Abstract
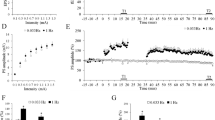
The effects of protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitors on the induction of long lasting potentiation (LLP) of field potentials in the feline somatosensory cortex were studied. LLP was induced by high frequency stimulation (HFS, 200 Hz) of the ventral posterolateral thalamic nucleus. First, the effects of a protein kinase inhibitor, H-7, and a specific PKC catalytic domain inhibitor, chelerythrine, on the LLP in the secondary somatosensory cortex (SII) were investigated. Intracortical microinjections of H-7 and chelerythrine at 30 min before HFS inhibited induction of LLP in SII, while an injection of chelerythrine at 60 min after LLP induction had no effect on the potentiation. Second, changes in PKC activity in the presence of calcium and phosphatidylserine were investigated in SII after induction of LLP. Triton-soluble membrane fractional PKC activity had increased to 350% of the control value with low frequency test stimulation (0.1 Hz) by five min after HFS. In contrast, PKC activities of cytosolic fractions decreased to 25.6% of the control value. At 60 min after HFS, the PKC activity level returned to the control value, despite persistent potentiation in all cases. PKC activation is considered to be one of the factors required for induction of LLP but not for maintenance in SII.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kawakami, Y., and Ashida, H. 1993. Long lasting potentiation of field potentials in primary and secondary somatosensory cortex. Brain Res. 605:147–154.
Miyata, M., and Kawakami, Y. 1995. Induction of long lasting potentiation in the secondary somatosensory cortex by thalamic stimulation requires corticocortical pathways from the primary somatosensory cortex. Neurosci. 68:47–55.
Huang, Y.-Y., Colley, P. A., and Rottenburg, A. 1992. Postsynaptic protein kinase C activity may be necessary for long-term potentiation. J. Neurosci. 49:819–826.
Malinow, R., Madison, D. V., and Tsien, R. W. 1988. Persistent protein kinase activity underlying long-term potentiation. Nature 335:820–824.
Malinow, R., Schulman, H., Tsien, R. W. 1989. Inhibition of postsynaptic PKC or CamKII blocks induction but not expression of LTP. Science 245:862–863.
Wang, J.-H., and Feng, D.-P. 1992 Postsynaptic protein kinase C essential to induction and maintenance of long-term potentiation in the hippocampal CA1 region. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 89:2576–2580.
Colley, P. A., Sheu, F.-S., and Rottenburg, A. 1990. Inhibition of protein kinase C blocks two components of LTP persistence leaving initial potentiation intact. J. Neurosci. 10:3353–3360.
Hu, G.-Y., Hvalby, O., Walaas, S. I., Albert, K. A., Skjefelo, P., Andersen, P., Greengard, P. 1987. Protein kinase C injection into hippocampal pyramidal cells elicits features of long-term potentiation. Nature 328:426–429.
Muller, D., Bittar, P., Boddeke, H. 1992. Induction of stable long-term potentiation in the presence of the protein kinase C antagonist staurosporine. Neurosci. Lett. 135:18–22.
Baranyi, A., Szente, M. B., Woody, C. D. 1987. Intracellular injection of phorbol ester increases the excitability of neurons of the motor cortex of awake cats. Brain Res. 424:396–401.
Baranyi, A., Szente, M. B., Woody, C. D. 1988. Activation of protein kinase C induced long-term changes of postsynaptic currents in neocortical neurons. Brain Res. 440:341–347.
Bank, B., DeWeer, A., Kuzirian, A. M., Rasmussen, H., Alkon, D. L. 1988. Classical conditioning induces long-term translocation of protein kinase C in rabbit hippocampal CA1 cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 85:1988–1992.
Kusuzaki, K. S., Lester, D. S., Schreurs, B. G., Alkon, D. L. 1993. Associative learning potentiates protein kinase C activation in synaptosomes of the rabbit hippocampus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 90: 4286–4289.
Olds, J. L., Anderson, M. L., McPhie, D. L., State, L. D., Alkon, D. L. 1989. Imaging of memory-specific changes in the distribution of protein kinase C in the hippocampus. Science 245:866–869.
Akers, R. F., Lovinger, D. M., Colley, P. A., Linden, D. J., and Rottenburg, A. 1986. Translocation of protein kinase C activity may mediate hippocampal long-term potentiation. Science 237:587–589.
Snider, R. S., Niemer, W. T. 1970. A Stereotaxic Atlas of the Cat Brain, The University of Chicago Press, Chicago.
Frey, U., Huang, Y.-Y., Kandel, E. R. 1993. Effects of cAMP stimulate a late state of LTP in hippocampal CA1 neurons. Science 260:1661–1664.
Hidaka, H., Inagaki, M., Kanemoto, S., Sasaki, Y. 1984. Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase A and protein kinase C. Biochem. 23: 5036–5041.
Szente, M. B., Baranyi, A., Woody, C. D. 1990. Effects of protein kinase C inhibitor H-7 on membrane properties and synaptic responses of neocortical neurons of awake cats. Brain Res. 506:281–286.
Klann, E., Chen, S.-J., Sweatt, J. D. 1993. Mechanism of protein kinase C activation during the induction and maintenance of long-term potentiation probed using a selective peptide substrate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 90:8337–8341.
Sacktor, T. C., Osten, P., Valsamis, H., Jiang, X., Naik, M. U., Sublette, E. 1993. Persistent activation of the isoform of protein kinase C in the maintenance of long-term potentiation, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 90:8342–8346.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kawakami, Y., Miyata, M., Tanaka, T. et al. Protein kinase C inhibitors affect induction of long-lasting potentiation in the somatosensory cortex. Neurochem Res 20, 1027–1032 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00995556
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00995556