Abstract
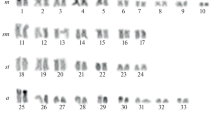
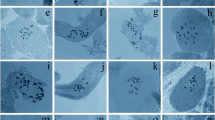
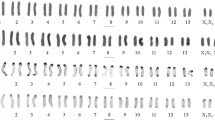
Detailed C-banded karyotypes of eight diploidArtemisia species from three different sections are reported together with preliminary observations on three additional related diploid species. In the majority, the overall amount of banding is relatively low. Bands are mostly confined to distal chromosome regions; intercalary banding is virtually absent and centromeric heterochromatin is also scarce. With the exception ofA. judaica there is in general great uniformity in karyotype structure but considerable interspecific variation in total karyotype length (and hence DNA content) ranging from 44 µm inA. capillaris (2n = 18) to 99 µm inA. atrata (2n = 18).A. judaica (2n = 16; total karyotype length 97 µm) was distinguished by its karyomorphology, with one large non-banded metacentric chromosome pair and 7 pairs of smaller terminally banded meta- or submetacentric chromosomes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ehrendorfer, F., Schweizer, D., Greger, H., Humphries, Ch., 1977: Chromosome banding and synthetic systematics inAnacyclus (Asteraceae-Anthemideae). — Taxon26, 387–394.
Geber, G., 1979: Bestimmung der DNS-Menge im Zellkern: Beispiele aus der GattungArtemisia. — M.Sc.-Diploma work, University of Vienna.
—, 1980: Cytophotometrische Bestimmung von DNA-Mengen: Vergleich einer neuen DAPI-Fluoreszenzmethode mit Feulgen-Absorptionsphotometrie. — Microscopica Acta, Suppl.4, 31–35.
Greger, H., 1977:Anthemideae—chemical review. — InHeywood, V. H., Harborne, J. B., Turner, B. L., (Eds.): The Biology and Chemistry of theCompositae, 899–941. — London, New York: Academic Press.
Humphries, C. J., 1980: Cytogenetic and cladistic studies inAnacyclus (Compositae:Anthemideae). — Nord. J. Bot.1, 83–96.
Nagl, W., Ehrendorfer, F., 1974: DNA content, heterochromatin, mitotic index, and growth in perennial and annualAnthemideae (Asteraceae). — Pl. Syst. Evol.123, 35–54.
Schweizer, D., Ehrendorfer, F., 1976: Giemsa banded karyotypes, systematics, and evolution inAnacyclus (Asteraceae-Anthemideae). — Pl. Syst. Evol.126, 107–148.
—, —, 1983: Evolution of C-band patterns inAsteraceae-Anthemideae. — Biol. Zentralbl.102, 637–655.
Stangl, R., 1984: Vergleichende Analysen ätherischer Blattöle der GattungArtemisia (Asteraceae-Anthemideae). — Ph.D. Thesis, University of Vienna.
Tohidast-Akrad, M., 1982: Beiträge zur Karyosystematik und Evolution vonAchillea (Asteraceae-Anthemideae): Chromosomenzahlen, Feulgen- und Giemsa-C-gebänderte Chromosomen. — Ph.D. Thesis, University of Vienna.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mendelak, M., Schweizer, D. Giemsa C-banded karyotypes of some diploidArtemisia species. Pl Syst Evol 152, 195–210 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00989427
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00989427