Summary
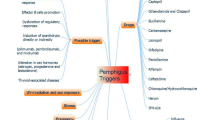
The reports on induced pemphigus have multiplied over the last 10 years. Several heterogeneous factors, such as drugs (penicillamine, pyritinol, captopril, rifampicin, etc.), physical agents (burns, UV, and ionizing radiation) and viruses, can play an inducing role. Usually, the disease in preceded by prodromal, non-specific lesions. The full-blown stage shows features of pemphigus foliaceus, erythematosus or herpetiformis. Histologically, acantholytic splits mostly occur at the highest malpighian layers. Intercellular antibodies and frequently concomitant other auto-antibodies are found in the serum, the titre of the former usually being low and unrelated to the severity or course of the disease.
The biological progress is variable and ranges from rapidly and definitively healing cases (induced pemphigus proper) to others which, in spite of the elimination of the inducing factor, self-perpetuate just like true pemphigus (triggered pemphigus). Pathogenic hypotheses are based on the fact that some inducing factors can alter the antigen distribution on keratinocyte membranes and/or interfere with immune surveillance by impairing T-suppressor cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alinovi A, Benoldi D, Manganelli P (1982) Pemphigus erythematosus induced by thiopronine. Acta Derm Venerol (Stockh) (in press)
Amos HE, Brigden WD, McKerron RA (1975) Untoward effects associated with practolol: demonstration of antibody binding to epithelial tissue. Br Med J I:598–600
Asboe-Hansen G (1975) Treatment of generalized scleroderma with inhibitors of connective tissue formation. Acta Derm Venerol (Stockh) 55:461–465
Benveniste M, Crouzet J, Homberg JC, Lessana M, Camus JP, Hewitt J (1975) Pemphigus induits par la d-pénicillamine dans la polyarthrite rhumatoïde. Nouv Presse Med 4:3125–3128
Berger BW (1973) Pemphigus foliaceus occurring in a roofer. J Occup Med 15:742–743
Beutner EH, Chorzelski TP (1976) Studies on etiologic factors in pemphigus. J Cutan Pathol 3:67–74
Beutner EH, Jordon RE, Chorzelski TP (1968) The immunopathology of pemphigus and bullous pemphigoid. J Invest Dermatol 51:63–80
Beutner EH, Chorzelski TP, Jordon RE (1970) Autosensitization in pemphigus and bullous pemphigoid. Charles C Thomas, Springfield, Ill
Blanchet P, Auffret N, Fouchard J, Lesavre P, Durupt G, Civatte J (1981) Association thymome, pemphigus superficiel, syndrome néphrotique et biologie lupique. Ann Dermatol Venereol 108:471–472
Böhm G, Holzmann H (1978) d-Penicillamin-induzierter Pemphigus erythematosus. Aktuel Dermatol 4:41–46
Boni P (1981) Infezione da virus citomegalico (review). Fed Med 34:278
Bonnetblanc JM, Roux J (1979) Bêtabloquants et peau. Ann Dermatol Venerol 106:927–930
Brigden WD, Almeyda J (1976) Adverse reaction to the β-adrenergic blocking drugs. Br J Dermatol 95:335–338
Bruns GR, Ablin RJ, Guinan PD (1978) Serum immunoglobulin E in pemphigus. J Invest Dermatol 95:335–338
Bruns GR, Ablin RJ, Guinan PD (1978) Serum immunoglobulin E in pemphigus. J Invest Dermatol 71:217–218
Caccialanza P, Bellone AG (1951) Tentativi di terapia penicillinica a dosi molto elevate in alcune dermatosi ad etiologia sconosciuta. G Ital Dermatol Sif 92:35–48
Cairns RJ (1976) Penicillamine-induced pemphigus. Proc R Soc Lond [Biol] 69:384
Camus JP, Crouzet J, Bach JF, Homberg JC (1976) Autoantibodies in d-Penicillamine treated rheumatoid arthritis. Agents Actions 6:351–354
Castro RM, Chorzelski TP, Jablonska S, Marquart A (1976) Antiepithelial antibodies in healthy people living in an endemic area of South American pemphigus foliaceus (fogo selvagem). Castellania 4:111–112
Chang GM, Deng JS, Lu YC (1973) Pemphigus vulgaris, a skin manifestation of epidermoid carcinoma. J Formosan Med Assoc 71:50
Chen DM, Di Sabato G, Field L, Gallo AA, Harshman S (1977) Some immunological effects of penicillamine. Clin Exp Immunol 30:317–322
Chinn RH, et al. (1978) mentioned in: Pemfigo foliaceo indotto da penicillamina. (Editorial) Stampa Medica, April I, 3. San Donato Milanese, Italy
Chorzelski TP (1974) Clinical aspects of the pathogenicity of pemphigus antibodies. In: Flarer F, Serri F, Cotton DWK (eds) Dermatology Proc XIV Int Cong Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam, pp 77–79
Chorzelski TP, Jablonska S, Blaszczyk M (1966) Autoantibodies in pemphigus. Acta Derm Venerol (Stockh) [Suppl] 46:26
Chorzelski TP, Jablonska S, Beutner EH, Kowalska M (1971) Can pemphigus be provoked by a burn? Br J Dermatol 85:320–325
Chorzelski TP, Beutner EH, Jablonska S (1979) Clinical significance of pemphigus antibodies. In: Beutner EH, Chorzelski TP, Bean SF (eds) Immunopathology of the skin. John Wiley & Sons, New York, pp 183–196
Chouvet B, Thivolet J, Bathias J, Forestier JY (1980) Pemphigus induit par la d-pénicillamine. Dermatologica 160:297–310
Christoph R, Genth E, Grussendorf EI, Hartl PW (1978) Pemphigus — Syndrom bei d-Penicillaminbehandelter rheumatoider Arthritis. Med Welt 29:1761–1763
Civatte J, Duterque M, Blanchet P, Belaïch S, Lazarovici C, Morel P, Foix C, Fischesser D (1978) Deux cas de pemphigus superficiel induit par le pyritinol. Ann Dermatol Venerol Venerol 105:573–577
Colliard H, Saurat JH (1976) Pemphigus induit pat la pénicillamine. Revue Stomat 77:741–746
Cram DL (1973) Photo-induction of lesions in patients with pemphigus and bullous pemphigoid. In: Beutner EH, Chorzelski TP, Bean SF, Jordon RE (eds) Immunopathology of the skin: labeled antibody studies. Dowden Hutchinson & Ross, Stroudsburg, Pa, pp 44–54
Cram DL, Fukuyama K (1972) Immunohistochemistry of ultraviolet-induced pemphigus and pemphigoid lesions. Arch Dermatol 106:819–824
Cram DL, Winkelmann RK (1965) Ultraviolet-induced acantholysis in pemphigus. Arch Dermatol 92:7–13
Danno K, Horio T (1980) Histochemical staining of sunburn cells for sulphhydryl and disulphide groups: a time course study. Br J Dermatol 102:535–539
David M, Zamir R, Segal R, Gazit E, Feuerman EJ (1981) HLA antigens in Jews with pemphigus vulgaris. Dermatologica 163:326–330
Davies MG, Holt P (1976) Pemphigus in a patient treated with penicillamine for generalized morphea. Arch Dermatol 112:1308–1309
Degos R, Touraine R, Belaïch S Revuz J (1969) Pemphigus chez un malade traité par pénicillamine pour maladie de Wilson. Bull Soc Fr Dermatol Syphiligr 76:751–753
De Jong MCJM, Doeglas HMG, Dijkstra JWE (1980) Immunohistochemical findings in a patient with penicillamine pemphigus. Br J Dermatol 102:333–337
Demento FJ, Grover RW (1973) Acantholytic herpetiform dermatitis. Arch Dermatol 107:883–887
De Moragas JM, Winkelmann RK, Jordon RE (1970) Immunofluorescence of epithelial skin tumors. I. Patterns of intercellular substance. Cancer 25:1399–1403
Duperrat B, Saurat JH, Bonnetblanc JM, Puissant A, Horay P, Colliard H (1975) Pemphigus et pénicillamine. Bull Soc Fr Dermatol Syphiligr 82:242–243
From E, Frederikson P (1976) Pemphigus vulgaris following d-penicillamine. Dermatologica 152:358–362
Frosch PJ, Kligman AM (1977) Rapid blister formation in human skin with ammonium hydroxide. Br J Dermatol 96:461–473
Gange RW, Rhodes EL, Edwards CO, Powell MEA (1976) Pemphigus induced by rifampicin. Br J Dermatol 95:445–448
Garcovich A (1980) Riacutizzazione di pemfigo volgare indotto da rifampicina. Communication at “Riunione della Sezione Centro-Sud Sicilia e Sardegna della Sides”. Sorrento, October 18–19
Godard W, Lambert D, Gavanou J, Chapuis JL (1980) Pemphigus induit après traitement par l'association propanolol-méprobamate. Ann Dermatol Venereol 107:1213–1216
Grupper C, Bermejo D, Durepaire R, Berretti B (1977) Pemphigus seborrheique de Senear Usher compliquant un psoriasis. Role aggravant de la PUVA-therapie. communication à la Soc Fr Derm Syph. Paris, Mars
Gschnait F, Pehamberger H, Holubar K (1978) Pemphigus acantholysis in tissue culture: studies on photoinduction. Acta Derm Venerol (Stockh) 58:237–239
Hay KD, Muller HK, Reade PC (1978) d-Penicillamine-induced mucocutaneous lesions with features of pemphigus. Oral Surg 45:385–395
Hewitt & Homberg (1977) mentioned by Sayag J, Weiller C (1979) in: Le pemphigus. Encycl Méd Chir, Paris, Dermatologie 12460 A10, 10-1979, pp 1–14
Hewitt J, Lessana-Leibowitch M, Benveniste M, Saporta L (1971) Un cas de pemphigus induit par la d-pénicillamine. Le pemphigus iatrogène existe-t-il? Ann Med Interne 122:1003–1009
Hofmann F, Cainelli T (1962) Pemfigo, gravidanza e terapia corticosteroidea. G Ital Dermatol Sif 75:193–198
Honeyman JF, Eguiguren G, Pinto A, Honeyman AR, de La Parra MA, Navarrete W (1981) Bullous dermatoses of pregnancy. Arch Dermatol 117:264–267
Jordon RE (1980) Immunopathology, pp 399–400. In: Ahmed AR (moderator) Pemphigus: current concepts. Ann Intern Med 92:396–405
Keilhauer A, Grussendorf EI (1980) d-Penicillamin-induzierter Pemphigus seborrhoicus sive erythematosus (Senear-Usher). Z Hautkr 55:948–951
Kennedy C, Hodge L, Sanderson KV (1978) Skin changes caused by d-penicillamine treatment of arthritis. Report of three cases with immunological findings. Clin Exp Dermatol 3:107–116
Kolarz G, Ludwig H, Sabeti M, Scherak O (1975) Autoimmunologische Phänomene unter d-Penicillamine-Therapie. Acta Med Austriaca 2:130–133
Krain LS (1974) Pemphigus: epidemiologic and survival characteristics of 59 patients, 1955–1973. Arch Dermatol 110:862–865
Kristensen JK, Wadskov S (1977) Penicillamine-induced pemphigus foliaceus. Acta Derm Venereol (Stockh) 57:69–71
Kudejko J, Buczkowska J, Trzebuchowska T (1973) Pemphigus erythematosus confined to the postburn scar. Dermatologica 147:174–178
Lagerholm B, Frithz A, Borglund E (1979) Light and electron microscopic aspects of pemphigus herpetiformis (eosinophilic spongiosis) In comparison with other acantholytic disorders. Acta Derm Venereol (Stockh) 59:305–314
Leoni A (1979) Probabile effetto inducente della rifampicina su pemfigosi trattati con corticosteroidi. Minerva Dermatol 114:459–460
Lunder M (1973) Una rara combinazione del pemfigo con cancro della mammella. Minerva Dermatol 108:576–577
Lynfield YL, Pertschuk LP, Zimmerman A (1973) Pemphigus erythematosus provoked by allergic contact dermatitis. Arch Dermatol 108:690–693
Malkinson FD, Pearson RW (1978) The year book of dermatology: 1978 (editors' footnote, p 233). Year Book Med, Chicago
Marsden RA, Ryan TJ, Van Hegan RI, Walshe M, Hill H, Mowat AG (1976) Pemphigus foliaceus induced by penicillamine. Br Med J IV:1423–1424
Marsden RA, Dawber RPR, Millard PR, Mowat AG (1977) Herpetiform pemphigus induced by penicillamine. Br J Dermatol 97:451–452
Matkaluk RM, Bailin PL (1981) Penicillamine-induced pemphigus foliaceus. A fatal outcome. Arch Dermatol 117:156–157
Miehlke K (1977) Basistherapie der chronischen Polyarthritis mit d-Penicillamin. In: von Kreysel H (ed) d-Penicillamin. Schattauer, Stuttgart
Noguchi S, Nishitani H (1976) Immunologic studies of a case of myasthenia gravis associated with pemphigus vulgaris after thymomectomy. Neurology 26:1075–1080
Ogawa H, Taneda A (1979) Characteristic distribution of sulfhydryl groups in human epidermal cancer by the new histochemical staining method. Arch Dermatol Res 264:77–81
Ogawa H, Tanada A, Morioka S (1978) Characterization of pemphigus antigen. J Invest Dermatol 70:194–196
Ogura R, Knox J (1964) Effect of ultraviolet light on the sulfhydryl and disulfide concentration in living human epidermis. Dermatologica 128:377–383
Parfrey PS, Clement M, Vandenburg MJ, Wright P (1980) Captopril-induced pemphigus. Br Med J 281:194
Park MS, Terasaki PI, Ahmed AR, Tiwari JL (1979) HLA-DRw4 in 91% of Jewish pemphigus vulgaris patients. Lancet II:441–442
Peck SM, Osserman KE, Rule AH (1972) Intercellular antibodies: presence in a trichophyton rubrum infection. J Invest Dermatol 58:133–138
Perrot H, Thivolet J, Hermier C (1974) Pemphigus à type de spongiose éosinophile associé à un cancer du poumon. Bull Soc Fr Dermatol Syphiligr 81:103–106
Rollet M (1977) Contribution à l'étude du pemphigus à spongiose éosinophile; à propos d'une observation. Thèse, Faculté de Médecine, Paris
Ruocco V (1980) Acantholytic cells: nullear changes and pemphigus autoantibodies. In: Cytodiagnosis in Dermatology CLU, Naples, pp 100–105
Ruocco V, Rossi A, Alviggi L, Catalano G (1977) Patomorfosi del pemfigo in primigravida. Minerva Derm 112:13–18
Ruocco V, Rossi A, Argenziano G, Astarita C, Alviggi L, Farzati B, Papaleo G (1978) Pathogenicity of the intercellular antibodies of pemphigus and their periodic removal from the circulation by plasmapheresis. Br J Dermatol 98:237–241
Ruocco V, Pisani M, Astarita C, Prota G (1979a) d(-)penicillamine and pemphigus: pathogenic hypothesis. Ann Ital Derm Clin Sper 33:3–9
Ruocco V, Rossi A, Pisani M, Astarita C, Alviggi L (1979b) An abortive form of pemphigus vulgaris probably induced by penicillin. Dermatologica 159:266–273
Ruocco V, Vitale O, Astarita C (1980) Transient pemphigus induced by sunburn. J Cutan Pathol 7:429–430
Ruocco V, de Luca M, Pisani M, de Angelis E, Vitale O, Astarita C (1982) Pemphigus provoked by d(-)penicillamine. An experimental approach using in vitro tissue cultures. Dermatologica 164:236–248
Saikia NK (1972) Extraction of pemphigus antibodies from a lymphoid neoplasm and its possible relationship to pemphigus vulgaris. Br J Dermatol 86:411–414
Saikia NK, McConnell LES (1972) Senear-Usher syndrome and internal malignancy. Br J Dermatol 87:1–5
Sakurai M, Takigawa M, Terasaki PI, Imamura S, Sakurami T, Ueno Y, Park MS (1981) Absence of HLA-DRw2 in Japanese pemphigus vulgaris. J Invest Dermatol 76:70–71
Samitz MH, Greenberg MS, Coletti JM (1953) Pemphigus in association with pregnancy. Observations of the effect of ACTH and cortisone on the pemphigus, the pregnancy and the infant. Arch Dermatol 67:10–17
Sayag J, Weiller C (1979) Le pemphigus. Encycl Méd Chir, Paris, Dermatologie 1240 A10, 10-1979, pp 1–14
Sbano E, Andreassi L, Baiocchi R, Fimiani M (1978) Anticorps du pemphigus et cellules épithéliales en culture: effects de la théophylline. In: Progrès en Immunopathologie Cutanée, vol 80. Coll INSERM, Paris, pp 93–100
Scherak O, Kolarz G, Holubar K (1977) Pemphigus erythematosus-like rash in a patient on penicillamine. Br Med J I:838
Schroeter A, Sams WM, Jorden RE (1969) Immunofluorescent studies of pemphigus foliaceus in a child. Arch Dermatol 100:736–740
Schumacher K (1975) Grundlagen der immunosuppressiven Wirkung von d-Penicillamin. Internist 16:460–465
Schumacher K, Maerker-Alzer G, Preuss R (1975a) Effect of d-penicillamine on lymphocyte function. Arzneim Forsch 25:603
Schumacher K, Maerker-Alzer G, Schaaf W (1975b) Influence of d-penicillamine on the immune response of mice. Arzneim Forsch 25:600–602
Schuppli R (1967) Zur Frage der Abgrenzung des Lyell-Syndroms. Hautarzt 18:518–521
Souteyrand P, Perthier-Boachon M, Thivolet J (1981) Association pemphigus et thymome: revue de la littérature et étiopathogénie. Ann Dermatol Venereol 108:457–467
Sparrow GP (1978) Penicillamine pemphigus and the nephrotic syndrome occurring simultaneously. Br J Dermatol 98:103–104
Stanley JR, Hawley-Nelson P, Poirier M, Katz SI, Yuspa SH (1980) Detection of pemphigoid antigen, pemphigus antigen, and keratin filaments by indirect immunofluorescence in cultured human epidermal cells. J Invest Dermatol 75:183–186
Stewart WM (1980) Pemphigus et pemphigoïde. Dermatologica 160:217–235
Stewart WM, Lauret P, Boullie MC, Thomine E, Avenel M (1977) A propos de deux cas d'accidents bulleux, dont un cas de pemphigus, dus a la pénicillamine. Ann Dermatol Venereol 104:542–548
Stoughton RB, Bagatell F (1959) The nature of cantharidin acantholysis. J Invest Dermatol 33:287–292
Szymczyk B, Jarzabek-Chorzelska M, Rzesa G (1975) A case of pemphigus erythematosus after burning. Przegl Dermatol 62:591
Talal N (1977) Immunologic and viral factors in autoimmune diseases. Med Clin North Am 61:205–215
Tan SG, Rowell NR (1976) Pemphigus-like syndrome induced by d-penicillamine. Br J Dermatol 95:99–100
Thorvaldsen J (1979) Two cases of penicillamine-induced pemphigus erythematosus. Dermatologica 159:167–170
Trau H, Schewach-Millet M, Gold I, Feinstein A, Horowitz I, Kaplinsky N (1980) Penicillamine-induced pemphigus. Arch Dermatol 116:721–722
Trunnell TN, Adelman HM, Waisman M (1981) Pemphigus-like eruption due to penicillamine. Cutis 27:402–404
van Joost T, Asghar SS, Cormane RH (1974) Skin reactions caused by phenylbutazone. Arch Dermatol 110:929–933
Vierira JP, Fonzari M, Goldman L (1954) Some recent studies in Brazilian pemphigus. J Trop Med 3:868–872
Weakley DR, Einbinder JM (1962) Enzymes, acantholysis, and pemphigus. Arch Dermatol 85:70–74
Yachiku KK, Takeuchi KT, Sonoda T (1970) Treatment of cystinuria with 2-mercaptopropionylglycine (MPG). Proceedings of the International Symposium on Thiola. Santen Pharm, Osaka, Japan, pp 50–54
Zuccarini N, Fuga GC (1955) Clinica del pemfigo. In: Tommasi L (ed) Dati statistici. II Pemfigo. Minerva Derm [Suppl] 30:354–382
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Guest lecture presented on the occasion of the Primo Corso Superiore di Alta Qualificazione Scientifica e Professionale in Dermatologia (Rome, June 22–26, 1981), directed by Professor F. Serri
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruocco, V., Pisani, M. Induced pemphigus. Arch Dermatol Res 274, 123–140 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00510366
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00510366