Abstract
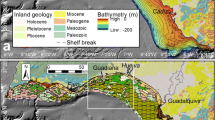
During the Quaternary, the Mac. Robertson shelf of East Antarctica was deeply eroded by glaciers and currents exposing the underlying basement, resulting in a scalped shelf. Major geomorphic zones are: (1) high-relief, ridge and valley topography (200–1400 m); (2) smooth sea floors associated with low-energy, depositional shelf valleys and basins (400–800 m); (3) low-relief, planated banktops (100–200 m); and (4) iceberg gouged and current reworked seaward-bank margins and upper slope (200 to < 630 m). About 90% of the shelf's surface has net erosional conditions and about 10% is net depositional. The sedimentary processes and deposits may be common to large areas of the East Antarctic margin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams CE, Wells JT, and Coleman JM (1986) Transverse bedforms on the Amazon shelf. Continental Shelf Research 6:175–187
Anderson JB and Molnia BF (1989) Glacial-Marine Sedimentation. Short Course in Geology 9, Washington DC: American Geophysical Union, 127 pp
Anderson JB, Brake C, Domack EW, Meyers N, and Singer J (1983) Sedimentary dynamics of the Antarctic continental shelf. In: Oliver RL, James PR, and Jago JB (Eds.), Proceedings of the Fourth International Symposium on Antarctic Earth Science. Canberra: Australian Academy of Science, pp 387–389
Ashley GM and panel members (1990) Classification of large-scale subaqueous bedforms: A new look at an old problem. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology 60:160–172
Barnes PW and Lien R (1988) Icebergs rework shelf sediments to 500 m off Antarctica. Geology 16:1130–1133
Barnes PW, Ashbury JL, Rearic DM, and Ross CR (1987) Ice erosion of a seafloor knickpoint at the inner edge of the Stamukhi Zone, Beaufort Sea, Alaska. Marine Geology 76:207–222
Domack EW (1988) Biogenic facies in the Antarctic glacimarine environment: Basis for a polar glacimarine summary. Palaeogeogrpahy, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 63:357–372
Domack EW, Jull AJT, and Nakao S (1991a) Advance of East Antarctic outlet glaciers during the Hypsithermal: Implications for the volume state of the Antarctic ice sheet under global warming. Geology 19:1059–1062
Domack EW, Jull, AJT, Anderson JB, and Linick TW (1991b) Mid-Holocene ice sheet recession from Wilkes Land continental shelf, East Antarctica. In: Thomson MRA, Crame JA, and Thomson JW (Eds.), Geological Evolution of Antarctica. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp 693–698
Dunbar RB, Anderson JB, Domack EW, and Jacobs SS (1985) Oceanographic influences on sedimentation along the Antarctic continental shelf. In Jacobs, S (Ed.), Oceanography of the Antarctic Continental Shelf. Washington D.C.: American Geophysical Union, pp 291–312
Flemming BW (1978) Underwater sand dunes along the southeast African continental margin—observations and implications. Marine Geology 26:177–198
Gordon JE and Harkness DD (1992) Magnitude and geographic variation of the radiocarbon content in Antarctic marine life: Implications for reservoir corrections in radiocarbon dating. Quaternary Science Reviews 11:697–708
Hambrey MJ (1994) Glacial Environments. London: UCL Press, 296 pp
Harris PT, Tsuji Y, Marshall JF, Davies PJ, Honda N, and Matsuda H (1996) Sand and rhodolith-gravel entrainment on the mid- to outer-shelf under a western boundary current: Fraser Island continental shelf, eastern Australia. Marine Geology 129:313–330
Hodgkinson RP, Colman RS, Kerry KR, and Robb M (1988) Water currents in Prydz Bay, Antarctica during 1985. ANARE Research Notes No. 59, Australian Antarctic Division, 127 pp
Hodgkinson RP, Colman RS, Robb M, and Williams R (1991a) Current meter moorings in the region of Prydz Bay, Antarctica, 1986. ANARE Research Notes No. 81, Australian Antarctic Division, 130 pp
Hodgkinson RP, Colman RS, Robb M, and Williams R (1991b) Current meter moorings in the region of Prydz Bay, Antarctica, 1987. ANARE Research Notes No. 82, Australian Antarctic Division, 68 pp
Ikehara K and Yasumasa K (1994) Distribution and origin of subaqueous dunes on the shelf of Japan. Marine Geology 120:75–87
Jacobs SS (1989) Marine controls on modern sedimentation on the Antarctic continental shelf. Marine Geology 85:121–153
James NP, Boreen TD, Bone Y, and Feary DA (1994) Holocene carbonate sedimentation on the west Eucla Shelf, Great Australian Bight: A shaved shelf. Sedimentary Geology 90:161–177
Johnson GL, Vanney JR, and Hayes D (1982) The Antarctic continental shelf. In: Craddock C (Ed.), Antarctic Geoscience. Madison: University of Wisconsin Press, pp 995–1002
Kenyon NH (1970) Sand ribbons of the European tidal seas. Marine Geology 9:25–39
Morgan VI and Budd WF (1978) Distribution, movement and melt rates of Antarctic icebergs. In: Husseiny AA (Ed.), International Conference and Workshop on Iceberg Utilisation for Fresh Water Production, Weather Modification and other Applications. New York: Pergamon Press, pp 220–228
O'Brien PE, Truswell EM, and Burton T (1994) Morphology, seismic stratigraphy and sedimentation history of the Mac. Robertson shelf, East Antarctica. Terra Antarctica 1(2):407–408
Quilty P (1985) Distribution of foraminiferids in sediments of Prydz Bay. South Australian Department of Mines and Energy Special Publication 5:329–340
Shepard FP (1963) Submarine Geology. New York: Harper and Row, 557 pp
Smith NR, Zhaoqian D, and Wright S (1984) Water masses and circulation in the region of Prydz bay, Antarctica. Deep-Sea Research 31(9):1121–1147
Stagg HMJ (1985) The structure and origin of Prydz Bay and Mac Robertson shelf, East Antarctica. Tectonophysics 114:315–340
Stagg HMJ, Ramsay DC, and Whitworth R (1983) A preliminary report of a marine geophysical survey between Davis and Mawson Stations, 1982. In: Oliver RL, James PR, and Jago JB (Eds.), Proceedings Fourth International Symposium on Antarctic Earth Science. Canberra: Australian Academy of Science, pp 527–532
Swift DJP, Stanley DJ, and Curray JR (1971) Relict sediments, a reconsideration. Journal of Geology 79:322–346
Vanney JR and Johnson GL (1985) GEBCO bathymetric sheet 5.18 (Circum-Antarctic). In: Jacobs SS (Ed.), Oceanology of the Antarctic Continental Shelf. Washington, D.C.: American Geophysical Union, pp 1–3
Walker RG (1984) Shelf and shallow marine sands. In: Walker RG (Ed.), Facies Models. Toronto: Geological Association of Canada, pp 141–170
Wong AP (1994) Structure and dynamics of Prydz Bay, Antarctica, as inferred from a summer hydrographic data set. Unpublished MS thesis. University of Tasmania, 104 pp
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harris, P.T., O'Brien, P.E. Geomorphology and sedimentology of the continental shelf adjacent to Mac. Robertson Land, East Antarctica: A scalped shelf. Geo-Marine Letters 16, 287–296 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01245559
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01245559