Abstract
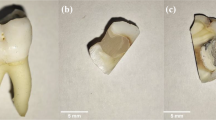
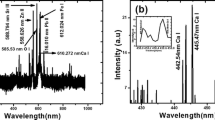
Experiments on the ablation of dental substance performed with picosecond laser pulses are reported for the first time. A mode locked Nd:YLF oscillator laser was used to generate 25 ps pulses at a wavelength of 1.053µm. These were seeded and amplified to pulse energies up to 1 mJ in a regenerative amplifier laser at repetition rates up to 1 kHz. Very precise cavities were ablated in the enamel of extracted human teeth by mounting the probes onto a computer controlled 3D translation stage. Scanning electron microscopy and dye penetration tests were performed there-after. In contrast to longer pulse durations, picosecond pulses ablate with no signs of thermal damage, if the laser pulses are spatially distributed over the target. Definitions of the physical mechanisms “plasma-induced ablation” and “photodisruption” are given. Furthermore, the generated plasma spark has been spectroscopically analyzed. Excitations of calcium and sodium have been observed. From the spectra, the plasma temperature and free electron density could be estimated. By converting part of the laser energy into the second harmonic using a LiNbO3 crystal, a reference amplitude was achieved for the spectra. With this reference signal, a clear distinction could be made between spectra obtained from healthy and caries infected teeth, thus enabling a better control of caries removal in the near future.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Bloembergen: IEEE J. QE-10, 375 (1974)
M.P. Felix, A.T. Ellis: Appl. Phys. Lett.19, 484 (1971)
F. Docchio: Appl. Opt.27, 3661 (1988)
F. Docchio: Appl. Opt.27, 3669 (1988)
C.E. Bell, J.A. Landt: Appl. Phys. Lett.10, 46 (1967)
B. Zysset, J.G. Fujimoto, T.F. Deutsch: Appl. Phys. B48, 139 (1989)
A. Vogel, P. Schweiger, A. Frieser, M.N. Asiyo, R. Birngruber: IEEE J. QE-26, 2240 (1990)
A.S. Epifanov: IEEE J. QE-17, 2018 (1981)
C.A. Sacchi: J. Opt. Soc. Am. B8, 337 (1991)
M.H. Niemz, T.P. Hoppeler, T. Juhasz, J.F. Bille: Lasers Light Ophthalmol.5, 149 (1993)
J.L. Boulnois: Lasers Med. Sci.1, 47 (1986)
R.H. Stern, R.F. Sognnaes: J. Dent. Res.43, 873 (1964)
L. Goldman, P. Hornby, R. Mayer, B. Goldman: Nature203, 417 (1964)
R.H. Stern, J. Vahl, R.F. Sognnaes: J. Dent. Res.51, 455 (1972)
J.W. Frame: Br. Dent. J.158, 125 (1985)
U. Keller, R. Hibst: Dtsch. Zahnärztl. Z.44, 600 (1989)
R. Hibst, U. Keller: Lasers Surg. Med.9, 338 (1989)
U. Keller, R. Hibst: Lasers Surg. Med.9, 345 (1989)
T. Liesenhoff, T. Bende, H. Lenz, T. Seller: Dtsch. Zahnärztl. Z.45, 14 (1990)
M. Frentzen, HJ. Koort: Dtsch. Zahnärztl. Z.46, 443 (1991)
P. Rechmann, T. Hennig, R. Kaufmann: Zahnärztl. Welt101, 150 (1992)
D. Stern, C.A. Puliafito, E.T. Dobi, W.T. Reidy: Arch. Ophmalmol.107, 587 (1989)
M.H. Niemz, E.G. Klancnik, J.F. Bille: Lasers Surg. Med.11, 426 (1991)
M. Frentzen, H.J. Koort, C. Tack: Dtsch. Zahnärztl. Z.45, 199 (1990)
P. Bado, M. Bouvier, J.S. Coe: Opt. Lett.12, 319 (1987)
J.E. Murray: IEEE J. QE-19, 488 (1983)
T.M. Pollak, W.F. Wing, R.J. Gasso, E.P. Chicklis, J.P. Jenssen: IEEE J. QE-18, 159 (1982)
R.C. Weast (ed.):Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (CRC, Boca Raton 1981) Chap. E
W. Lochte-Holtgreven:Plasma Diagnostics (North-Holland, Amsterdam 1968) p. 181
H.R. Griem:Plasma Spectroscopy (McGraw-Hill, New York 1964) p. 496
M.H. Niemz, L. Eisenmann, T. Pioch: Schweiz. Monatsschr. Zahnmed.103, 1252 (1993)