Abstract
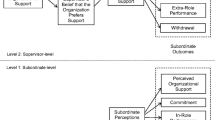
Previous research suggests that a supervisor's liking of a subordinate biases evaluations of that subordinate's performance. Other research suggests that supervisor liking influences the treatment of the subordinate, which may in turn influence the subordinate's performance. The present study investigated these influences in a laboratory simulation. Subjects (N=140) worked on their own tasks and supervised an alleged subordinate during a 30-min work period. Supervisor liking of a subordinate was manipulated by altering the personality characteristics and the attitude similarity of the subordinate. Reward context was manipulated by rewarding supervisors for either the total performance of both the supervisors and subordinates or for the individual performance of each supervisor only. Supervisor liking positively influenced the expected leader-member exchange, treatment of the subordinate, and evaluations of subordinate performance. The reward context influenced supervisor treatment of the subordinate and the number of problems the supervisor solved.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, E. R., III, & Wilkins, R. D. (1982). Performance rating validity: The relationship of objective and subjective measures of performance.Group and Organization Studies, 7 485–496.
Anderson, N. H. (1968). Likableness ratings of SSS personality-trait nords.Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 9 272–279.
Backman, C. W., & Secord, P. F. (1959). The effect of perceived liking on interpersonal attraction.Human Relations, 12 379–384.
Byrne, D. (1971).The attraction paradigm. New York: Academic Press.
Cardy, R. L., & Dobbins, G. H. (1986). Affect and appraisal accuracy: Liking as an integral dimension in evaluating performance.Journal of Applied Psychology, 71 672–678.
Cooper, W. H. (1981). Ubiquitous halo.Psychological Bulletin, 90 218–244.
Crouch, A., & Yetton, P. (1988). Manager-subordinate dyads: Relationships among task and social contact, manager friendliness and subordinate performance in management groups.Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 41 65–82.
Curtis, R. C., & Miller, K. (1986). Believing another likes or dislikes you: Behaviors making the beliefs come true.Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 51 284–290.
Dansereau, F., Graen, G., & Haga, W. J. (1975). A vertical dyad linkage approach to leadership within formal organizations.Organizational Behavior and Human Performance, 13 46–78.
Dienesch, R. M., & Liden, R. C. (1986). Leader-member exchange model of leadership: A critique and further development.Academy of Management Review, 11 618–634.
Dipboye, R. L. (1985). Some neglected variables in research on discrimination in performance appraisals.Academy of Management Review, 10 116–127.
Dobbins, G. H., & Russell, J. M. (1986). The biasing effects of subordinate likeableness on leaders' responses to poor performers: A laboratory and a field study.Personnel Psychology, 39 759–777.
Duchon, D., Green, S. G., & Taber, T. D. (1986). Vertical dyad linkage: A longitudinal assessment of antecedents, measures, and consequences.Journal of Applied Psychology, 71 56–60.
Eden, D. (1990).Pygmalion in management: Productivity as a self-fulfilling prophecy. Lexington, MA: Lexington Books.
Eden D., & Shani, A. B. (1982). Pygmalion goes to boot camp: Expectancy, leadership, and trainee performance.Journal of Applied Psychology, 67 194–199.
Field, R. H. G. (1989). The self-fulfilling prophecy leader: Achieving the metharme effect.Journal of Management Studies, 26 151–175.
Feren, D. B., Carroll, S. J., & Olian, J. D. (1988). Effects of managerial performance and attitudinal similarity on interpersonal attraction.Basic and Applied Social Psychology, 9 33–44.
Graen, G., & Cashman, J. F. (1975). A role-making model of leadership in formal organizations: A developmental approach. In J. G. Hunt & L. L. Larson (Eds.),Leadership frontiers (pp. 143–165). Kent, OH: Kent State University Press.
Graen, G., Dansereau, F., Minami, T., & Cashman, J. (1973). Leadership behaviors as cues to performance evaluations.Academy of Management Journal, 16 611–623.
Graen, G., & Ginsburgh, S. (1977). Job resignation as a function of role orientation and leader acceptance: A longitudinal investigation of organizational assimilation.Organizational Behavior and Human Performance, 19 1–17.
Graen, G., Novak, M., & Sommerkamp, P. (1982). The effects of leader-member exchange and job design on productivity and satisfaction: Testing a dual attachment model.Organizational Behavior and Human Performance, 30 109–131.
Graen, G. B., Scandura, T. A., & Graen, M. R. (1986). A field experiment test of the moderating effects of growth need strength on productivity.Journal of Applied Psychology, 71 484–491.
Graen, G., & Schiemann, W. (1978). Leader-member agreement: A vertical dyad linkage approach.Journal of Applied Psychology, 63 206–212.
Graves, L. M., & Powell, G. N. (1988). An investigation of sex discrimination in recruiters' evaluation of actual applicants.Journal of Applied Psychology, 73 20–29.
Harris, M. J., & Rosenthal, R. (1985). Mediation of interpersonal expectancy effects: 31 metaanalyses.Psychological Bulletin, 97 363–386.
Harris, M. J., & Rosenthal, R. (1986). Four factors in the mediation of teacher expectancy effect. In R. S. Feldman (Ed.),The social psychology of education: Current research and theory (pp. 91–114). Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Ilgen, D. R., Mitchell, T. R., & Fredrickson, J. W. (1981). Poor performers: Supervisors' and subordinates' responses.Organizational Behavior and Human Performance, 27 386–410.
Johnson, D. W., Johnson, R. T., & Maruyama, G. (1983). Interdependence and interpersonal attraction among heterogeneous and homogeneous individuals: A theoretical formulation and a meta-analysis of the research.Review of Educational Research, 53 5–54.
Johnson, D. W., Maruyama, G., Johnson, R., Nelson, O., & Skon, L. (1981). Effects of cooperative, competitive, and individualistic goal structures on achievement: A meta-analysis.Psychological Bulletin, 89 47–62.
Jussim, L. (1986). Self-fulfilling prophecies: A theoretical and integrative review.Psychological Bulletin, 93 429–445.
Keenan, A. (1977). Some relationships between interviewers' personal feelings about candidates and their general evaluations of them.Journal of Occupational Psychology, 50 275–283.
Kingstrom, P. O., & Mainstone, L. E. (1985). An investigation of rater-ratee acquaintance and rater bias.Academy of Management Journal, 28 641–653.
Larson, J. R., Jr. (1986). Supervisors' performance feedback to subordinates: The impact of subordinate performance valence and outcome dependence.Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 37 391–408.
Latane, B. Williams, K. & Harkins, S. (1979). Many hands make light the work: The causes and consequences of social loafing.Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 37 822–832.
Liden, R., & Graen, G. (1980). Generalizability of the vertical dyad linkage model of leadership.Academy of Management Journal, 23 451–465.
Mitchell, T. R., & Liden, R. C. (1982). The effects of the social context on performance evaluations.Organizational Behavior and Human Performance, 29 241–256.
O'Reilly, C. A. (1977). Superiors and peers as information sources, work group supportiveness and individual decision-making performance.Journal of Applied Psychology, 62 632–635.
Raza, S. M., & Carpenter, B. N. (1987). A model of hiring decisions in real employment interviews.Journal of Applied Psychology, 72 596–603.
Regan, D. T. Straus, E., & Fazio, R. (1974). Liking and the attribution process.Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 10 385–397.
Scandura, R. A., & Graen, G. B. (1984). Moderating effects of initial leader-member exchange status on the effects of a leadership intervention.Journal of Applied Psychology, 69 428–436.
Seers, A., & Graen, G. (1984). The dual attachment concept: A longitudinal investigation of task characteristics and leader-member exchange.Organizational Behavior and Human Performance, 33 283–306.
Shrout, P. E., & Fleiss, J. L. (1979). Intraclass correlations: Uses in assessing rater reliability.Psychological Bulletin, 86 420–428.
Tetlock, P. E. (1985). Accountability: The neglected social context of judgment and choice. In L. L. Cummings & B. M. Staw (Eds.),Research in Organizational Behavior (pp. 297–332). Greenwich, CT: JAI Press.
Tjosvold, D. (1985). Power and social context in superior-subordinate interaction.Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 35 281–293.
Tjosvold, D. (1988a) Cooperative and competitive dynamics within and between organizational units.Human Relations, 41 425–436.
Tjosvold, D. (1988b). Cooperative and competitive interdependence: Collaboration between departments to serve customers.Group and Organization Studies, 13 274–289.
Tjosvold, D. (1989). Interdependence and power between managers and employees: A study of the leader relationship.Journal of Management, 15 49–62.
Tsui, A. S., & Barry, B. (1986). Interpersonal affect and rating errors.Academy of Management Journal, 29 586–599.
Tsui, A. S., & O'Reilly, C. A., III (1989). Beyond simple demographic effects: The importance of relational demography in superior-subordinate dyads.Academy of Management Journal, 32 402–423.
Turban, D. B., & Jones, A. P. (1988). Supervisor-subordinate similarity: Types, effects, and mechanisms.Journal of Applied Psychology, 73 228–234.
Vecchio, R., & Gobdel, B. (1984). The vertical dyad linkage model of leadership: Problems and prospects.Organizational Behavior and Human Performance, 34 5–20.
Williams, K., Harkins, S., & Latane, B. (1981). Identifiability as a deterrent to social loafing: Two cheering experiments.Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 40 303–311.
Zajonc, R. B. (1980). Feeling and thinking: Preferences need no inferences.American Psychologist, 35 151–175.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The authors appreciate the help of Julie Glisky, Ingrid Gunn, Leilani Jennings, Gary Loss, Armida Montemayor, Kim Robinson, and Leena Weisglass during various phases of the study. Appreciation is also expressed to Tom Dougherty, Milt Hakel, Jim Phillips, and Debra Steele-Johnson for their comments on earlier drafts of this manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Turban, D.B., Jones, A.P. & Rozelle, R.M. Influences of supervisor liking of a subordinate and the reward context on the treatment and evaluation of that subordinate. Motiv Emot 14, 215–233 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00995570
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00995570