Abstract
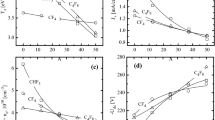
Chemical relaxation mass spectrometry has been used to study the kinetics and mechanism in the silane-hydrogen-solid silicon system under conditions of glow discharge. The emphasis was on the main processes related to the deposition of amorphous and nanocrystalline silicon thin films. It is shown that under conditions of the deposition of a-Si and nc-Si the dominant reaction channel is the electron impact induced fragmentation of silane into molecular hydrogen and SiH2 radical. The role of other processes, such as hydrogen abstraction, is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Proc. of the 11th Int. Conf. on Amorphous and Liquid Semiconductors, F. Evangelisti and J. Stuke, eds., Rome, 1985;J. Non-Cryst. Solids 77, 78 (1985).
G. Turban,Pure Appl. Chem. 56, 215 (1984).
F. J. Kampas, inHydrogenated Amorphous Silicon, Vol. A, J. I. Pankove, ed., Academic Press, New York (1984).
G. Turban, Y. Catherine, and B. Grolleau,Thin Solid Films 67, 309 (1980).
G. Turban, Y. Catherine, and B. Grolleau,Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2, 61 (1982).
A. G. Bruno, P. Capezzuto, G. Cicala, and F. Cramarossa,Plasma Chem. Plama Process. 6, 109 (1986);
R. Robertson and A. Gallagher,J. Appl. Phys.,59, 3402 (1986);
M. J. Kushner,IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. PS-14, 1988 (1986).
P. A. Longeway, R. D. Estes, and H. A. Weakliem,J. Phys. Chem. 88, 73 (1984).
P. A. Longeway, H. A. Weakliem, and R. D. Estes,J. Chem. Phys. 88, 3282 (1984).
M. Eigen and L. De Mayer, Relaxation Methods, inTechniques of Organic Chemistry, Vol. VIII, Part II, Chapter XVIII, A. Weisenberger, ed., Wiley, New York (1963).
G. H. Czerlinski,Chemical Relaxation, Marcel Dekker, New York (1966).
D. N. Hague,Fast Reactions, Wiley, New York (1971).
J. J. Wagner and S. Veprek,Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 3, 219 (1983).
S. Veprek, K. Ensslen, and J. J. Wagner, Proc. 6th Int. Symp. on Plasma Chem., Montreal (1983), p. 772.
J. J. Wagner and S. Veprek,Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2, 95 (1982).
S. Veprek,Pure Appl. Chem. 54, 1197 (1982).
S. Veprek, inPoly-Micro-Crystalline and Amorphous Semiconductors, P. Pinard and S. Kalbitzer, eds., Les Éditions de Physique, Les Ulis, France (1984), p. 425.
R. Brewer, J. K. Gimzewski, and S. Veprek, unpublished results; K. Yamashita, J. K. Gimzewski, and S. Veprek,J. Nucl. Mater. 128–129, 705 (1984).
P. John and J. H. Purnell,J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 69, 1455 (1973).
J. Villermaux,Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 14, 1963 (1971).
H. Wagner and H. Ibach, inFestkörperprobleme (Advances in Solid State Physics), Vol. XXIII, Vieweg, Braunschweig (1983), p. 165.
W. E. Spear and P. G. Le Comber,Philos. Mag. 33, 935 (1976).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ensslen, K., Vepřek, S. Dominant reaction channels and the mechanism of silane decomposition in a H2-Si(s)-SiH4 glow discharge. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 7, 139–153 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01019174
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01019174