
Pringheim, E. G., 1955: The genusPolytomella. J. Protozool.2, 137–145.
Sheeler, P., M. Cantor, andJ. Moore, 1970: Studies on the growth and encystment ofPolytomella agilis. J. Protozool.69, 171–185.
Tibbs, J., 1968: Fine structure ofColpoda steinii during encystment and excystment. J. Protozool.15, 725–732.
Tomlinson, G., andE. A. Jones, 1962: Isolation of cellulose from the cyst wall of a soil amoeba. Biochim. biophys. Acta63, 194–200.
Willison, J. H. M., andE. C. Cocking, 1975: Microfibril synthesis at the surfaces of isolated tobacco mesophyll protoplasts, a freeze-etch study. Protoplasma84, 147–159.
Woodcock, C. L. F., andG. J. Miller, 1973 a: Ultrastructural features of the life cycle ofAcetabularia mediterranea. I. Gametogenesis. Protoplasma77, 313–329.
— —, 1973 b: Ultrastructural features of the life cycle ofAcetabularia mediterranea. II. Events associated with the division of the primary nucleus and the formation of cysts. Protoplasma77, 331–341.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by grant A6353 from the National Research Council of Canada to D. L.Brown and by the Inland Waters Directorate of Environment Canada.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brown, D.L., Leppard, G.G. & Massalski, A. Fine structure of encystment of the quadriflagellate alga,Polytomella agilis . Protoplasma 90, 139–154 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01276484
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01276484