Summary
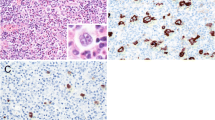
Tissue from primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL) which developed in five patients with acquired immuno deficiency syndrome (AIDS), nine patients without immunodeficiency, and two Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-positive control cell lines (B95-8 and Raji) were examined for the presence of EBER-1 RNA. The tissues were hybridized with digoxigenin-labeled sense or anti-sense EBER-1 riboprobes. In all five AIDS-related PCNSLs, strong hybridization signals were found with the EBER-1 anti-sense probe. Signals could be eliminated by preincubation of the tissues with RNase-A. Hybridization with the EBER-1 sense probe showed no signal. All PCNSLs from immunocompetent patients (five paraffin-embedded, four frozen) showed no hybridization signals with EBER-1 sense or antisense probe but good hybridization signals with probes to immunoglobulin kappa or lambda light chain indicating RNA preservation. The paraffin-embedded B95-8-positive control cell-line showed positive hybridization in most cells with the anti-sense EBER-1 probe, and up to one percent of the cells had a weak signal with the sense probe. Most Raji cells showed a uniform signal with the anti-sense EBER-1 probe only. We conclude that, PCNSLs that arise in AIDS patients are associated with latent EBV infections, whereas PCNSLs from immunocompetent patients are not indicating a probable role for EBV in pathogenesis of these tumors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
So YT, Beckstead JH, Davis RL: Primary central nervous system lymphoma in acquired immune deficiency syndrome: A clinical and pathological study. Ann Neurol 20: 566–574, 1986
Eby NL, Grufferman S, Flannelly CMet al.: Increasing incidence of primary brain lymphoma in the US. Cancer 62: 2461–2465, 1988
Levine A: Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-related lymphoma. Blood 80: 8–20, 1992
Rosenberg NL, Hochberg FH, Miller G, Kleinschmidt-De-Masters BK: Primary central nervous system lymphoma related to Epstein-Barr virus in a patient with acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Ann Neurol 20: 98–102, 1986
Bashir R, Harris N, Hochberg Fet al.: Detection of Epstein-Barr virus in primary CNS lymphoma in immunocompromised patients. Neurol 39: 813–817, 1989
Borisch-Chappnis B, Nezelofc, Muller Het al.: Different Epstein-Barr virus expression in lymphomas from immunocompromised and immunocompetent patients. Am J Pathol 136: 751–758, 1990
Rouah E, Rogers BB, Wilson DRet al.: Demonstration of Epstein-Barr virus in primary central nervous system lymphomas by the polymerase chain reaction andin situ hybridization. Human Path 21: 545–550, 1990
Nakhleh RE, Manivel JC, Copenhaver CM, Sung JH, Strickler JG:In situ hybridization for the detection of Epstein-Barr virus in central nervous system lymphomas. Cancer 67: 444–448, 1991
Morgello S: Epstein-Barr and human immunodeficiency viruses in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-related primary central nervous system lymphoma. Amer J Path 141: 441–450, 1992
Ambinder R, Lambe B, Mann Ret al: Oligonucleotides for polymerase chain reaction amplification and hybridization detection of Epstein-Barr virus DNA in clinical specimens. Mol Cell Probes 4: 397–407, 1990
DeAngelis LM, Wong E, Rosenblum M, Furneaux H: Epstein-Barr virus in acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) and non-AIDS primary central nervous system lymphoma. Cancer 70: 1607–1611, 1992
Bignon YJ, Clavelou P, Ramos Fet al.: Detection of Epstein-Barr viral sequences by genomic amplification in primary lymphoma cells from 10 patients without immunodeficiency. Neurology 41: 1152–1153, 1991
Howe JG, Steitz JA: Localization of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded small RNAs byin situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83: 9006–9010, 1986
Glickman JN, Howe JG, Steitz JA: Structural analyses of EBER1 and EBER2 ribonucleoprotein particles present in Epstein-Barr virus-infected cells. J Virol 62: 902–911, 1988
MacMahon EME, Glass JD, Hayward SDet al.: Epstein-Barr virus in AIDS-related primary central nervous system lymphoma. Lancet 338: 969–973, 1991
Chang KL, Flaris N, Hickey WF, Johnson RM, Meyer JS, Weiss LM: Brain lymphomas of immunocompetent and immunocompromised patients: study of the association with Epstein-Barr virus. Modern Path 6: 427–432, 1993
Bashir RB, Hochberg F, Singer RH: Detection of Epstein-Barr virus byin-situ hybridization. Progress toward development of a non-isotopic diagnostic test. Am J Pathol 135: 1035–1044, 1989
Bashir RM, Harris NL, Hochberg FH, Singer RM: Detection of Epstein-Barr virus in CNS lymphomas byin situ hybridization. Neurology 39: 813–817, 1989
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma pathologic classification project: National Cancer Institute sponsored study of classifications of non-Hodgkin's lymphomas: Summary and of a working formulation for clinical usage. Cancer 49: 2115, 1982
Bashir R, Coakham H, Hochberg F: Expression of LFA-1/ICAM-1 in CNS lymphomas: possible mechanism for lymphoma homing into the brain. J Neuro-Oncology 12: 103–110, 1992
Bashir R, Freedman A, Harris N, Bain K, Nadler L, Hochberg F: Immunophenotypic profile of CNS lymphoma: a review of eighteen cases. J Neuro-Oncology 7: 249–254, 1989
Vroman B, Luka J, Rodriguez M, Pearson G: Characterization of a major protein with a molecular weight of 160,000 associated with the viral capsid antigen of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol 53: 107–112, 1985
Hamilton-Dutoit SJ, Polksen G, Franzmann MBet al.: AIDS-related lymphoma: Histopathology, immunophenotype, and association with EBV as demonstrated byin situ nucleic acid hybridization. Am J Pathol 138: 149–154, 1991
Meeker TC, Shiramizu B, Kaplan Let al.: Evidence of molecular subtypes of HIV-associated lymphoma: Division into peripheral monoclonal, polyclonal and central nervous system lymphoma. AIDS 5: 669–675, 1991
Medawar PB: Immunity to homologous grafted skin: II. The fate of skin homografts transplanted to the brain, to subcutaneous tissue and to the anterior chamber of the eye. Br J Exp Pathol 29: 58–64, 1948
Ljunggren H, Yamasaki T, Collins P, Klein G, Karre K: Selective acceptance of MHC Class I-deficient tumor grafts in the brain. J Exp Med 167: 730–735, 1988
Wekerle H, Linington C, Lassmann H, Meyermann R: Cellular immune reactivity within the CNS. TINS 9: 271–277, 1986
Nilsson K, Giovanella BC, Stehlin JS, Klein G: Tumorigenicity of human hematopoietic cell lines in athymic nude mice. Int J Cancer 19: 337–342, 1977
Bashir RM, Masih A, Kallweit Ket al.: Evolution of clonality and invasive behavior of Epstein-Barr virus immortalized lymphoblastoid cell lines in SCID mice brains. Lab Invest 67: 450–456, 1992
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bashir, R., McManus, B., Cunningham, C. et al. Detection of Eber-1 RNA in primary brain lymphomas in immunocompetent and immunocompromised patients. J Neuro-Oncol 20, 47–53 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01057960
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01057960