Summary
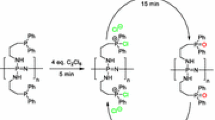
A new methodology is described for the synthesis of reactive polymers bearing triphenylphosphine dichloride groups by the use of triphosgene. These materials show high reactivity for the room temperature conversion of benzyl alcohol to benzyl chloride. In one hour, yields higher than 90% were achieved using reactive copolymers with up to 25 w% divinylbenzene (DVB). The functional groups can be easily and efficiently regenerated using 1.0 mol of triphosgene for every 2.6 moles of phosphine in the polymer. Preliminary results showed up to 40% conversion of benzyl alcohol in column reactions using regenerated polymers at 5 to 10 min contact times.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hodge P, Sherrington DC (1980) Polymer-supported reactions in organic synthesis. Wiley, London.
Mathur NK, Narang CK, Williams RE (1980) Polymers as aids in organic chemistry. Academic Press, New York.
Hodge P, Sherrington DC (1988) Synthesis and separations using functional polymers. Wiley, Chichester (West Sussex) New York.
Akelah A, Moet A (1990) Functionalized polymers and their applications. Chapman and Hall, London New York Tokyo Melbourne.
Frechet JMJ, Amaratunga W, Halgas J (1982) Nouv. J. Chim. 6:609
Ford WT (1986) ACS Symp. Ser. 308:155
Horner L, Oediger H, Hoffmann H (1959) Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. 626:26
Sherrington DC, Craig, DJ, Dagleish J, Domin G, Taylor J (1977) Eur. Polym. J. 13:73
Harrison CR, Hodge P, Hunt BJ, Khoshdel E, Richardson G (1983) J. Org. Chem. 48:3721.
Harrison CR, Hodge P, Rogers WJ (1977) Synthesis 41.
Appel R, Willms L (1976) Tetrahedron Lett. 12:905
Appel R, Willms L (1977) Chem. Ber. 110:3209
Relles HM, Schluenz RW (1974) J. Am. Chem. Soc. 96:6469
Rabinowitz R, Marcus R (1961). J. Org Chem. 26:4157
Rivero IA, Somanathan R, Hellberg LH (1993) Synth. Comm. 23:711
Rabinowitz R, Marcus R, Pellon J (1964). J. Polym. Sci. A-2: 1241
Brandrup J, Immergut EH (1989) Polymer handbook. Wiley-Interscience, New York Chichester Brisbane Toronto Singapore.
Bernard M, Ford WT (1983). J. Org. Chem. 48:326
Appel R, Willms L (1981) Chem. Ber. 114:858
Bergbreiter DE (1986) ACS Symp. Ser. 308:17
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Licea-Claveríe, A., Rivero, I.A. & García, B.L. Synthesis and regeneration of reactive polymers bearing triphenylphosphine dichloride functional groups using triphosgene. Polymer Bulletin 37, 415–421 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00556799
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00556799