Abstract
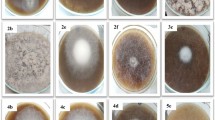
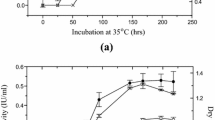
Biodegradation of pure cellulose powder, bagasse and wheatstraw by five cellulolytic fungi,Aspergillus niger, Chaetomium globosum, Scopulariopsis brevicaulis, Trichoderma koningii andTrichothecium roseum, was studied in solid culture conditions. Minimum degradation was with pure cellulose. Bagasse and wheatstraw were the most suitable for growth and activity of cellulolytic fungi. All fungi contained cellulase activity.
Résumé
On a étudié la biodégradation de la poudre de cellulose pure, de la bagasse et de la paille de froment chez cinq moisissures cellulolytiques,Aspergillus niger, Chaetomium globosum, Scopulariopsis brevicaulis, Trichoderma koningii etTrichothecium roseum, en condition de culture sur milieu solide. La dégradation minimum a lieu avec la cellulose pure. La bagasse et la paille de froment offrent la meilleure croissance et la meilleure activité cellulolytique fungale. Toutes les moisissures exhibent l'activité de la cellulase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Canevascini, G. &Gattlen, C. 1981 A comparative investigation of various cellulase assay procedures.Biotechnology andBioengineering 23, 1573–1590.
Domsch, K.H. &Gans, W. 1972Fungi in Agricultural Soils. Edinburgh: Longman.
Hohn, H. P. &Sahm, H. 1983 Induction of cellulases inTrichoderma reesei. Enzyme Technology IIIRotenburg Fermentation Symposium 1982. (Ed. R.M. Lafferty). Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag.
Jain, M.K., Kapoor, K.K. &Mishra, M.M. 1979 Cellulase activity, degradation of cellulose and lignin, and humus formation by thermophilic fungi.Transactions of the British Mycological Society 73, 85–89.
Mandels, M., Andreotti, R.E. &Roche, C. 1976 Measurement of saccharifying cellulase.Biotechnology andBioengineering Symposium 6, 21–33.
Miller, G.L. 1959 Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar.Analytical Chemistry 31, 425–428.
Trivedi, L.S. &Rao, K.K. 1980 Cellulose induction inAspergillus fumigatus M-216,Indian Journal of Experimental Biology 18, 240–242.
Wabnegg, F., Messner, K. &Rohr, M. 1980 A screening method for the estimation of filter paper activity.Journal of General Microbiology 117, 267–269.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lakshmikant Cellulose degradation and cellulase activity of five cellulolytic fungi. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 6, 64–66 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01225357
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01225357