Summary
The haemodynamic effects of a standard meal were assessed in a balanced cross-over study in eight normal fasting subjects, investigated under conditions applicable to many drug tests.
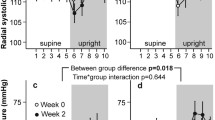
Both the supine and erect diastolic blood pressure were reduced on average by 10 mmHg over the 4 h following the meal.
The supine systolic pressure was increased on average by 2 mmHg, a difference of no biological relevance. Erect systolic blood pressure was not affected by eating.
Supine heart rate was slightly but significantly increased, but the erect heart rate did not change.
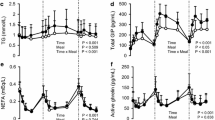
Postprandial plasma renin activity was increased. Venous plasma noradrenaline levels in the supine position were not affected by eating and after standing erect, and immobile for 5 min they were only slightly and not-significantly increased.
A food-induced vasodepressor response combined with baroreceptor resetting is considered to have occurred in this population. The changes had a gradual onset, reaching their maximum about 2 h after eating and they were still evident after 3 h. Eating should be considered as an important potential source of bias in cardiovascular studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Packer M, Medina N, Yushak M (1985) Hemodynamic changes mimicking a vasodilator drug response in the absence of drug therapy after right heart catheterization in patients with chronic heart failure. Circulation 71: 761–766
Cornyn JW, Massie BM, Unverferth DV, Leier CV (1986) Hemodynamic changes after meals and placebo treatment in chronic congestive heart failure. Am J Cardiol 57: 238–241
Grollman A (1929) The effect of ingestion of food on cardiac output, pulse rat, blood pressure and oxygen consumption in man. Am J Physiol 89: 366–370
Gladstone SA (1935) Cardiac output and renal functions under basal and post-prandial conditions. Arch Intern Med 55: 553–546
Abramson DI, Fierst SM (1941) Peripheral vascular responses in man during digestion. Am J Physiol 133: 686–693
Bagatell MS, Heymsfield SB (1984) Effect of meal size on myocardial oxygen requirements: implications for post-myocardial infarction diet. Am J Clin Nutr 39: 321–426
Fagan TC, Sawyer PR, Gourley LA, Lee JT, Gaffney TE (1986) Postprandial alterations in hemodynamics and blood pressure in normal subjects. Am J Cardiol 58: 636–641
Burgess CD, Crane J (1986) The comparative effects of digoxin and food alone and in combination in normal males. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 29: 685–689
Fagan TC, Conrad KA, Mar JH, Nelson L (1986) Effects of meals on hemodynamics: implications for antihypertensive drug studies. Clin Pharmacol Ther 39: 255–260
Herrick JF, Essex HE, Mann FC, Baldes EJ (1934) The effect of digestion on the blood flow in certain blood vessels of the dog. Am J Physiol 108: 621–628
Orrego H, Mena I, Baraona E, Palma R (1965) Modifications in hepatic blood flow and portal pressure produced by different diets. Am J Dig Dis 10: 239–248
Brandt JL, Castleman L, Ruskin HD, Greenwald JJ, Kelly J (1965) The effect of oral protein and glucose feeding on splanchnic blood flow and oxygen utilization in normal and cirrhotic subjects. J Clin Invest 34: 1017–1025
Norryd C, Denker H, Lunderquist A, Olin T, Tylen U (1975) Superior mesenteric blood flow during digestion in man. Acta Chir Scand 141: 197–202
Marigold JH, Gilmore IT, Thompson RPH (1981) Effects of a meal on plasma clearance of C14-glycocholic acid and indo cyanine green in man. Clin Sci 61: 325–330
Svensson CK, Edwards DJ, Mauriello PM, Barde SH, Foster AC, Lanc RA, Middleton E, Lalka D (1983) Effect of food on hepatic blood flow: implications in the “food effect” phenomenon. Clin Pharmacol Ther 34: 316–323
Ren J, Leithe M, Huss P, Unverferth D, Leier C (1983) The effects of ibopamine on cardiovascular and renal function in normal subjects. Curr Ther Res 34: 667–675
Eckberg DL (1980) Parasympathetic cardiovascular control in human disease: a critical review of methods and results. Am J Physiol 239: H581-H593
de Mey C, Enterling D (1986) Assessment of the hemodynamic response to single passive head up tilt by non-invasive methods in normotensive subjects. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 8: 449–457
de Mey H, Enterling D (1986) Variant responses to passive upright tilt. Lancet 2: 221
Spodick DH, Lance VQ (1977) Comparative orthostatic responses: standing vs head-up tilt. Aviat Space Environ Med 48: 432–433
Hines S, Houston M, Robertson D (1981) The clinical spectrum of autonomic dysfunction. Am J Med 70: 1091–1096
Lipsitz LA, Nyquist RP, Wei JY, Rowe JW (1983) Postprandial reduction in blood pressure in the elderly. N Engl J Med 309: 81–83
Robertson D, Wade D, Roberston RM (1981) Postprandial alterations in cardiovascular hemodynamics in autonomic dysfunctional states. Am J Cardiol 48: 1048–1052
Turnbull CJ, Palmer KT, Taylor BB (1981) Autonomic failure with postprandial hypotension. NZ Med J 93: 6–8
Brandenberger G, Follenius M, Muzet A, Ehrhart J, Schieber JP (1985) Ultradian oscillations in plasma renin activity: their relationships to meals and sleep stages. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 61: 280–284
Angeras U, Farnebo LO, Graffner H, Hamberger B, Uvnas-Moberg K, Jarhult J (1982) Effects of food on plasma catecholamine and gastrin levels in patients with duodenal ulcer and normal volunteers. Digestion 25: 205–210
Knoll E, Mueller FW, Ratge D, Bauersfeld W, Wisser H (1984) Influence of food intake on concentrations of plasma catecholamines and cortisol. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem 22: 597–602
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Mey, C., Enterling, D., Brendel, E. et al. Postprandial changes in supine and erect heart rate, systemic blood pressure and plasma noradrenaline and renin activity in normal subjects. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 32, 471–476 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00637672
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00637672