Summary
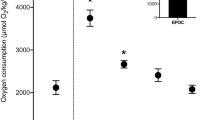
Ventilation and metabolic rate were measured during exercise in adult female green turtles at Tortuguero, Costa Rica. Six turtles were studied at night on the beach while actively covering their nests. Five turtles, captured after nesting, were studied at rest, during 20 min of spontaneous activity, and during recovery from the activity. Arterial blood samples were obtained from the latter animals and analyzed for pH,\(P_{CO_2 } , P_{O_2 } \), O2 concentration and lactate concentration. Blood was obtained by heart puncture from 8 turtles immediately after nesting and analyzed for blood lactate. Active metabolism (\(\dot V_{O_2 } \)) in both groups was almost 10 times the standard resting value (0.024 l/kg·h). The increase in ventilation during exercise, due exclusively to higher breathing frequency, exceeded the increase in\(\dot V_{O_2 } \), so that the ratio\(\dot V_{E_2 } /\dot V_{O_2 } \) (the air convection requirement), more than doubled. The respiratory exchange ratio,\(\dot V_{CO_2 } /\dot V_{O_2 } \), that averaged 0.56 in the resting turtles, increased to 1.08 during exercise in the captured turtles and was 0.90 in the nesting animals. Arterial\(P_{O_2 } \) and O2 saturation remained unchanged during exercise, indicating efficient gas exchange in the lungs. Pre-exercise values of all variables were restored 1 h after the end of exercise. Blood acid-base changes associated with activity in the captive turtles were variable and not statistically significant, but suggested partially compensated metabolic acidosis. Lactate concentrations were significantly elevated in the nesting turtles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett, A.F.: Ventilation in two species of lizards during rest and activity. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.46A, 653–671 (1973a)
Bennett, A.F.: Blood physiology and oxygen transport during activity in two lizards,Varanus gouldii andSauromalus hispidus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.46A, 673–690 (1973b)
Bennett, A.F., Dawson, W.R.: Metabolism. In: Biology of the reptilia, Vol. 5, Physiology A. Gans, C., Dawson, W.R. (eds.), pp. 127–223. New York: Academic Press 1976
Berkson, H.: Physiological adjustments to prolonged diving in the Pacific green turtle (Chelonia mydas agassizii). Comp. Biochem. Physiol.18, 101–119 (1966)
Carr, A.F.: So excellent a fishe. Garden City, New York: Natural History Press 1967
Carr, A.F., Giovannoli, L.: The ecology and migrations of sea turtles, 2. Results of field work in Costa Rica. Am. Mus. Novit.1835, 1–32 (1957)
Carr, A.F., Ogren, L.: The ecology and migrations of sea turtles, 4. The green turtle in the Caribbean Sea. Bull. Am. Mus. Nat. Hist.121, 1–48 (1960)
Gans, C., Hughes, G.M.: The mechanism of lung ventilation in the tortoiseTestudo graeca Linné. J. Exp. Biol.47, 1–20 (1967)
Gatten, R.E., Jr.: Effects of temperature and activity on aerobic and anaerobic metabolism and heart rate in the turtlesPseudemys seripta andTerrepene ornata. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.48A, 619–648 (1974)
Hochachka, P.W., Owen, T.G., Allen, J.F., Whittow, G.C.: Multiple end products of anaerobiosis in diving vertebrates. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.50B, 17–22 (1975)
Hughes, G.M., Gaymer, R., Moore, M., Woakes, A.J.: Respiratory exchange and body size in the Aldabra giant tortoise. J. Exp. Biol.55, 651–665 (1971)
Jackson, D.C., Kraus, D.R., Prange, H.D.: Ventilatory response to inspired CO2 in the sea turtle: Effects of body size and temperature. Respir. Physiol.38, 71–81 (1979)
Moberly, W.R.: The metabolic responses of the common iguana,Iguana iguana, to activity under restraint. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.27, 1–20 (1968a)
Moberly, W.R.: The metabolic responses of the common iguana,Iguana iguana, to walking and diving. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.27, 21–32 (1968b)
Prange, H.D.: Energetics of swimming of a sea turtle. J. Exp. Biol.64, 1–12 (1976)
Prange, H.D., Jackson, D.C.: Ventilation, gas exchange and metabolic scaling of a sea turtle. Respir. Physiol.27, 369–377 (1976)
Reeves, R.B.: Temperature-induced changes in blood acid-base status: pH and PCO2 in a binary buffer. J. Appl. Physiol.40, 752–761 (1976)
Reeves, R.B.: The interaction of body temperature and acid-base balance in ectothermic vertebrates. Ann. Rev. Physiol.39, 559–586 (1977)
Roughton, F.J.W., Scholander, P.F.: Micro gasometric estimation of the blood gases. I. Oxygen. J. Biol. Chem.148, 541–550 (1943)
Scholander, P.F.: Analyzer for accurate estimation of respiratory gases in one-half cubic centimeter samples. J. Biol. Chem.167, 235–250 (1947)
Wasserman, K., Van Kessel, A.L., Burton, G.G.: Interaction of physiological mechanisms during exercise. J. Appl. Physiol.22, 71–85 (1967)
Wood, S.C., Johansen, K., Glass, M.L., Maloiy, G.M.O.: Aerobic metabolism of the lizardVaranus exanthematicus: effects of activity, temperature, and size. J. Comp. Physiol.127, 331–336 (1978)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jackson, D.C., Prange, H.D. Ventilation and gas exchange during rest and exercise in adult green sea turtles. J Comp Physiol B 134, 315–319 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00709998
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00709998