Abstract
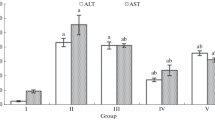
Effects of glycyrrhizin (GR) on an injury of the liver caused by ischemia-reperfusion in rats were determined. In the liver ischemia-reperfusion model, levels of serum AST, ALT and LDH, lipid peroxides in the liver tissue, and blood superoxide dismutase activity were significantly increased. On the contrary, total glutathione content in the liver tissue was decreased. When rats were given GR 100 mg/kg for 10 days, GR suppressed the elevation of the lipid peroxide level, serum AST, ALT, LDH level, and the decrease in glutathione content during the period of reperfusion. The suppressive effect of GR was similar with that of α-tocopherol (VE). GR showed neither 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) nor 5,5-dimethyl-1-pyrroline-N-oxide (DMPO)-OOH radical-trapping ability, but exhibited DMPO-OH radical-trapping action, while, VE exhibited both DPPH and DMPO-OOH radical-trapping ability. These results indicate that the hydroxyl radical trapping action of GR is the likely mechanism suppressing liver injury caused by ischemia-reperfusion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adkison D, Höilwarth ME, Benoit JN, Parks DA, McCord JM, Granger DN (1986) Role of free radicals in ischemia-reperfusion injury to the liver. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl 548:101–107
Arroyo CM, Kramer JH, Dickens BF, Weglicki WB (1987) Identification of free radicals in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion by spin trapping with nitrone DMPO. FEBS Lett 221:101–104
Bolli R, Zhu WX, Hartley CJ, Michael LH, Repine JE, Hess ML Kukreja RC, Roberts R (1987) Attenuation of dysfunction in the postischemic ‘stunned’ myocardium by dimethylthiourea. Circulation 76:458–468
Bulkley GB (1987) Free radical-mediated reperfusion injury: A selective review. Br J Cancer Suppl 8:66–73
Das DK, George A, Liu X, Rao PS (1989) Detection of hydroxyl radical in the mitochondria of ischemic-reperfused myocardium by trapping with salicylate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 165:1004–1009
Ganote CE, Sims M, Safavi S (1982) Effects of dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) on the oxygen paradox in perfused rat hearts. Am J Pathol 109:270–276
Griffith OW (1980) Determination of glutathione and glutathione disulfide using glutathione reductase and 2-vinylpyridine. Anal Biochem 106:207–212
Hiramatsu M, Edamatsu R, Kohno M, Mori A (1986) The possible involvement of free radicals in seizure mechanism. Jap J Psychiat Neurol 40:349–352
Kiso Y, Tohkin M, Hikino H, Hattori M, Sakamoto T, Namba T (1984) Mechanism of antihepatotoxic activity of glycyrrhizin, I: Effect on free radical generation and lipid peroxidation. Planta Med 50:298–302
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NF, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Marubayashi S, Dohi K, Ochi K, Kawasaki T (1986) Role of free radicals in ischemic rat liver cell injury: Prevention of damage by α-tocopherol administration. Surgery 99:184–191
McCord JM (1985) Oxygen-derived free radicals in postischemic tissue injury. N Engl J Med 312:159–163
Miyagawa H, Yoshikawa T, Tanigawa T, Yoshida N, Sugino S, Kondo M, Nishikawa H, Kohno M (1988) Measurement of serum Superoxide dismutase activity by electron spin resonance. J Clin Biochem Nutr 5:1–7
Nagai T, Egashira T, Yamanaka Y (1990) Effect of bifemelane hydrochloride on an injury of the liver caused by ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Jap J Pharmacol 52:383–385
Nordström G, Seeman T, Hasselgren PO (1985) Beneficial effect of allopurinol in liver ischemia. Surgery 97:679–684
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Romani F, Vertemati M, Frangi M, Aseni P, Monti R, Codeghini A, Belli L (1988) Effect of Superoxide dismutase on liver ischemia-reperfusion injury in the rat: A biochemical monitoring. Eur Surg Res 20:335–340
Shibayama Y (1989) Prevention of hepatotoxic responses to chemicals by glycyrrhizin in rats. Exp Mol Pathol 51:48–55
Slater TF (1984) Free-radical mechanisms in tissue injury. Biochem J 222:1–15
Toledo-Pereyra LH (1988) The role of allopurinol and oxygen free radical scavengers in liver preservation. Basic Life Sci 49: 1047–1052
Ueno I, Kohno M, Mitsuta K, Mizuta Y, Kanegasaki S (1989) Reevaluation of the spin-trapped adduct formed from 5,5-dimethyl-1-pyrroline-1-oxide during the respiratory burst in neutrophils. J Biochem 105:905–910
Yoshikawa T, Oyamada H, Ichikawa H, Naito Y, Ueda S, Tainaka K, Takemura T, Tanigawa T, Sugino S, Kondo M (1990) Role of active oxygen species and lipid peroxidation in liver injury induced by ischemia-reperfusion. Nippon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi 87:199–205 (Eng. Abstr)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagai, T., Egashira, T., Yamanaka, Y. et al. The protective effect of glycyrrhizin against injury of the liver caused by ischemia-reperfusion. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 20, 432–436 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01064416
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01064416