Summary
-
1)
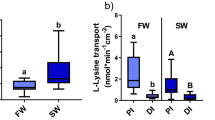
Unidirectional transmembrane transport of3H-lysine across the mucosal border of the midgut from the freshwater shrimp,Macrobrachium rosenbergii, has been examined using an in vitro perfusion procedure.
-
2)
Influx of this amino acid appeared to take place through a high-affinity, carrier-mediated transport system displaying Michaelis-Menten kinetics (Kt=18.0±2.1 μM;J maxmc =0.50±0.06 nm/g min) and an apparent low-affinity mechanism that had a transfer rate which was a linear function of luminal lysine concentration. The latter system cannot be conclusively distinguished from simple diffusion at this time.
-
3)
The high-affinity process was sodium-dependent (lithium adequately substituting for sodium) and inhibited by arginine and iodoacetic acid.
-
4)
The apparent low-affinity transport mechanism displayed homoexchange diffusion and was sodium-independent, inhibited by arginine and unaffected by iodoacetic acid.
-
5)
Entry of lysine by either process was unresponsive to NaCN, ouabain and alteration of luminal pH.
-
6)
These results suggest that cationic amino acid influx in crustacean intestine appears similar to processes reported for these solutes from a large variety of cell types. The major difference found for the shrimp gut is the apparent adaptation of the high-affinity carrier process for very low lysine concentrations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahearn, G.A.: Glycine transport by the isolated midgut of the junbo shrimp,Penaeus marginatus. Amer. Zool.13, 1311–1312 (1973)
Ahearn, G.A.: Kinetic characteristics of glycine transport by the isolated midgut of the marine shrimp,Penaeus marginatus. J. exp. Biol.61, 677–696 (1974)
Ahearn, G.A.: Co-transport of glycine and sodium across the mucosal border of the midgut epithelium in the marine shrimp,Penaeus marginatus. J. Physiol.258, 499–520 (1976)
Ahearn, G.A., Maginniss, L.A., Song, Y.K., Tornquist, A.: Intestinal water and ion transport in freshwater malacostracan prawns (Crustacea). In: Water relations in membrane transport in animals and plants (eds. A.M. Jungreis, T. Hodges, A.M. Kleinzeller, S.G. Schultz), pp. 129–142. New York: Academic Press 1977
Akedo, H., Christensen, H.N.: Transfer of amino acids across the intestine: a new model amino acid. J. biol. Chem.237, 113–117 (1962)
Ausiello, D.A., Segal, S., Thier, S.O.: Cellular accumulation of L-lysine in rat kidney cortex in vivo. Amer. J. Physiol.222, 1473–1478 (1972)
Balazs, G.H., Ross, E., Brooks, C.C.: Preliminary studies on the preparation and feeding of crustacean diets. Aquaculture2, 369–377 (1972)
Battistin, L., Piccoli, P., Lajtha, A.: Heteroexchange of amino acids in incubated slices of brain. Arch. Biochem. Biophys.151, 102–111 (1972)
Brick, R.W.: Transport of lysine across the intestine of the freshwater prawn,Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Ph.D. dissertation, University of Hawaii 1975
Brick, R.W.: Epithelial transport of lysine in the prawnMacrobrachium rosenbergii. Amer. Zool.16, 225 (1967)
Christensen, H.N.: Some observations from amino acid transport. In: Role of membranes in secretory processes (eds. L. Bolis, R.R. Keynes, W. Wilbrandt), pp. 433–447. New York: American Elsevier Publ. 1971
Christensen, H.N.: Biological transport. Reading, Massachusetts: Benjamin, Inc. 1975
Christensen, H.N., Liang, M.: On the nature of the “non-saturable” migration of amino acids into Ehrlich cells and into rat jejunum. Biochem. Biophys. Acta.112, 524–531 (1966)
Crawford, R.L., Hampton, J.R.: Further characterization of lysine uptake byTrypanosoma cruzi. Int. J. Biochem.3, 145–150 (1972)
Crogan, P.C.: The mechanism of osmotic regulation inArtemia salina (L.): The physiology of the gut. J. exp. Biol.35, 243–249 (1958)
Dall, W.: Studies on the physiology of a shrimp,Metapenaeus sp. (Crustacea: Decapoda: Penaeidae). Aust. J. Mar. Freshwater Res.16, 181–203 (1965)
Dall, W.: The functional anatomy of the digestive tract of a shrimpMetapenaeus bennettae Racek & Dall (Crustacea: Decapoda: Penaeidae). Aust. J. Zool.15, 699–714 (1967)
Eposito, G., Czaky, T.Z.: Extracellular space in the epithelium of rat's small intestine. Amer. J. Physiol.226, 50–65 (1974)
Florkin, M.: Ecology and metabolism. In: The physiology of crustacea, Vol. 1 (ed. T. Waterman), pp. 395–410. New York: Academic Press 1960
Frederick, P.K., Reiser, S., Christiansen, P.A.: Effect of inhibitors on Na+-independent lysine transport in intact intestine. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol.142, 988–992 (1973)
Gillespie, E.: Homo- and hetero-exchange diffusion of amino acids in Ehrlich ascites carcinoma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Acta135, 1016–1029 (1967)
Gross, W., Burkhardt, K.L.: Multiple transportation systems for basic amino acids inStreptomyces hydrogenans. Biochem. Biophys. Acta298, 437–445 (1973)
Hajjar, J.J., Khuri, R.N., Bizri, H.: Lysine transport in turtle ventricle. I. Effect of ouabain and extracellular ions on lysine accumulation. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.46, 45–56 (1973a)
Hajjar, J.J., Khuri, R.N., Bizri, J.: Lysine transport in turtle ventricle. II. Effect of extracellular ions and ouabain on lysine fluxes. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.46, 57–64 (1973b)
Hampton, J.R.: Lysine transport in the form ofTrypanosoma cruzi: kinetics and inhibition of uptake by structural analogues. Int. J. Biochem.1, 706–714 (1970)
Herzberg, G.R., Lerner, J.: The effect of preloaded amino acids on lysine and homoarginine transport in chicken small intestine. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.44, 1–16 (1973)
Herzberg, G.R., Sheerin, H., Lerner, J.: Catronic amino acid transport in chicken small intestine. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.40, 229–247 (1971)
Jeuniaux, C.: Hemolymph —Arthropoda. In: Chemical zoology, Vol. VI (Part B) (eds. M. Florkin, B.T. Scheer), pp. 64–118. New York: Academic Press 1971
Jungreis, A.M.: Comparative aspects of invertebrate epithelial transport. In: Water relations in membrane transport in animals and plants (eds. A.M. Jungleis, T. Hodges, A.M. Kleinzeller, S.G. Schultz), pp. 89–96. New York: Academic Press 1977
Jungreis, A.M., Vaughan, G.L.: Insensitivity of lepidopteran tissues to ouabain. I. Absence of ouabain binding and Na-K ATPase in larval and adult midgut. J. Insect Physiol.23, 503–509 (1977)
Lineweaver, H., Burk, D.: The determination of enzyme dissociation constants. J. Amer. Chem. Soc.56, 658–666 (1934)
Maginniss, L.A., Ahearn, G.A.: Kinetics of glucose transport by the perfused midgut of the freshwater shrimp,Macrobrachium rosenbergii. J. Physiol.271, 319–336 (1977)
Mantel, L.H.: The foregut ofGecarcinus lateralis as an organ of salt and water balance. Amer. Zool.8, 434–442 (1968)
Maynard, L.A., Loosli, J.K.: Animal nutrition. New York: McGraw-Hill Co. 1969
McIver, D.J.L., Macknight, A.D.C.: Extracellular space in some isolated tissues. J. Physiol.239, 31–59 (1974)
Munck,, B.G., Schultz, S.G.: Lysine transport across isolated rabbit ileum. J. gen. Physiol.53, 157–182 (1969)
Parsons, D.S., Prichard, J.S.: Properties of some model systems for transcellular active transport. Biochem. Biophys. Acta126, 471–486 (1966)
Peterson, S.C., Goldner, A.M., Curran, P.F.: Glycine transport in rabbit ileum. Amer. J. Physiol.219, 1027–1032 (1970)
Prosser, C.L. (ed.): Comparative Animal Physiology. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Co. 1973
Reiser, S., Christiansen, P.A.: Stimulation of basic amino acid uptake by certain neutral amino acids in isolated intestinal epithelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Acta241, 102–113 (1971)
Reiser, S., Christiansen, P.A.: A basis for the difference in the inhibition of the uptake of various neutral amino acids by lysine in intestinal epithelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Acta226, 217–229 (1972)
Reiser, S., Christiansen, P.A.: The properties of Na+-dependent and Na+-independent lysine uptake by isolated intestinal epithelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Acta307, 212–222 (1973a)
Reiser, S., Christiansen, P.A.: Exchange transport and amino acid charge as the basis for Na+-independent lysine uptake by isolated intestinal epithelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Acta307, 223–233 (1973b)
Schultz, S.G., Curran, P.F.: Coupled transport of sodium and organic solutes. Physiol. Rev.50, 637–718 (1970)
Smith, P.G.: The ionic relations ofArtemia salina (L.). II. Fluxes of sodium, chloride, and water. J. exp. Biol.51, 739–757 (1969)
Southworth, G.C., Read, C.P.: Absorption of some amino acids by the haemoflagellate,Trypanosoma gambiense. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.41A, 905–911 (1972)
Speck, U., Urich, K.: Das Schicksal der Nährstoffe bei dem FlußkrebsOrcomectes limosus. II. Resorption U-14C-markierter Nährstoffe und ihre Verteilung auf die Organe. Z. vergl. Physiol.68, 318–333 (1970)
Thier, S.O.: Amino acid accumulation in the toad bladder. Relationship to transepithelial Na transport. Biochem. Biophys. Acta150, 253–262 (1968)
Thomas, E.L., Shao, T.C., Christensen, H.N.: Structural selectivity in interaction of neutral amino acids and alkali metal ions with a cationic amino acid transport system. J. biol. Chem.246, 1677–1681 (1971)
Vaughan, G.L., Jungreis, A.M.: Insensitivity of lepidopterous tissues to ouabain. Physiological mechanisms which block inhibition of ouabain in ouabain-sensitive tissues. J. Insect Physiol.23, (In press, 1977)
Vonk, H.J.: Digestion and metabolism. In: The physiology of crustacea, Vol. 1 (ed. T.H. Waterman), pp. 291–316. New York: Academic Press 1960
Weel, P.B. van: Processes of secretion, restitution and resorption in gland of mid-gut (glandula media intestini) ofAtya spinipes (Decapoda-Brachyura). Physiol. Zool.28, 40–54 (1955)
Yonge, C.M.: Studies on the comparative physiology of digestion. II. The mechanism of feeding, digestion and assimilation inNephrops norvegicus. J. exp. Biol.1, 343–390 (1924)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Contribution No. 539 from the Hawaii Institute of Marine Biology, Kaneohe, Hawaii
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brick, R.W., Ahearn, G.A. Lysine transport across the mucosal border of the perfused midgut in the freshwater shrimp,Macrobrachium rosenbergii . J Comp Physiol B 124, 169–179 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00689178
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00689178