Abstract
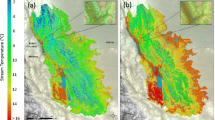
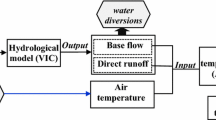
The effect of projected global climate change due to a doubling of atmospheric CO2 on water temperatures in five streams in Minnesota was estimated using a deterministic heat transport model. The model calculates heat exchange between the atmosphere and the water and is driven by climate parameters and stream hydrologic parameters. The model is most sensitive to air temperature and solar radiation. The model was calibrated against detailed measurements to account for seasonally variable shading and wind sheltering. Using climate projections from the GISS, GFDL and OSU GCMs as input; stream temperature simulations predict a warming of freely flowing river reaches by 2.4 °C to 4.7 °C when atmospheric CO2 doubles. In small shaded streams water temperatures are predicted to rise by an additional 6 °C in summer if trees along stream banks should be lost due to climate change or other human activities (e.g. logging). These projected water temperature changes have significant consequences for survival and growth of fishes. Simulation with the complete heat budget equations were also used to examine simplified water temperature/air temperature correlations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-Zeid, M. A. and Biswas, A. K. (eds.): 1992,Climatic Fluctuations and Water Management, Butterworth-Heinemann Ltd., Oxford.
American Water Resources Association: 1992,Proc. Conf. and Symp. on ‘Managing Water Resources During Global Climate Change’, AWRA, Bethesda, MD.
Baltz, D. M., Vondracek, B., Brown, L. R., and Moyle, P. B.: 1987, ‘Influence of Temperature on Microhabitat Choice by Fishes in a California Stream’,Trans. Amer. Fish. Soc. 116.
Bolin, B. and Doos, B. R.: 1986,The Greenhouse Effect, Climate Change and Ecosystem, John Wiley and Sons (Publishers), New York, 541 pp.
Bowles, S. B., Fread, D. L., and Grenney, W. J.: 1977, ‘Coupled Dynamic Streamflow-Temperature Models’,J. Amer. Soc. Civ. Eng. Hydraul. Div. 103.
Brady, D. K., Graves, W. L., Jr., Gayer, J. C.: 1969,Surface Heat Exchange of Power Plant Cooling Lakes, Cooling Water Studies for Edison Electric Institute, The Johns Hopkins University, Report No. 5.
Brown, G. W.: 1969, ‘Predicting Temperatures of Small Streams’,Water Resourc. Res. 5 (1).
Brylinski, M.: 1980, ‘Estimating the Productivity of Lakes and Reservoirs’,Intern. Biol. Progr. 22.
Burt, W. V.: 1958,Heat Budget Terms for Middle Snake River Reservoir, in Water Temperature Studies on the Snake River, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Serv. Tech. Rept. 6.
Coutant, C. C.: 1990, ‘Temperature-Oxygen Habitat for Freshwater and Coastal Striped Bass in a Changing Climate’,Trans. Amer. Fish. Soc. 119, 240–253.
Delay, W. H. and Seaders, J.: 1966, ‘Predicting Temperature in Rivers and Reservoirs’,J. Saint. Eng. Dev., Proc. Amer. Soc. Civ. Eng. 92.
Donahue, M.: 1992,Climate and Global Change: ‘The Response and Policy Issues Related to Climate Change in the Great Lakes Basin’, Great Lakes Comm., Ann Arbor, MI.
Duttweiler, D. W.: 1963,A Mathematical Model of Stream Temperature, Ph.D. Dissertation, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland.
Edinger, J. E., Duttweiler, D. W., and Geyer, J. G.: 1968, ‘The Response of Water Temperatures to Meteorological Conditions’,Water Resourc. Res. 4 (5).
Edinger, J. E., Brady, D. K., and Geyer, J. C.: 1974,Heat Exchange and Transport in the Environment, Report No. 14, prepared for Electric Power Research Institute, Proj. RP-49.
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): 1988,Ecoregions of the Upper Midwest States, USEPA/ERL Corvallis, OR.
Frank, K. T., Perry, R. I., and Drinkwater, K. T.: 1990, ‘Predicted Response of Northwest Atlantic Invertebrate and Fish Stocks to CO2-Induced Climate Change’,Trans. Amer. Fish. Soc. 119, 353–365.
Gleick, P. H.: 1987a, ‘The Development and Testing of a Water Balance Model for Climate Impact Assessment: Modeling the Sacramento Basin’,Water Resourc. Res. 23, 1049–1061.
Gleick, P. H.: 1987b, ‘Global Climate Changes and Regional Hydrology: Impacts and Responses’, inThe Influence of Climate Change and Climatic Variability on the Hydrologic Regime and Water Resources, IHAS, publication No. 168, 389–402.
Graham, J. R. and Orth, D. J.: 1986, ‘Effects of Temperature and Streamflow on Time and Duration of Spawning by Smallmouth Bass’,Trans. Amer. Fish. Soc. 115.
Hansen, J., Russell, G., Rind, D., Stone, P., Lacis, A., Lebedeff, S., Ruedy, R., and Travis, L.: 1983, ‘Efficient Three-Dimensional Global Models for Climate Studies: Models I and II’,Mon. Wea. Rev. III (4, 609–662.
Hanson, J. S., Malanson, G. P., and Armstrong, M. P.: 1990, ‘Landscape Fragmentation and Dispersal in a Model of Riparian Forest Dynamics’,Ecol. Model. 49, 277–296.
Harrington, J. B.: 1987, ‘Climate Change: A Review of Causes’,Canad. J. For. Res. 17, 1313–1339.
Hokanson, K. E. F., Biesinger, K. E., and Goodno, B.: 1991,Temperature Requirements of Stream Fishes with Applications to Global Climate Warming Impact Assessment, USEPA-ERLD, Duluth, MN.
Houghton, R. A. and Woodwell, G. M.: 1989, ‘Global Climate Change’, Scientific American 260, No. 4, 30-44.
Idso, S. B. and Brazel, A. I.: 1984, ‘Rising Atmospherivc Carbon Dioxide Concentrations May Increase Streamflow’,Nature 312 (5989, 51–53.
Jobson, H. E.: 1973, ‘The Dissipation of Excess Heat From Water Systems’,J. Power Div., Proc. Amer. Soc. Civ. Eng. 99.
Jobson, H. E.: 1977, ‘Bed Conduction Computation for Thermal Models’,J. Hydraul. Div., Proc. Amer. Soc. Civ. Eng. 103, No. HY10.
Leopold, L. B. and Maddock, T.: 1953, ‘The Hydraulic Geometry of Stream Channels and Some Physiographic Implications’, U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 252.
Liu, Z. J. and Malanson, G. P.: 1992, ‘Long-Term Cyclic Dynamics of Simulated Riparian Forest Stands’,Forest Ecol. Managem. 48, 217–231.
Magnuson, J. J., Meisner, J. D., and Hill, D. K.: 1990, ‘Potential Changes in Thermal Habitat of Great Lakes Fish After Global Climate Warming’,Trans. Amer. Fish. Soc. 119, 254–264.
Meisner, J. D.: 1990, ‘Potential Loss of Thermal Habitat for Brook Trout, Due to Climate Warming, in Two Southern Ontario Streams’,Trans. Amer. Fish. Soc. 119, 282–291.
Minnesota Pollution Control Agency (MPCA): 1988,Minnesota Water Quality (Water Years 1986–1987).
Munson, B. H., McCormick, J. H., and Collins, H. L.: 1980, ‘Influence of Thermal Challenge on Conditioned Feeding Forays of Juvenile Rainbow Trout’,Trans. Amer. Fish. Soc. 116.
National Academy of Sciences (NAS): 1979,Carbon Dioxide and Climate: A Scientific Assessment, National Academy Press, Washington, D.C.
National Academy of Sciences (NAS): 1988,Global Environmental Change, Recommendations for President-Elect Bush, National Academy Press, Washington, D.C.
National Research Council: 1977,Climate, Climatic Change, and Water Supply, National Academy Press, Washington, D.C.
National Research Council: 1982,Carbon Dioxide/Climate Review Panel, Carbon Dioxide and Climate: A Second Assessment, National Academy Press, Washington, D.C., 72 pp.
National Research Council: 1983,Changing Climate: Report of the Carbon Dioxide Assessment Committee, National Academy Press, Washington, D.C., 496 pp.
Pluhowski, E. J.: 1970,Urbanization and Its Effect on the Temperature of the Streams on Long Island, New York, USGS Prof. Paper 627-D, Washington, D.C., 35 pp.
Preud'homme, E. B. and H. G. Stefan, Relationship between Water Temperatures and Air Temperatures for Central U.S. Streams, University of Minnesota, St. Anthony Falls Hydraulic Laboratory, Report No. 333, Sept. 1992, 132 pp.
Raphael, J. M.: 1962, ‘Prediction of Temperature in Rivers and Reservoirs’,J. Power Divis., Proc. Amer. Soc. Civ. Eng. 88, No. PO2.
Regier, H. A., Magnuson, J. J., and Coutant, C. C.: 1990a, ‘Introduction to Proceedings: Symposium on Effects of Climate Change on Fish’,Trans. Amer. Fish. Soc. 119, 173–175.
Regier, H. A., Holmes, J. A., and Pauly, D.: 1990b, ‘Influence of Temperature Change on Aquatic Ecosystem: An Introduction of Empirical Data’,Trans. Amer. Fish. Soc. 119, 374–389.
Revelle, R. R. and Waggoner, P. E.: 1983, ‘Effects of a Carbon Dioxide-Induced Climatic Chnge on Water Supplies in the Western United States’, inChanging Climate, National Academy of Sciences, National Academy Press, Washington, D.C., 419–432.
Rex, K. D. and Malanson, G. P.: 1990, ‘The Fractal Shape of Riparian Forest Patches’,Landsc. Ecol. 4 (4, 249–258.
Richards, K.: 1982,Rivers: Form and Process in Alluvial Channels, Methuen (Publishers), New York, NY.
Rishel, G. B., Lynch, J. A., and Corbett, E. S.: 1982, ‘Seasonal Stream Temperature Changes Following Forest Harvesting’,J. Environm. Qual. 11 (1).
Salvatore, S. R., Mundahl, N. D., and Wissing, T. E.: 1987, ‘Effect of Water Temperature on Food Evacuation Rate and Feeding Activity of Age-0 Gizzard Shad’,Trans. Amer. Fish. Soc. 116.
Schneider, S. H.: 1989, ‘The Greenhouse Effect: Science and Policy’,Science 243 (10, 771–781.
Sibley, T. H. and Stickland, R. M.: 1985, ‘Fisheries: Some Relationships to Climate Change and Marine Environmental Factors’, in White, M. R. (ed.),Characterization of Information Requirements for Studies of CO 2 Effects: Water Resources, Agriculture, Fisheries, Forests and Human Health, U.S. Department of Energy, DOE/ER-0236, Washington, D.C., pp. 95–143.
Sinokrot, B. A. and Stefan, H. G.: 1992,Deterministic Modeling of Stream Water Temperatures: Development and Applications to Climate Change Effects on Fish Habitat, University of Minnesota, St. Anthony Falls Hydraulic Laboratory Report No. 337, Minneapolis, MN.
Song, C. S., Pabst, A. F., and Bowers, C. E.: 1973, ‘Stochastic Analaysis of Air and Water Temperatures’, ASCEJ. Environm. Eng. Div. 99, 785–800.
Stefan, H. G., Gulliver, J., Hahn, M. G., and Fu, A. Y.: 1980,Water Temperature Dynamics in Experimental Field Channels: Analysis and Modeling, University of Minnesota, St. Anthony Falls Hydraulic Laboratory Report No. 193, Minneapolis, MN.
Stefan, H. G., Hondzo, M., Sinokrot, B. A., and Fang, X.: 1992,A Methodology to Estimate Global Climate Change Impacts on Lake and Stream Environmental Conditions and Fishery Resources with Application to Minnesota, University of Minnesota, St. Anthony Falls Hydraulic Laboratory Report No. 323, Minneapolis, MN.
Taylor, E. B.: 1988, ‘Water Temperature and Velocity as Determinants of Microhabitats of Juvenile Chinook and Coho Salmon in a Laboratory Stream Channel’,Trans. Amer. Fish. Soc. 117.
Tonn, W. M.: 1990, ‘Climate Change and Fish Communities: A Conceptual Framework’,Trans. Amer. Fish. Soc. 119, 337–352.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: 1988,The Potential Effects of Global Climate Change on the United States: Draft: Report to Congress.
U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service: 1984, Instream Water Temperature Model. Parts 1–4, Fort Collins, Colorado, Sept.
Wangila, B. C. C. and Dick, T. A.: 1988, ‘Influence of Genotype and Temperature on the Relationship between Specific Growth Rate and Size of Rainbow Trout’,Trans. Amer. Fish. Soc. 117.
Waters, T. F.: 1977,The Streams and Rivers of Minnesota, University of Minnesota Press (Publishers), Minneapolis, MN.
World Meteorological Organization: 1989,Conference on Climate and Water, Vol. 1 and 2, Government Printing Center, Helsinki.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stefan, H.G., Sinokrot, B.A. Projected global climate change impact on water temperatures in five north central U.S. streams. Climatic Change 24, 353–381 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01091855
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01091855