Summary
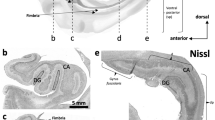
During development in the cochlea, NCAM is present on all neuronal systems — radial fibres, inner spiral bundle, inner pillar bundle (described by Sobkowicz & Emmerling, 1989), and outer spiral fibres. In cochleae from E17 mice, NCAM-positive puncta, possibly associated with growth cones, dot the area of the inner spiral bundle. The region overlying the basilar membrane is also NCAM positive. Until about P7, NCAM immunoreactivity surrounds the inner and outer hair cells. During the second postnatal week, NCAM no longer covers the hair cell surfaces. At this time, NCAM is present on the inner spiral and inner pillar bundles. In the outer hair cell region, immunoreactivity concentrates in neuronal endings with ‘Y’-like or ‘dot’-like appearances typical of cholinergic efferents. At a time when neuronal fibres are regenerating in the cochlea of the Bronx waltzer mutant mouse, many NCAM-positive puncta dot the regions of the inner spiral bundle and inner spiral sulcus, suggesting that these puncta correspond to growth cones. In organotypic culture, hair cells and nerve fibres retain their immunoreactivity up to 7 days. In conclusion, NCAM is present on the surfaces of neurons and on their cochlear targets at the time when nerve-target recognition is proceeding. NCAM disappears from targets during the time of maturation of efferent synapses. NCAM is also present along the growth path of the nerve fibres. These studies suggest that NCAM is properly positioned in the cochlea for possible roles in axon guidance and nerve-target interactions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berglund, A. M. &Ryugo, D. K. (1987) Hair cell innervation by spiral ganglion neurons in the mouse.Journal of Comparative Neurology 255, 560–70.
Bhat, S. &Silberberg, D. H. (1987) C6 glioma cells express modified neural cell adhesion molecule-like glyco- proteins.Brain Research 412, 144–7.
Bixby, J. L. &Reichardt, L. F. (1987) Effects of antibodies to neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) on the differentiation of neuromuscular contacts between ciliary ganglion neurons and myotubesin vitro.Developmental Biology 119, 363–72.
Bixby, J. L., Pratt, R. S., Lilien, J. &Reichardt, L. (1987) Neurite outgrowth on muscle cell surfaces involves extracellular matrix receptors as well as Ca2+- dependent and -independent cell adhesion molecules.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 84, 2555–59.
Buskirk, D. R., Thiery, J.-P., Rutishauser, U. &Edelman, G. M. (1980) Antibodies neural cell adhesion molecule disrupt histogenesis in cultured chick retinae.Nature 285, 488–9.
Chuong, C. -M. &Edelman, G. M. (1985a) Expression of cell adhesion molecules in embryonic induction. II. Morphogenesis of adult feathers.Journal of Cell Biology 101, 1027–43.
Chuong, C. -M. &Edelman, G. M. (1985b) Expression of cell adhesion molecules in embryonic induction. I. Morphogenesis of nestling feathers.Journal of Cell Biology 101, 1009–26.
Covault, J. &Sanes, J. R. (1986) Distribution of NCAM in synaptic and extrasynaptic portions of developing and adult skeletal muscle.Journal of Cell Biology 102, 716–30.
Dahl, D. &Bignami, A. (1977) Preparation of antisera to neurofilament proteins from chick brain and human sciatic nerve.Journal of Comparative Neurology 176, 645–58.
Daniloff, J. K., Levi, G., Grumet, M., Rieger, F. &Edelman, G. M. (1986) Altered expression of neuronal cell adhesion molecules induced by nerve injury and repair,journal of Cell Biology 103, 929–45.
Deol, M. S. (1980) Genetic malformations of the inner ear in the mouse and in man. Birth Defects: Original Article Series, Volume XVI, Number 4, p. 243–61.
Deol, M. S. &Gluecksohn-Waelsch, S. (1979) The role of inner hair cells in hearing.Nature 278, 250–2.
Ehret, G. (1979) Quantitative analysis of nerve fibre densities in the cochlea of the house mouse (Mus musculus).Journal of Comparative Neurology 183, 73–89.
Emmerling, M. E., Sobkowicz, H. M., Rose, J. E., Levenick, C. V., Scott, G. L. &Slapnick, S. M. (1990) Biochemical and morphological differentiation of acetyl- cholinesterase-positive efferent fibres in the mouse cochlea,journal of Electron Microscopy Techniques 15, 123–43.
Fraser, S. E., Murray, B. A., Chuong, C.-M. &Edelman, G. M. (1984) Alteration of the retinotectal map in Xenopus by antibodies to neural cell adhesion molecules.Proceedings of the National Academy of Science (USA) 81, 4222–6.
Grumet, M., Rutishauser, U. &Edelman, G. M. (1982) Neural cell adhesion molecule is on embryonic muscle cells and mediates adhesion to nerve cellsin vitro.Nature 295, 693–5.
Hall, A. K. &Rutishauser, U. (1985) Phytogeny of a neural cell adhesion molecule.Developmental Biology 110, 39–46.
Held, H. (1926) Die Cochlea der Sauger and der Vogel, ihre entwickelung und ihr Bau. In:Hanbuch der Normalen und Pathologischen Physiologie (edited byBethe, A., Bergman, G., Embden, G. &Ellinger, A.) Berlin: Julius Springer, p. 467–534.
Hoffman, S. &Edelman, G. M. (1983) Kinetics of homophilic binding by embryonic and adult forms of the neural cell adhesion molecule.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 80, 5762–66.
Keilhauer, G., Faissner, A., Schachner, M. (1985) Differential inhibition of neurone-neurone, neurone-astrocyte and astrocyte-astrocyte adhesion by L1, L2 and NCAM antibodies.Nature 316, 728–31.
Kiang, N. Y. S., Rho, J. M., Northrop, C. C., Liberman, M. C. &Ryugo, D. K. (1982) Hair cell innervation by spiral ganglion cells in adult cats.Science 217, 175–77.
Landmesser, L., Dahm, L., Schultz, K. &Rutishauser, U. (1988) Distinct roles for adhesion molecules during innervation of embryonic chick muscle.Developmental Biology 130, 645–70.
Letourneau, P. C. &Shattuck, T. A. (1989) Distribution and possible interactions of actin associated proteins and cell adhesion molecules of nerve growth cones.Development 105, 505–19.
Nicke, J. &Schachner, M. (1985) Expression of the neural cell adhesion molecules L1 and NCAM and their common carbohydrate epitope L2/HNK-1 during the development and after transection of the mouse sciatic nerve.Differentiation 30, 141–51.
Noble, M., Albrechtsen, M., MØller, C., Lyles, J., Bock, E., Goridis, C., Watanabe, M. &Rutishauser, U. (1985) Glial cells express NCAM/D2-CAM-like polypeptidesin vitro.Nature 316, 725–28.
Perkins, R. E. &Morest, D. K. (1975) A study of cochlear innervation patterns in cats and rats with the Golgi method and Nomarski optics.Journal of Comparative Neurology 163, 129–58.
Richardson, G. P., Crossin, K. L., Chuong, C. -M. &Edelman, G. M. (1987) Expression of cell adhesion molecules during embryonic induction. III. Development of the otic placode.Developmental Biology 119, 217–30.
Rieger, F., Grumet, M. &Edelman, G. M. (1985) NCAM at the vertebrate neuromuscular junction.Journal of Cell Biology 101, 285–93.
Rutishauser, U. (1986) Differential cell adhesion through spatial and temporal variations of NCAM.Trends in Neuroscience 9, 374–8.
Rutishauser, U., Gall, W. E. &Edelman, G. M. (1978a) Adhesion among neural cells of the chick embryo. IV. Role of the cell surface molecule CAM in the formation of neurite bundles in cultures of spinal ganglia.Journal of Cell Biology 79, 382–93.
Rutishauser, U., Thiery, J. -P., Brackenbury, R. &Edelman, G. M. (1978b) Adhesion among neural cells of the chick embryo. III. Relationship of the surface molecule CAM to cell adhesion and the development of histotypic patterns.Journal of Cell Biology 79, 371–81.
Rutishauser, U., Hoffman, S. &Edelman, G. M. (1982) Binding properties of a cell adhesion molecule from neural tissue.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 79, 685–9.
Rutishauser, U. &Jessell, T. M. (1988) Cell adhesion molecules in vertebrate neural development.Physiological Reviews 68, 819–57.
Schachner, M., Faissner, A., Kruse, J., Lindner, J., Meier, D. H., Rathjen, F. G. &Wernecke, H. (1983) Cell-type specificity and developmental expression of neural cell-surface components involved in cell interactions and of structurally related molecules.Cold Spring Harbor Symposium on Quantitative Biology 48, 557–68.
Silver, J. &Rutishauser, U. (1984) Guidance of optic axonsin vivo by a preformed adhesive pathway on neuroepithelial endfeet.Developmental Biology 106, 485–99.
Sobkowicz, H. M., Bereman, G. &Rose, J. E. (1975) Organotypic development of the organ of Corti in culture.Journal of Neurocytology 4, 543–72.
Sobkowicz, H. M. &Emmerling, M. E. (1989) Development of acetylcholinesterase-positive neuronal pathways in the cochlea of the mouse.Journal of Neurocytology 18, 209–24.
Sobkowicz, H. M. &Rose, J. E. (1983) Innervation of the organ of Corti of the fetal mouse in culture. In:Development of Auditory and Vestibular systems (edited byRomand, R.) p. 27–45. Academic Press, New York.
Sobkqwicz, H. M., Rose, J. E., Levenick, C. &Scott, G. (1988) Morphology of the cochlea of the developing Bronx waltzer mouse.Association for Research in Otolaryngology (Abstract).
Sobkowicz, H. M., Rose, H. E., Scott, G. L. &Holy, H. M. (1983) The ultrastructure of the developing organ of Corti of the mouse in culture. In:Ultrastructural Atlas of the Inner Ear. (Edited byFriedmann, I. &Ballantyne, J. C.). Butterworth, pp. 61–97.
Sobkowicz, H. M., Rose, J. E., Scott, G. L. &Levenick, C. V. (1986) Formation of afferent synapses in the intact and cultured organ of Corti.Journal of Neurocytology 15, 693–714.
Sobkowicz, H. M., Rose, J. E., Scott, G. E. &Slapnick, S. M. (1982) Ribbon synapses in the developing intact and cultured organ of Corti of the mouse.Journal of Neuroscience 2, 942–57.
Spoendlin, H. (1972) Innervation densities of the cochlea.Acta Oto-laryngologica 73, 235–48.
Takeichi, M. (1988) The cadherins: cell-cell adhesion molecules controlling animal morphogenesis.Development 102, 639–55.
Tello, J. R. (1931-32) Le réticule de cellules ciliées du labyrinthe chez la souris et son indépendance des terminaisons nerveuses de la VIII paire.Trabajos del Laboratorio de investigaciones biológicas des la Universidad de Madrid 27, 151–86.
Thanos, S., Bonhoeffer, F. &Rutishauser, U. (1984) Fibre-fibre interaction and tectal cues influence the development of the chicken retinotectal projection.Proceedings of the National Academy of Science (USA) 81, 1906–10.
Thiery, J. -P., Duband, J. -L., Rutishauser, U. &Edelman, G. M. (1982) Cell adhesion molecules in early chicken embryogenesis.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 79, 6737–41.
Tosney, K. W., Watanabe, M., Landmesser, L. &Rutis Hauser, U. (1986) The distribution of NCAM in the chick hindlimb during axon outgrowth and synaptogenesis.Developmental Biology 114, 437–52.
Van Den Pol, A. N., Di Porzio, U. &Rutishauser, U. (1986) Growth cone localization of neural cell adhesion molecule on central nervous system neuronsin vitro.Journal of Cell Biology 102, 2281–94.
Warr, W. B. &Guinan, J. J. (1979) Efferent innervation of the organ of Corti: two separate systems.Brain Research 173, 152–55.
Warr, W. B., Guinan, J. J. &White, J. S. (1986) Organization of the efferent fibres: The lateral and medial olivocochlear systems. In:Neurobiology of Hearing: The Cochlea (Edited byAltschuler, R. A., Hoffman, D. W. &Bobbin, R. P.) p. 333–48. Raven Press, New York.
White, J. S. &Warr, W. B. (1983) The dual origins of the olivocochlear bundle in the albino rat.Journal of Comparative Neurology 219, 203–14.
Whitehead, M. C. &Morest, D. K. (1985) The growth of cochlear fibres and the formation of their synaptic endings in the avian inner ear: a study with the electron microscope.Neuroscience 14, 277–300.
Whitlon, D. S. &Sobkowicz, H. M. (1988) Neuron specific enolase during the development of the organ of Corti.International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience 6, 77–87.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Whitlon, D.S., Rutishauser, U.S. NCAM in the organ of Corti of the developing mouse. J Neurocytol 19, 970–977 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01186824
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01186824