Summary
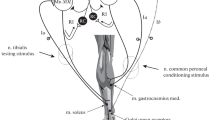
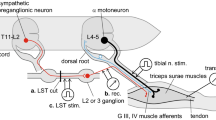
The response of identified gastrocnemius γ-efferents to stretch of the triceps surae muscle was recorded in the acute spinal cat before and after the injection of Dopa. A strong tonic inhibition during static muscle extension was detectable only in those γ-efferents which had no resting and reflex activity in the spinal cat, but which responded to Dopa injection with an initially high discharge rate. In contrast γ-motoneurons with background and reflex activity before Dopa, and some previously quiescent units acquiring a low discharge rate after Dopa did not exhibit any signs of a stretch-dependent inhibition. It is concluded that the observed autogenetic inhibition is limited to the static γ-motoneurons. The responsiveness to stretch-evoked inhibition was found to be correlated with that to antidromic inhibition induced by repetitive stimulation of the ventral root. This could imply that the activation of α-motoneurons by muscle stretch leads to a Renshaw inhibition of the γ-motoneurons. However, this pathway may be only partly responsible for the autogenetic inhibition of γ-motoneurons in the spinal cat after Dopa, since the inhibitory effects of muscle stretch were more pronounced than those obtained by antidromic activation of α motor axons in the ventral root.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alnaes, E., Jansen, J. K. S., Rudjord, T.: Fusimotor activity in the spinal cat. Acta physiol. scand.63, 197–212 (1965)
Andén, N.-E., Jukes, M. G. M., Lundberg, A., Vyklicky, L.: The effect of Dopa on the spinal cord. 1. Influence on transmission from primary afferents. Acta physiol. scand.67, 373–386 (1966)
Appelberg, B., Bessou, P., Laporte, Y.: Action of static and dynamic fusimotor fibres on secondary endings of cat's spindles. J. Physiol. (Lond.)185, 160–171 (1966)
Bergmans, J., Grillner, S.: Changes in dynamic sensitivity of primary endings of muscle spindle afferents induced by Dopa. Acta physiol. scand.74, 629–636 (1968)
Bergmans, J., Grillner, S.: Reciprocal control of spontaneous activity and reflex effects in static and dynamic flexor γ-motoneurones revealed by an injection of Dopa. Acta physiol. scand.77, 106–124 (1969)
Brown, M. C., Lawrence, D. G., Matthews, P. B. C.: Reflex inhibition by I a afferent input of spontaneously discharging motoneurones in the decerebrate cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.)198, 5–7P (1968)
Brown, M. C., Lawrence, D. G., Matthews, P. B. C.: Static fusimotor fibres and the position sensitivity of muscle spindle receptors. Brain Res.14, 173–187 (1969)
Ellaway, P. H.: Recurrent inhibition of fusimotor neurones exhibiting background discharges in the decrebrate and the spinal cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.)216, 419–439 (1971)
Fromm, Chr., Haase, J., Noth, J.: Length-dependent autogenetic inhibition of extensor γ-motoneurones in the decerebrate cat. Pflügers Arch.346, 251–262 (1974)
Grillner, S.: The influence of Dopa on the static and the dynamic fusimotor activity to the triceps surae of the spinal cat. Acta physiol. scand.77, 490–509 (1969a)
Grillner, S.: Supraspinal and segmental control of static and dynamic γ-motoneurones in the cat. Acta physiol. scand., Suppl.327, 1–34 (1969b)
Grillner, S., Hongo, T., Lund, S.: Descending monosynaptic and reflex control of γ-motoneurones. Acta physiol. scand.75, 592–613 (1969)
Grillner, S., Hongo, T., Lundberg, A.: The effect of Dopa on the spinal cord. 7. Reflex activation of static γ-motoneurones from the flexor reflex afferents. Acta physiol. scand.70, 403–411 (1967)
Hunt, C. C.: The reflex activity of mammalian small-nerve fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond.)115, 456–469 (1951)
Hunt, C. C.: Drug effects on mammalian muscle spindles. Fed. Proc.11, 75 (1952)
Hunt, C. C., Paintal, A. S.: Spinal reflex regulation of fusimotor neurones. J. Physiol. (Lond.)143, 195–212 (1958)
Jansen, J. K. S., Matthews, P. B. C.: The central control of the dynamic response of muscle spindle receptors. J. Physiol. (Lond.)161, 357–378 (1962a)
Jansen, J. K. S., Matthews, P. B. C.: The effect of fusimotor activity on the static responsiveness of primary and secondary endings of muscle spindles in the decerebrate cat. Acta physiol. scand.55, 376–386 (1962b)
Liddell, E. G. T., Sherrington, C. S.: Reflexes in response to stretch. Proc. roy. Soc. B96, 212–242 (1924)
Matthews, P. B. C.: The differentiation of two types of fusimotor fibre by their effects on the dynamic response of muscle spindle primary endings. Quart. J. exp. Physiol.47, 324–333 (1962)
Noth, J.: Recurrente Hemmung der Extensor-Fusimotoneurone? Pflügers Arch.329, 23–33 (1971)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fromm, C., Noth, J. Autogenetic inhibition of γ-motoneurons in the spinal cat uncovered by Dopa injection. Pflugers Arch. 349, 247–256 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00592452
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00592452