Summary
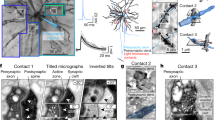
The ultrastructure of synapses from the nervous systems of seven species of ctenophores has been studied. All synaptic contacts so far observed show a peculiar organization characteristic of this phylum: the pre-synaptic neurite contains in sequence from the plasma membrane: a row of vesicles lining the synaptic membrane, a sac of endoplasmic reticulum which is connected with the rough reticulum of the neuron, and one or several mitochondria. The arrangement of these closely associated organelles is constant, forming a complex referred to as thepre-synaptic triad.
The pre-synaptic triad is found both in interneural synapses—which may be polarized, symmetrical or reciprocal — and in various neuro-receptor and neuro-effector junctions.
The possible functional implications of these features are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akert, K., Moor, H., Pfenninger, K. andSandri, C. (1969) Contributions of new impregnation methods and freeze-etching to the problems of synaptic fine structure.Progress in Brain Research 31, 223–40.
Bisby, M. A. andFillenz, M. (1970) Isolation of two types of vesicles containing endogenous noradrenaline in sympathetic nerve terminals.Journal of Physiology (London) 210, 49–50P.
Bloom, F. E. (1970) Correlating structure and function of synaptic ultrastructure. InThe Neurosciences: 2nd Study Program (edited bySchmidt, F. O.) pp. 729–47. New York, Rockfeller University Press.
Buisson, B. (1970) Les supports morphologiques de l'intéegration dans la colonie deVeretillum cynomorium Pall. (Cnidaria, Pennatularia).Zeitschrift für Morphologie der Tiere 68, 1–36.
Bunt, A. H. (1969) Formation of coated and ‘synaptic’ vesicles within neurosecretory axon terminals of the crustacean sinus gland.Journal of Ultrastructure Research 28, 411–21.
Couteaux, R. (1961) Principaux critéres morphologiques et cytochimiques utilisables aujourd'hui pour définir les divers types de synapses.Actualites neurophysiologiques 3, 145–73.
Ceccarelli, B., Hurlbut, W. P. andMauro, A. (1972) Depletion of vesicles from frog neuromuscular junctions by prolonged tetanic stimulation.Journal of Cell Biology 54, 30–8.
Courteaux, R. andPecot-Dechavassine, M. (1970a) Vésicules synaptiques et poches au niveau des ‘zones actives’ de la jonction neuro-musculaire.Comptes Rendus de l'Académie des Sciences, Paris 271, 2346–9.
Courteaux, R. andPecot-Dechavassine, M. (1970b) L'ouverture des vésicules synaptiques au niveau des ‘zones actives’. InSeventh International Congress for Electron Microscopy,3 (edited byFavard,P.), pp. 709–10. Paris, Société Française de Microscopic électronique.
Dahlström, A. (1971) Axoplasmic transport (with particular respect to adrenergic neurons).Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, Series B 261, 325–58.
De Robertis, E. andBennett, H. S. (1955) Some features of the submicroscopic morphology of synapses in frog and earthworm.Journal of Biophysical and Biochemical Cytology 1, 47–58.
Fillenz, M. (1970) The innervation of the cat spleen.Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, Series B 174, 459–68.
Fillenz, M. (1971) Fine structure of noradrenaline storage vesicles in nerve terminals of the ratvas deferens.Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, Series B 261, 319–23.
Gray, E. G. (1961) The granule cells, mossy synapses and Purkinje spine synapses of the cerebellum: light and electron microscope observations.Journal of Anatomy (London) 95, 345–56.
Gray, E. G. (1971) The fine structural characterization of different types of synapses.Progresses in Brain Research 34, 149–60.
Hernandez-Nicaise, M. L. (1968a) Distribution et ultrastructure des synapses symétriques dans le systéme nerveux des Cténaires.Comptes Rendus de l'Académie des Sciences, Paris 267, 1731–4.
Hernandez-Nicaise, M. L. (1968b) Specialized connections between nerve cells and mesenchymal cells in Ctenophores.Nature (London) 217, 1075–6.
Hernandez-Nicaise, M. L. (1973) Le systéme nerveux des Cténaires. L Structure et ultrastructure des réseaux épithéliaux.Zeitschrift für Zellforschung und mikroskopische Anatomie 137, 223–50.
Holtzman, E., Freeman, A. R. andKashner, L. A. (1971) Stimulation-dependent alterations in peroxidase uptake at lobster neuromuscular junctions.Science 173, 733–6.
Horridge, G. A. (1965) Non-motile sensory cilia and neuromuscular junctions in a Ctenophore independent effector organ.Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, Series B 162, 333–50.
Horridge, G. A. andMackay, B. (1964) Neurociliary synapses inPleurobrachia (Ctenophora).Quarterly Journal of Microscopical Science 105, 163–74.
Hubbard, J. I. (1971) Mechanism of transmitter release from nerve terminals.Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 183, 131–46.
Jha, R. K. andMackie, G. O. (1967) The recognition, distribution and ultrastructure of hydrozoan nerve elements.Journal of Morphology 123, 43–61.
Karnovsky, M. J. (1967) The ultrastructural basis of capillarity permeability studied with peroxydase as a tracer.Journal of Cell Biology 35, 213–36.
Koelle, G. B. (1970) Neurohumoral transmission and the autonomic nervous system. InThe pharmacological basis of therapeutics (edited byGoodman, L. S. andGilman, A.) pp. 402–40. New York, MacMillan.
Lehninger, A. L. (1970) Mitochondria and their neurofunction. InThe Neurosciences 2nd Study Program (edited bySchmidt, F. O.) pp. 827–39. New York, Rockfeller University Press.
Machado, A. B. M. (1971) Electron microscopy of developing sympathetic fibers in the rat pineal body. The formation of granular vesicles.Progress in Brain Research 34, 171–85.
Nagasawa, J., Douglas, W. W. andSchulz, R. A. (1970) Ultrastructural evidence of secretion by exocytosis and of ‘synaptic vesicle’ formation in posterior pituitary glands.Nature (London) 227, 407–9.
Palay, S. L. (1958) The morphology of synapses in the central nervous system.Experimental Cell Research Supplement 5, 275–93.
Pecot-Dechavassine, M. andCouteaux, R. (1972) Potentiels miniatures d'amplitude anormale obtenus dans des conditions expérimentales et changements concomitants des structures présynaptiques.Comptes Rendus de l' Académie des Sciences Paris 275, 983–6.
Pfenninger, K. H. (1971a) The cytochemistry of synaptic densities. I. An analysis of the bismuth iodide impregnation method.Journal of Ultrastructure Research 35, 451–75.
Pfenninger, K. H. (1971b) The cytochemistry of synaptic densities. II. Proteinaceous components and mechanisms of synaptic connectivity.Journal of Ultrastructure Research 35, 451–75.
Smith, A. D. (1971a) Secretion of proteins (chromogranin A and dopamine-β-hydroxylase) from a sympathetic neuron.Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, Series B 261, 363–70.
Smith, A. D. (1971b) Summing up: some implications of the neuron as a secreting cell.Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, Series B 261, 423–37.
Szöllösi, D. andHunter, R. H. F. (1973) A special attachment complex between the rough endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria in porcine oocytes.Journal de Microscopie 16, 105–10.
Tauc, L. (1967) Transmission in Invertebrate and Vertebrate ganglia.Physiological Reviews 47, 521–93.
Taxi, J. (1969) Morphological and cytochemical studies on the synapses in the autonomic nervous system.Progress in Brain Research 31, 5–20.
Tranzer, J. P. andThoenen, H. (1968) Various types of amine-storing vesicles in peripheral adrenergic nerve terminals.Experientia 24, 484–6.
Westfall, J. A. (1970) Ultrastructure of synapses in a primitive Coelenterate.Journal of Ultrastructure Research 32, 237–46.
Westfall, J. A. (1973) Ultrastructural evidence for a granule-containing sensory-motor-interneuron inHydra littoralis.Journal of Ultrastructure Research 42, 268–82.
Westfall, J. A., Yakamata, S. andEnos, P. D. (1971) Ultrastructural evidence of polarized synapses in the nerve net ofHydra.Journal of Cell Biology 51, 318–23.
Whittaker, V. P. andGray, E. G. (1962) The synapse: Biology and morphology.British medical Bulletin 18, 223–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hernandez-Nicaise, ML. The nervous system of ctenophores III. Ultrastructure of synapses. J Neurocytol 2, 249–263 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01104029
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01104029