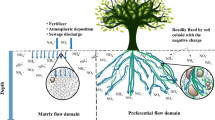
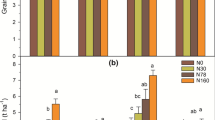
Abstract
A review is made of the recent literature pertaining to the reactions and processes that soil and fertilizer N undergo in lowland rice soils in relation to the improved N management and overal N economy of lowland rice soils. Topics discussed include: nitrogen leaching, ammonium fixation and release, ammonia volatilization, N2 fixation, mineralization-immobilization, nitrification-denitrification, dissimilatory nitrate reduction, urea hydrolysis, critical pathways for control of nitrogen loss.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abichandan CT and Patnaik S (1958) Nitrogenous fertilizers for rice-ammonium or nitrate form? Rice News Teller 6:6–10
Abichandani CT and Patnaik S (1961) Effect of lime application on nitrogen availability and rice yields in waterlogged soils. J Indian Soc Soil Sci 9:55–62
Acharya CN (1935) Studies on the anaerobic decomposition of plant materials. III. Comparison of the course of decomposition under anaerobic, aerobic and partially aerobic conditions. Biochem J 29:1116–1120
Avnimelech Y and Laher M (1977) Ammonia volatilization from soils: Equilibrium considerations. Soil Sci Soc Am J 41:1080–1084
Bajwa MI (1982) Soil clay mineralogies in relation to fertility management: Effect of clay mineral types on ammonium fixation under conditions of wetland rice culture. Agron J 74:143–144
Borthakur HP and Mazundar NN (1968) Effect of lime on nitrogen availability in paddy soil. J Indian Soc Scoil Sci 16:143–147
Broadbent FE (1978) Transformations of soil nitrogen. In Nitrogen and rice, pp. 543–559. Los Baños, Philippines: IRRI
Broadbent FE (1979) Mineralization of organic nitrogen in paddy soils. In Nitrogen and rice, pp. 105–118. Los Baños, Philippines: IRRI
Broadbent FE and Tusneem ME (1971) Losses of nitrogen from some flooded soils in tracer experiments. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 35:922–926
Buresh RJ and Patrick WH Jr (1978) Nitrate reduction to ammonium in anaerobic soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J 42:913–918
Buresh RJ and Patrick WH Jr (1981) Nitrate reduction to ammonium and organic nitrogen in an estuarine sediment. Soil Biol Biochem 13:279–283
Buresh RJ, Casselman ME and Patrick WH Jr (1980) Nitrogen fixation in flooded soil systems, a review. Adv Agron 33:149–192
Byrnes BH, Savant NK and Craswell ET (1983) Effect of a urease inhibitor phenyl phosphorodiamidate on the efficiency of urea applied to rice. Soil Sci Soc Am J 47:270–274
Caskey WH and Tiedje JM (1979) Evidence for Clostridia as agents of dissimilatory reduction of nitrate to ammonium in soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 43:931–936
Chandler RF Jr (1979) Rice in the tropics: A guide to the development of National Agencies. Westview Press, Boulder, Colorada 256 p
Craswell ET and Vlek PLG (1979) Fate of fertilizer nitrogen applied to wetland rice.In Nitrogen and rice, pp. 175–192. Los Baños, Philippines: IRRI
Craswell ET and DeDatta SK (1980) Recent developments in research on nitrogen fertilizers for rice. IRRI Res Pap Ser 49:11 p
Craswell ET, DeDatta SK, Obcemea WN and Hartantyo M (1981) Time and mode of nitrogen fertilizer application to tropical wetland rice. Fert Res 2:247–259
Daikuhara G and Imasaki T (1907) On the behaviour of nitrate in paddy soils (in Japanese). Bull Imp Cent Agric Expt Stn (Japan) 1:7–37
De PK (1936) The problems of the nitrogen supply of rice. I. Fixation of nitrogen in the rice soils under waterlogged conditions. Indian J Agric Sci 6:1237–1245
DeDatta SK and Magnaye CP (1969) A survey of the forms and sources of fertilizer nitrogen for flooded rice. Soils Fert 32:103–109
DeDatta SK (1981) Principles and practices of rice production. John Wiley & Sons, New York, 618 p
DeDatta SK and Kerim MSAAA (1974) Water nitrogen economy of rainfed rice as affected by soil puddling. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 38:515–518
DeLaune RD and Patrick WH Jr (1970) Urea conversion to ammonia in waterlogged soils. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 34:603–607
Delwiche CC (1978) Biological production and utilization of N2O. Pageoph 116:414–422
Delwiche CC (ed.) (1981) Denitrification, nitrification, and nitrous oxide. John Wiley, New York
Denmead OT, Freney JR, Simpson Jr (1979) Nitrous oxide emission during denitrification in a flooded field. Soil Sci Soc Am J 43:716–718
Dei Y and Yamasaki S (1979) Effect of water and crop management on the nitrogen-supplying capacity of paddy soils.In Nitrogen and rice, pp. 451–463. Los Baños, Philippines: IRRI
Firestone MK (1982) Biological denitrification.In Stevenson FJ (ed) Nitrogen in agricultural soils. Agronomy 22:289–326. Am Soc Agron, Madison, Wis
Focht DD (1979) Microbial kinetics of nitrogen losses in flooded soils.In Nitrogen and rice, pp. 119–134. Los Baños, Philippines: IRRI
Focht DD and Verstraete W (1977) Biochemical ecology of nitrification and denitrification.In Alexander M (ed) Advances Microbiol Ecology, 1:135–214. Plenum Press, New York
Freney JR, Denmead OT, Watanabe I and Craswell ET (1981) Ammonia and nitrous oxide losses following applications of ammonium sulfate to flooded rice. Aust J Agric Res 32:37–45
Fried M and Dean LA (1952) A concept concerning the measurement of available soil nutrients. Soil Sci 73:263–271
Hauck RD (1979) Methods for studying N transformations in paddy soils: Review and comments.In Nitrogen and rice, pp. 73–93. Los Baños, Philippines: IRRI
IAEA (1978) Isotope studies on rice fertilization. Joint FAO/IAEA Div of Atomic Energy in Food Agric Tech Rep Ser No 181, IAEA, Vienna
IRRI (1974) Annual report for 1973. Los Baños, Philippines: IRRI
Ishizuka Y (1965) Nutrient uptake at different stages of growth.In The Mineral nutrition of the rice plant, pp. 199–217. Johns Hopkins Press, Baltimore, Maryland
Isirimah NO and Keeney DR (1973) Nitrogen transformations in aerobic and waterlogged histosols. Soil Sci 115:123–129
Jansson SL and Persson J (1982) Mineralization and immobilization of soil nitrogen.In Stevenson FJ (ed) Nitrogen in agricultural soils. Agronomy 22:229–252. Am Soc Agron, Madison, Wis
Kai H and Wada K (1979) Chemical and biological immobilization of nitrogen in paddy soils.In Nitrogen and rice, pp. 157–174. Los Baños, Philippines: IRRI
Kelley WP (1911) The assimilation of nitrogen by rice. Hawaii Agric Expt Stn Bull No. 24:20 p
Keeney DR (1973) The nitrogen cycle in sediment-water systems. J Environ Qual 2:15–29
Keeney DR, Chen RL and Graetz DA (1971) Denitrification and nitrate reduction in sediments: Importance to the nitrogen budget of lakes. Nature 233:66–67
Keerthisinghe G, Mengel K and DeDatta SK (1984) The release of nonexchangeable ammonium (15N labelled) in wetland rice soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 48:291–294
Koike J and Hattori A (1978) Denitrification and ammonia formation in anaerobic coastal sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 35:278–282
Koyama T (1981) The transformations and balance of nitrogen in Japanese paddy fields. Fert Res 2:261–278
MacRae IC, Ancajas RR and Salandanan S (1968) The fate of nitrate in some tropical soils following submergence. Soil Sci 105:327–334
Manguiat IJ and Broadbent FE (1977)15N studies on nitrogen losses and transformations of residual nitrogen in a flooded soil-plant system. Philipp Agric 60:354–366
Matzel W, Heber R, Ackermann W and Teske W (1978) Ammoniakverlustre bei Harnstoffdungung. 3. Beeinflussung der Ammoniakverfluchtignung durch Ureasehemmer. Arch Acker-Pflanzenbau Bodenkunde 22:185–191
Mengel K (1982) Factors of plant nutrient availability relevant to soil testing. Plant Soil 64:129–138
Mikkelsen DS and DeDatta SK (1979) Ammonia volatilization from wetland rice soils.In Nitrogen and rice, pp. 135–156. Los Baños, Philippines: IRRI
Mikkelsen DS, DeDatta SK and Obcemae WN (1978) Ammonia volatilization losses from flooded rice soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 42:725–730
Mitsui S (1955) Inorganic nutrition, fertilization and soil amelioration for lowland rice. Yokendo Ltd, Tokyo
Mulvaney RL and Bremner JM (1981) Control of urea transformations in soils.In Paul EA and Ladd JN (eds) Soil Biochemistry 5:153–196. Marcel Dekker, New York
Nelson DW (1982) Gaseous loss of nitrogen other than through denitrification.In Stevenson FJ (ed) Nitrogen in agricultural soisl. Agronomy 22:327–363. Am Soc Agron, Madison, Wis
Nemeth K (1979) The availability of nutrients in the soil as determined by electroultrafiltration (EUF). Adv Agron 31:155–188
Nommik H and Vahtras K (1982) Retention and fixation of ammonium and ammonia in soils.In Stevenson FJ (ed) Nitrogen in agricultural soils. Agronomy 22:123–171. Am Soc Agron, Madison, Wis
Park K, Hood DW and Odum HT (1958) Diurnal pH variations in Texas bays and its application of primary production estimates. Publ Inst Mar Sci Univ Texas 5:47–64
Patrick WH Jr (1982) Nitrogen transformations in submerged soils.In Stevenson FJ (ed) Nitrogen in agricultural soils. Agronomy 22:449–465. Am Soc Agron, Madison, Wis
Patrick WH Jr and Mahapatra IC (1968) Transformation and availability to rice of nitrogen and phosphorus in waterlogged soils. Adv Agron 20:323–359
Patrick WH Jr and Sturgis MB (1955) Concentration and movement of oxygen as related to absorption of ammonium and nitrate nitrogen by rice. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 19:59–62
Payne WJ (1981) Denitrification. Wiley, New York, 214 p
Pearsall WH (1950) The investigation of wet soils and its agricultural implications. Emp J Agric 18:289–298
Pearsall WH and Mortimer CH (1939) Oxidation-reduction potentials in waterlogged soils, natural waters and muds. J Ecol 27:483–501
Ponnamperuma FN (1958) Lime as a remedy for a physiological disease of rice associated with excess iron. Int Rice Comm Newsl 7:10–13
Ponnamperuma FN (1965) Dynamic aspects of flooded soils.In Mineral nutrition of the rice plant, pp. 295–328. John Hopkins Press, Baltimore, Maryland
Ponnamperuma FN (1972) The chemistry of submerged soils. Adv Agron 24:29–96
Ponnamperuma FN (1978) Electrochemical changes in submerged soils and the growth of rice.In Soils and rice, pp. 421–441. Los Baños, Philippines: IRRI
Prasad R and DeDatta SK (1979) Increasing fertilizer nitrogen efficiency in wetland rice.In Nitrogen and rice, pp. 465–484. Los Baños, Philippines: IRRI
Qi Z and Hua-Kuei C (1983) The activity of nitrifying and denitrifying bacteria in paddy soil. Soil Sci 135:31–34
Reddy KR (1982) Nitrogen cycling in a flooded-soil ecosystem planted to rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Soil 67:209–220
Reddy KR, Patrick WH Jr and Phillips RE (1976) Ammonium diffusion as a factor in nitrogen loss from flooded soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J 40:528–533
Reddy KR, Patrick WH Jr and Phillips RE (1978) The role of nitrate diffusion in determining the order and rate of denitrification in flooded soil: I. Experimental results. Soil Sci Soc Am J 42:268–272
Reddy KR, Patrick WH Jr and Phillips RE (1980) Evaluation of selected processes controlling nitrogen loss in flooded soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J 44:1241–1246
Sahrawat KL (1979a) Nitrogen losses in rice soils. Fert News 24:38–48
Sahrawat KL (1979b) Evaluation of some chemical extractants for determination of exchangeable ammonium in tropical rice soils. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 10:1005–1013
Sahrawat KL (1979c) Ammonium fixation in some tropical rice soils. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 10:1015–1023
Sahrawat KL (1980a) Nitrogen mineralization in acid sulfate soils. Plant Soil 57:143–146
Sahrawat KL (1980b) Urease activity in tropical rice soils and flood water. Soil Biol Biochem 12:195–196
Sahrawat KL (1980c) Control of urea hydrolysis and nitrification in soil by chemicals-prospects and problems. Plant Soil 57:335–352
Sahrawat KL (1981) Ammonification in air-dried tropical lowland histosols. Soil Biol Biochem 13:323–324
Sahrawat KL (1982a) Evaluation of some chemical indexes for predicting mineralizable nitrogen in tropical rice soils. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 13:363–377
Sahrawat KL (1982b) Simple modification of the Walkley-Black method for simultaneous determination of organic carbon and potentially mineralizable nitrogen in tropical rice soils. Plant Soil 69:73–77
Sahrawat KL (1982c) Nitrification in some tropical soils. Plant Soil 65:281–286
Sahrawat KL (1983a) Mineralization of soil organic nitrogen under waterlogged conditions in relation to other properties of tropical rice soils. Aust J Soil Res 21:133–138
Sahrawat KL (1983b) Nitrogen availability indexes for submerged rice soils. Adv Agron 36:415–451
Sahrawat KL (1983c) Relationships between soil urease activity and other properties of some tropical wetland rice soils. Fert Res 4:145–150
Sahrawat KL and Burford JR (1982) Modification of the alkaline permanganate method for assessing the availability of soil nitrogen in upland soils. Soil Sci 133:53–57
Sanchez PA (1972) Nitrogen fertilization and management in tropical rice. North Carolina Agric Expt Stn Tech Bull 213:1–31
Sanchez PA (1973) Puddling tropical rice soils. II. Effect of water losses. Soil Sci 115:303–308
Savant NK and DeDatta SK (1980) Movement and distribution of ammonium-N following deep placement of urea in a wetland rice soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J 44:559–565
Savant NK and DeDatta SK (1982) Nitrogen transformations in wetland rice soils. Adv Agron 35:241–302
Sethunathan N, Rao VR, Adhya TK and Raghu K (1983) Microbiology of rice soils. CRC Critic Rev Microbiol 10:125–172
Shiga H and Ventura W (1976) Nitrogen supplying ability of paddy soils under field conditions in the Philippines. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 22:387–399
Shioiri M (1948) Effect of drying in paddy fields during fallow period. Bull Agric Expt Stn Minist Agric (Japan) 64:1–24
Shioiri M, Aomine S, Uno Y and Harada T (1941) Effect of air-drying of paddy soil (in Japanese). J Sci Soil Manure (Japan) 15:331–333
Smith CJ, Brandon M and Patrick WH Jr (1982) Nitrous oxide emission following urea-N fertilization of wetland rice. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 28:161–171
Sorensen J (1978) Capacity for denitrification and reduction of nitrate to ammonia in a coastal marine sediment. Appl Environ Microbiol 35:301–305
Stanford G (1978) Evaluation of ammonium release by alkaline permanganate extraction as an index of soil nitrogen availability. Soil Sci 126:244–253
Stanford G, Legg JO, Dzienia S and Simpson EC Jr (1975) Denitrification and associated nitrogen transformations in soils. Soil Sci 120:147–152
Tanji KK (1982) Modeling of the soil nitrogen cycle.In Stevenson FJ (ed) Nitrogen in agricultural soils. Agronomy 22:721–772. Am Soc Agron, Madison, Wis
Terman GL (1979) Volatilization losses of nitrogen as ammonia from surfaceapplied fertilizers, organic amendments, and crop residues. Adv Agron 31:189–223
Tiedje JM, Firestone RB, Firestone MK, Betlach MR, Kaspar HF and Sorensen J (1981) Use of nitrogen-13 in studies of denitrification.In Krohn KA and Root JW (eds) Recent developments in biological and chemical research with short-lived isotopes. Advances in Chemistry, Am Chem Soc, Washington
Tilo SN, Caramoncion MDV, Manguiat IJ and Paterno ES (1977) Naturally occurring fixed ammonium in some Philippine soils. Philipp Agric 60:413–419
Tusneem ME and Patrick WH Jr (1971) Nitrogen transformations in waterlogged soil. Louisiana State Univ Agric Expt Stn Bull 657:1–75
Ventura W and Watanabe I (1978) Dry season soil conditions and soil nitrogen availability to wet season wetland rice. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 24:533–545
Vlek PLG, Byrnes BH and Craswell ET (1980) Effect of urea placement on leaching losses of nitrogen from flooded rice soils. Plant Soil 54:441–449
Vlek PLG and Craswell ET (1981) Ammonia volatilization from flooded soils. Fert Res 2:227–245
Vlek PLG, Stumpe JM and Byrnes BJ (1980) Urease activity and inhibition in flooded soil systems. Fert Res 1:191–202
Watanabe I and Cholitkul W (1979) Field studies on nitrogen fixation in paddy soils.In Nitrogen and rice, pp. 223–239. Los Baños, Philippines: IRRI
Williams WA, Mikkelsen DS, Mueller KE and Ruckman JR (1968) Nitrogen immobilization by rice straw incorporated in lowland rice production. Plant Soil 28:49–60
Yoshida T (1975) Microbial metabolism of flooded soils.In Paul EA and McLaren AD (eds) Soil Biochemistry 3:83–122
Yoshida T (1978) Microbial metabolism in rice soils.In Soils and rice, pp. 445–463. Los Baños, Philippines: IRRI
Yoshida T and Ancajas RR (1971) Nitrogen fixation by bacteria in the root zone of rice. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 35:156–157
Yoshida T and Ancajas RR (1973) Nitrogen-fixing activity in upland and flooded rice fields. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 37:42–46
Yoshida T and Padre BC Jr (1974) Nitrification and denitrification in submerged Maahas clay soil. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 20:241–247
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Keeney, D., Sahrawat, K. 2. Nitrogen transformations in flooded rice soils. Fertilizer Research 9, 15–38 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01048694
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01048694