Abstract
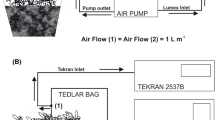
Historical studies for crop and weed species documented elemental Hg vapor (Hg°) deposition to foliage, but they used Hg° concentrations that were orders of magnitude higher than levels now known to occur under background conditions, possibly creating artificially high gradients between the atmosphere and landscape surfaces. Measurements of Hg° exchange with white oak (Quercus alba L.), red maple (Acer rubrum L.), Norway spruce (Picea abies L.), and yellow-poplar (Liriodendron tulipifera L.) foliage were conducted in an open gas exchange system that allows for simultaneous measurements of CO2, H2O and Hg° exchange under controlled environmental conditions. When Hg° concentrations were held at 0.5 to 1.5 ng m−3, red maple (Acer rubrum L.), Norway spruce (Picea abies L.), yellow-poplar (Liriodendron tulipifera L.), and white oak (Quercus alba L.) foliage exhibited mean Hg° emissions of 5.5, 1.7, 2.7, and 5.3 ng m−2 h−1, respectively. At Hg° concentrations between 9 and 20 ng m−3 little net exchange of Hg° was observed. However at concentrations between 50 and 70 ng m−3 the Hg° was deposited to foliage at rates between 22 and 38 ng m−2 h−1. These data suggest that dry foliar surfaces in terrestrial forest landscapes may be a dynamic exchange surface that can function as a source or sink dependent on the magnitude of current Hg° concentrations. These data provide evidence of species-specific compensation concentrations (or compensation points) for Hg° deposition to seedling foliage in the 10–25 ng m−3 range.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beauford, W., Barber, J., Barringer, A.R.: 1977,Physiol. Plant. 39, 261–265.
Bloom, N., Fitzgerald, W.F.: 1988,Anal. Chem. Acta. 208, 151–161.
Browne, C.L. and Fang, S.C.: 1978.Plant Physiol. 61, 430–433.
Dolar, S.G., Keeney, D.R., Chesters, G.: 1971,Environ. Letters 1, 191–198.
Du, S. and Fang, S.C.: 1983,Environ. Exp. Bot. 23, 347–353.
Du, S. and Fang, S.C.: 1982.Environ. Exp. Bot. 22, 437–443.
Farquhar, G.D. and Firth, P.M., Wetselaar, R. et al.: 1980,Plant Physiol. 66, 710–714.
Fitzgerald, W.F. and Gill, G.A.: 1979,Anal. Chem. 51, 1714–1720.
Hanson, P.J. and Lindberg, S.E.: 1991,Atmospheric Environment 25A, 1615–1634.
Hanson, P.J., Rott, K., Taylor, G.E.Jr., et al.: 1989,Atmospheric Environ. 23, 1783–1794.
Johansson, C.: 1987.Tellus 39B, 426–438.
Kim, K.-H. and Lindberg, S.E.: 1994,J. Geophys. Res. 99(D3), 5379–5384.
Kothny, E.L., 1973.Trace elements in the environment. p. 48–80.
Kozuchowski, J. and Johnson, D.L.: 1978,Nature 274, 468–469.
Lindberg, S.E., Meyers, T.P., Taylor, G.E.Jr., et al.: 1992.J. Geophys. Res. 97(D2), 2519–2528.
Lindberg, S.E., Jackson, D.R., Huckabee, J.W., et al.: 1979,J. Environ. Qual. 8, 572–578.
Lindqvist, O.: 1985,Tellus 37B, 136–159.
Parkhurst, D.F.: 1994,New Phytol. 126, 449–479.
Rasmussen, P.E., Mierle, G., Nriagu, J.O.: 1991,Water Air Soil Pollut. 56, 379–390.
Schroeder, W.H., Munthe, J., Lindqvist, O.: 1989,Water Air Soil Pollut. 48, 337–347.
Siegel, S.M., Puemer, N.J., Speitel, T.W.: 1974,Physiol. Plant. 32, 174–176.
Siegel, S.M. and Siegel, B.Z.: 1988,Water Air Soil Pollut. 40, 443–448.
Siegel, S.M., Siegel, B.Z., Okasako, J.: 1981,Water Air Soil Pollut. 15, 371–374.
Swain, E.B., Engstrom, D.R., Brigham, M.E., et al.: 1992,Science 257, 784–787.
Taylor, G.E.Jr. and Tingey, D.T.: 1983,Plant Physiol. 72, 237–244.
Taylor, G.E. Jr., Tingey, D.T., Ratsch H.: 1982,Oecologia 53, 179–186.
Taylor, G.E. Jr., Hanson, P.J. Baldocchi, D.D.: 1988,Assessment of Crop Loss From Air Pollutants. pp. 227–257
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hanson, P.J., Lindberg, S.E., Tabberer, T.A. et al. Foliar exchange of mercury vapor: Evidence for a compensation point. Water Air Soil Pollut 80, 373–382 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01189687
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01189687