Summary
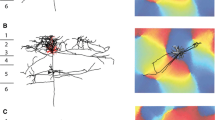
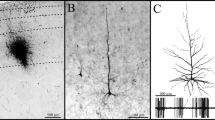
Three types of neuron with smooth (aspiny) dendrites could be distinguished in the Golgi-impregnated rat neostriatum. Examples of each type of aspiny neuron were found with local axon collaterals within the neostriatum and these were selected for gold-toning and examination in the electron microscope. One type of aspiny neuron had an elongated, usually spindle-shaped, medium-size soma with two, or rarely three, primary dendrites originating from opposite poles of the cell; one example of this type of neuron had two separate axons. The second type of aspiny neuron had a nearly round, medium-size soma with four primary dendrites that branched profusely quite close to the cell body. A third type of aspiny neuron had a very large polygonal-shaped cell body. Afferent axon terminals were found in synaptic contact with the dendrites and cell bodies of all three types of aspiny neuron.
Axon collaterals of each type of neuron displayed varicosities which, when examined in the electron microscope, were frequently found to be boutons making synaptic contact. All such synaptic contacts had symmetrical membrane specializations and the most common postsynaptic targets were dendritic shafts, sometimes spine-bearing. Dendritic spines themselves also received synapses from each type of neuron. No axosomatic synapses involving boutons of identified axons were found. One example of a synapse between an axon collateral of an aspiny neuron and one of the same neuron's dendrites (an ‘autapse’) was demonstrated by electron microscopy.
It is concluded that the synaptic terminals of at least four types of neuron, the three aspiny types described here and the medium-size densely spiny neuron, participate in local circuit interactions in the neostriatum.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bishop, G. A., Chang, H. T. &Kitai, S. T. (1982) Morphological and physiological properties of neostriatal neurons: an intracellular horseradish peroxidase study in the ratNeuroscience 7, 179–91.
Bolam, J. P., Clarke, D. J., Smith, A. D. &Somogyi, P. (1983a) A type of aspiny neuron in the rat neostriatum accumulates [3H]γ-aminobutyric acid: combination of Golgi-staining, autoradiography and electron microscopy.Journal of Comparative Neurology 213, 121–34.
Bolam, I. P., Ingham, C. A. &Smith, A.D. (1984) The section Golgi impregnation procedure. 3. Combination of Golgi-impregnation with enzyme histochemistry and electron microscopy to characterize acetylcholinesterase-containing neurons in the rat neostriatum.Neurosdence (in press).
Bolam, J. P., Ingham, C. A., Wainer, B. &Smith, A. D. (1983b) Golgi-impregnation of neurons containing acetylcholinesterase (AChE) or choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) in rat neostriatum: cholinergic pathways VI.Society for Neurosdence Abstracts 10, 964.
Bolam, J. P., Somogyi, P., Takagi, H., Fodor, I. &Smith, A. D. (1983c) Localization of substance P-like immunoreactivity in neurons and nerve terminals in the neostriatum of the rat: a correlated light and electron microscopic study.Journal of Neurocytology 12, 325–44.
Bolam, J. P., Somogyi, P., Totterdell, S. &Smith, A. D. (1981) A second type of striatonigral neuron: a comparison between retrogradely labelled and Golgi-stained neurons at the light and electron microscopic levels.Neurosdence 6, 2141–57.
Braak, H. &Braak, E. (1982) Neuronal types in the striatum of man.Cell and Tissue Research 227, 319–42.
Calvet, M.-C. &Privat, A. (1980) Mise en évidence d'autapsesin vitro par la mioroscopie électronique combinée à l'injection iontophorétique intracellulaire de peroxydase.Comptes rendues de l'académie des Sdences, Paris D 290, 61–3.
Chang, H. T. &Kitai, S. T. (1982) Large neostriatal neurons in the rat: an electron microscopic study of gold-toned Golgi-stained cells.Brain Research Bulletin 8, 631–43.
Chang, H. T., Wilson, C. J. &Kitai, S. T. (1981) Single neostriatal efferent axons in the globus pallidus: a light and electron microscopic study.Sdence 213, 915–18.
Chang, H. T., Wilson, C. J. &Kitai, S. T. (1982) A Golgi study of rat neostriatal neurons: light microscopic analysis.Journal of Comparative Neurology 208, 107–26.
Danner, H. &Pfister, C. (1981) 4 spine-lose Neurontypen im Neostriatum der Ratte.Journal für Hirnforschung 22, 465–77.
Difiglia, M. &Aronin, N. (1982) Ultrastructural features of immunoreactive somatostatin neurons in the rat caudate nucleus.Journal of Neurosdence 2, 1267–74.
Difiglia, M., Aronin, N. &Martin, J. B. (1982) Light and electron microscopic localization of immunoreactive leu-enkephalin in the monkey basal ganglia.Journal of Neurosdence 2, 303–20.
Difiglia, M., Pasik, P. &Pasik, T. (1976) A Golgi study of neuronal types in the neostriatum of monkeys.Brain Research 114, 245–56.
Difiglia, M., Pasik, T. &Pasik, P. (1980) Ultrastructure of Golgi-impregnated and gold-toned spiny and aspiny neurons in the monkey neostriatum.Journal of Neurocytology 9, 471–92.
Dimova, R., Vuillet, J. &Seite, R. (1980) Study of the rat neostriatum using a combined Golgi-electron microscope technique and serial sections.Neurosdence 5, 1581–96.
Fairen, A., Peters, A. &Saldanha, J. (1977) A new procedure for examining Golgiimpregnated neurons by light and electron microscopy.Journal of Neurocytology 6, 311–37.
Fox, C. A., Andrade, A. N., Schwyn, R. C. &Rafols, J. A. (1971/72) The aspiny neurons and the glia in the primate striatum: a Golgi and electron microscopic study.Journal für Hirnforschung 13, 341–62.
Freund, T. F., Powell, J. F. &Smith, A. D. (1984) Tyrosine hydroxylase-immunoreactive boutons in synaptic contact with identified striatonigral neurons, with particular reference to dendritic spines.Neurosdence (submitted).
Freund, T. F. &Somogyi, P. (1983) The section Golgi impregnation procedure. 1. Description of the method and its combination with histochemistry after intracellular iontophoresis or retrograde transport of horseradish peroxidase.Neurosdence 9, 463–74.
Gobel, S. (1975) Neurons with two axons in the substantia gelatinosa of the spinal trigeminal nucleus of the cat.Brain Research 88, 333–38.
Gray, E. G. (1959) Axo-somatic and axo-dendritic synapses of the cerebral cortex: an electron microscope study.Journal of Anatomy 93, 420–33.
Hassler, R., Chung, J. W., Wagner, A. &Rinne, U. (1977) Experimental demonstration of intrinsic synapses in cat's caudate nucleus.Neurosdence Letters 5, 117–21.
Henderson, Z. (1981) Ultrastructure and acetylcholinesterase content of neurons forming connections between the striatum and substantia nigra of rat.Journal of Comparative Neurology 197, 185–96.
Jayaraman, A. (1980) Anatomical evidence for cortical projections from the striatum in the cat.Brain Research 195, 29–36.
Kemp, J. M. &Powell, T. P. S. (1971) The structure of the caudate nucleus of the cat: light and electron microscopy.Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society 262, 383–401.
Kitai, S. T. (1981) Anatomy and physiology of the neostriatum. InGABA and the Basal Ganglia (edited byDi Chiara, G. andGessa, G. L.), pp. 1–21. New York: Raven Press.
Leontovich, T. A. (1977) Morphology of subcortical forebrain Golgi type II neurons. InNeuron Concept Today (edited bySzentágothai, J., Hamori, J. &Vizi, E. S.), pp. 163–75. Budapest: Akademiai Kiado.
Levey, A. I., Wainer, B. H., Mufson, E. J. &Mesulam, M.-M. (1983) Co-localization of acetylcholinesterase and choline acetyltransferase in the rat cerebrum.Neurosdence 9, 9–22.
Lighthall, J. W., Park, M. R. &Kitai, S. T. (1981) Inhibition in slices of neostriatum.Brain Research 212, 182–87.
Meyer, G. (1982) Short-axon neurons with two axon-like processes in the visual cortex of the cat. A Golgi study.Brain Research 232, 455–59.
Parent, A., Boucher, R. &O'Reilly-Fromentin, J. (1981) Acetylcholinesterase-containing neurons in cat pallidal complex: morphological characteristics and projection towards the neocortex.Brain Research 230, 356–61.
Pasik, P., Pasik, T. &Difiglia, M. (1976) Quantitative aspects of neuronal organization in the neostriatum of the Macaque monkey. InThe Basal Ganglia (edited byYahr, M. D.), pp. 57–90. New York: Raven Press.
Pasik, P., Pasik, T. &Difiglia, M. (1979) The internal organization of the neostriatum in mammals. InThe Neostriatum (edited byDivac, I. &Öberg, R. G. E.), pp. 5–36. Oxford: Pergamon Press.
Pasik, T., Pasik, P. &Difiglia, M. (1977) Interneurons in the neostriatum of monkeys. InNeuron Concept Today (edited bySzentágothai, J., Hamori, J. &Vizi, E. S.), pp. 153–62. Budapest: Akademiai Kiado.
Pickel, V. M., Beckley, S. C., Joh, T. H. &Reis, D. J. (1981) Ultrastructural immunocytochemical localization of tyrosine hydroxylase in the neostriatum.Brain Research 255, 373–85.
Preston, R. J., Bishop, G. A. &Kitai, S. T. (1980) Medium spiny neuron projection from the rat striatum: an intracellular horseradish peroxidase study.Brain Research 183, 253–63.
Rafols, J. A. &Fox, C. A. (1979) Fine structure of the primate striatum.Applied Neurophysiology 42, 13–16.
Ramón Y Cajal, S. (1911)Histologie du Systeme Nerveux de l'Homme et des Vertebres. Paris: Malonie.
Reinoso-Suarez, F., Llamas, A. &Arendano, C. (1982) Pallido-cortical projections in the cat studied by means of the horseradish peroxidase retrograde transport technique.Neurosdence Letters 29, 225–29.
Reynolds, E. S. (1963) The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron opaque stain in electron microscopy.Journal of Cell Biology 17, 208–12.
Ribak, C. E., Vaughn, J. E. &Roberts, E. (1979) The GABA neurons and their axon terminals in rat corpus striatum as demonstrated by GAD immunocytochemistry.Journal of Comparative Neurology 187, 261–84.
Satoh, K., Staines, W. A. Atmadja, S. &Fibiger, H. C. (1983) Ultrastructural observations of the cholinergic neuron in the rat striatum as identified by acetylcholinesterase pharmaco- histochemistry.Neuroscience 10, 1121–36.
Smith, A. D., Bolam, J. P. &Somogyi, P. (1981) An approach to the identification of neuro-transmiters in characterized synapses of complex neuronal networks: application to the basal ganglia of the rat. InChemical Neurotransmission 75 Years (edited byStjärne, L., Hedqvist, P., Lagercrantz, H. &Wennmalm, A.), pp. 463–79. London: Academic Press.
Somogyi, P., Bolam, J. P. &Smith, A. D. (1981a) Monosynaptic cortical input and local axon collaterals of identified striatonigral neurons. A light and electron microscopic study using the Golgi-peroxidase transport-degeneration procedure.Journal of Comparative Neurology 195, 567–84.
Somogyi, P., Freund, T. F., Halasz, N. &Kisvarday, Z. F. (1981b) Selectivity of neuronal [3H]GABA accumulation in the visual cortex as revealed by Golgi staining of the labelled neurons.Brain Research 225, 431–36.
Somogyi, P., Freund, T. F., Wu, J.-Y. &Smith, A. D. (1983b) The section-Golgi procedure. 2. Immunocytochemical demonstration of glutamate decarboxylase in Golgi-impregnated neurons and in their afferent synaptic boutons in the visual cortex of the cat.Neurosdence 9, 475–90.
Somogyi, P., Hodgson, A. J. &Smith, A. D. (1979) An approach to tracing neuron networks in the cerebral cortex and basal ganglia. Combination of Golgi staining, retrograde transport of horseradish peroxidase and anterograde degeneration of synaptic boutons in the same material.Neurosdence 4, 1805–52.
Somogyi, P., Nunzi, M. G., Gorio, A. &Smith, A. D. (1983a) A new type of specific interneuron in the monkey hippocampus forming synapses exclusively with the axon initial segments of pyramidal cells.Brain Research 259, 137–42.
Somogyi, P., Priestley, J. V., Cuello, A. C., Smith, A. D. &Takagi, H. (1982) Synaptic connections of enkephalin-immunoreactive nerve terminals in the neostriatum: a correlated light and electron microscopic study.Journal of Neurocytology 11, 779–807.
Somogyi, P. &Smith, A. D. (1979) Projection of neostriatal spiny neurons to the substantia nigra. Application of a combined Golgi-staining and horseradish peroxidase transport procedure at both light and electron microscopic levels.Brain Research 178, 3–15.
Somogyi, P. &Takagi, H. (1982) A note on the use of picric acid-paraformaldehyde-glutaral- dehyde fixative for correlated light and electron microscopic immunocytochemistry.Neurosdence 7, 1779–83.
Takagi, H., Somogyi, P., Somogyi, J. &Smith, A. D. (1983) Fine structural studies on a type of somatostatin-immunoreactive neuron and its synaptic connections in the rat neostriatum: a correlated light and electron microscopic study.Journal of Comparative Neurology 214, 1–16.
Tanaka, D. (1980) Development of spiny and aspiny neurons in the caudate nucleus of dog during the first postnatal month.Journal of Comparative Neurology 192, 247–63.
Van Der Loos, H. &Glaser, E. M. (1972) Autapses in neocortex cerebri: synapses between a pyramidal cell's axon and its own dendrites.Brain Research 48, 355–60.
Vogt, C. &Vogt, O. (1920) Zur Lehre der Erkrankungen des striären Systems.Journal für Psychiatrie und Neurologie 25, 627–846.
Wainer, B. H., Bolam, J. P., Clarke, D. J., Freund, T., Henderson, Z., Smith, A. D. &Totterdell, S. (1983) Ultrastructural evidence of cholinergic synapses in different regions of rat brain: cholinergic pathways V.Society for Neurosdence Abstracts 10, 963.
Wilson, C. J. &Groves, P. M. (1980) Fine structure and synaptic connections of the common spiny neuron of the rat neostriatum: a study employing intracellular injection of horseradish peroxidase.Journal of Comparative Neurology 194, 599–615.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takagi, H., Somogyi, P. & Smith, A.D. Aspiny neurons and their local axons in the neostriatum of the rat: a correlated light and electron microscopic study of Golgi-impregnated material. J Neurocytol 13, 239–265 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01148118
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01148118