Summary
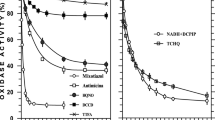
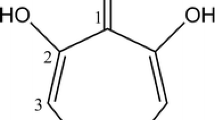
Enzymatic release of iron from ferripyoverdine through a reductive mechanism was demonstrated in cell-free extracts ofPseudomonas fluorescens. Ferripyoverdine reductase activity was localized primarily in the cytoplasm and/or periplasm and appeared not to be affected by the iron status of the cells. The reaction required a strict anaerobic environment and was fully inhibited by oxygen, whereas NADH was the most effective reductant. Ferripyoverdines from other bacterial sources (P. aeruginosa ATCC 15692,P. fluorescens ATCC 13525,P. fluorescens ATCC 17400) were able to serve as iron sources as well as ferric citrate. However, the activity with ferric citrate was not strongly affected by oxygen and did not display the characteristic lag phase observed with ferripyoverdines, suggesting the occurrence of a specific ferric citrate iron reductase. FMN should play a critical role in the reductive mechanism since it was absolutely required for the activity to occur with an intensively dialyzed cell-free extract, whereas it greatly stimulated (50-fold) the NADH-mediated activity of a crude extract.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arteneaux JEL, Byers BR (1980) Ferrisiderophore reductase activity inBacillus megaterium. J Bacteriol 141:715–721
Brown KA, Ratledge C (1975) Iron transport inMycobacterium smegmatis: ferrimycobactin reductase [NAD(P)H:ferrimycobactin oxidoreductase], the enzyme releasing iron from its carrier. FEBS Lett 53:262–266
Carter P (1971) Spectrophotometric determination of serum iron at the submicrogram level with a new reagent (ferrozine). Anal Biochem 40:450–458
Cox CD (1980) Iron reductases fromPseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 141:199–204
Cox CD, Graham R (1979) Isolation of an iron-binding compound fromPseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 137:357–364
Dailey HA, Lascelles J (1977) Reduction of iron and synthesis of protoheme bySpirillum itersonii and other organisms. J Bacteriol 129:815–820
Demange P, Wendenbaum S, Bateman A, Dell A, Meyer JM, Abdallah MA (1986) Bacterial siderophores: structure of pyoverdins and related compounds. In: Swinburne TR (ed) Iron, siderophores and plant diseases. NATO ASI Series A Life sciences, vol 117. Plenum, New York, pp 131–147
Emery T (1987) Reductive mechanisms of iron assimilation. In: Winkelmann G, van der Helm D, Neilands JB (eds) Iron transport in microbes, plants and animals VCH Verlagsgesellschaft, Weinheim, pp 235–250
Ernst JF, Winkelmann G (1977) Enzymatic release of iron from sideramines in fungi. NADH:sideramine oxidoreductase inNeurospora crassa. Biochim Biophys Acta 500:27–41
Gaines CG, Lodge JS, Arteneaux JEL, Byers BR (1981) Ferrisiderophore reductase activity associated with an aromatic biosynthetic enzyme complex inBacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 148:527–533
Harris WR, Carrano CJ, Cooper SR, Sofen SR, Avdeef AE, McArdle JV, Raymond KN (1979) Coordination chemistry of microbial iron transport compounds. 19. Stability constants and electrochemical behavior of ferric enterobactin and model complexes. J Am Chem Soc 101:6097–6104
Hohnadel D, Meyer JM (1988) Specificity of pyoverdine-mediated iron uptake among fluorescentPseudomonas strains. J Bacteriol 170:4865–4873
Lodge JS, Gaines CG, Arceneaux JEL, Byers BR (1982) Ferrisiderophore reductase activity inAgrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol 149:771–774
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
McCready KA, Ratledge C (1979) Ferrimycobactin reductase activity fromMycobacterium smegmatis. J Gen Microbiol 113:67–72
Meyer JM, Abdallah MA (1978) The fluorescent pigment ofPseudomonas fluoreseens: biosynthesis, purification and physicochemical properties. J Gen Microbiol 107:319–328
Meyer JM, Hornsperger JM (1978) Role of pyoverdinepf, the iron-binding fluorescent pigment ofPseudomonas fluorescens, in iron transport. J Gen Microbiol 107:329–331
Moody MD, Dailey HA (1983) Aerobic ferrisiderophore reductase assay and activity stain for native polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 134:235–239
Moody MD, Dailey HA (1985) Ferric iron reductase ofRhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. 163:1120–1125
Neilands JB (1957) Some aspects of microbial iron metabolism. Bacteriol Rev 21:101–105
Neilands JB (1982) Microbial envelope proteins related to iron. Annu Rev Microbiol 36:285–309
Sokol PA (1984) Production of the ferripyochelin outer membrane receptor byPseudomonas species. FEMS Microbiol Lett 23:313–317
Straka JG, Emery T (1979) The role of ferrichrome reductase in iron metabolism ofUstilago sphaerogena. Biochim Biophys Acta 569:277–286
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hallé, F., Meyer, JM. Ferripyoverdine-reductase activity inPseudomonas fluorescens . Biol Metals 2, 18–24 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01116196
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01116196