Abstract
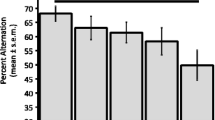
Spontaneous alternation was examined in a free running Y-maze task after various pharmacological manipulations. Whereas scopolamine reduced alternation to chance levels, d-amphetamine in some doses resulted in alternation significantly below chance (perseveration). Physostigmine treatment increased levels of alternation whereas reserpine was without effect. Concurrent administration of drugs revealed that reserpine effectively reversed the effects of scopolamine, while the perseveration induced by d-amphetamine was antagonized by physostigmine. When animals were pre-exposed to the Y-maze the effects of d-amphetamine were enhanced, but effects of scopolamine were not modified. Finally, scopolamine treatment augmented the perseverative effects of d-amphetamine. It was suggested that cholinergic agents modify alternation by effects on habituation. On the other hand d-amphetamine produces genuine perseveration without effects on habituation per se. Alternation performance and perseveration were suggested to be mediated by the interaction between the distinct behavioral effects of cholinergic and catecholaminergic activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adkins, J., Packwood, J. W., Marshall, G. L., Jr.: Spontaneous alternation and d-amphetamine. Psychon. Sci. 17, 167–168 (1969)
Anisman, H.: Time dependent variations in aversively motivated behaviors: Nonassociative effects of cholinergic and catecholaminergic activity. Psychol. Rev. 82, 359–385 (1975a)
Anisman, H.: Dissociation of the disinhibitory effects of scopolamine: effects on activity and habituation. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 3, 613–618 (1975b)
Anisman, H., Cygan, D.: Central effects of scopolamine and d-amphetamine on locomotor activity: Interaction with strain and stress variables. Neuropharmacology 14, 835–840 (1975)
Anisman, H., Kokkinidis, L.: Effects of scopolamine, d0amphetamine and other drugs affecting catecholamines on spontaneous alternation and locomotor activity in mice. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 45, 55–63 (1975)
Arnfred, T., Randrup, A.: Cholinergic mechanism in brain inhibiting amphetamine-induced stereotyped behaviour. Acta pharmacol. (Kbh.) 26, 384–394 (1968)
Bainbridge, J. G.: The inhibitory effect of amphetamine on exploration in mice. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 18, 314–319 (1970)
Bartholini, G., Stadler, H., Lloyd, K. G.: Cholinergic-dopaminergic relation in different brain structures. In: Frontiers in catecholamine research. E. Usdin and S. H. Snyder, eds. New York: Pergamon Press 1973
Bignami, G.: Nonassociative explanations of behavioral changes induced by central cholinergic drugs. Acta neurobiol. exp. (in press 1976)
Carlton, P. L.: Augmentation of the behavioral effects of amphetamine by scopolamine. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 2, 377–380 (1961)
Carlton, P. L.: Cholinergic mechanisms in the control of behavior by the brain. Psychol. Rev. 70, 19–39 (1963)
Carlton, P. L.: Brain-acetylcholine and inhibition. In: Reinforcement and behavior. J. T. Tapp, ed., pp. 286–327. New York: Academic Press 1969
Costall, B., Naylor, R. J., Olley, J. E.: The involvement of the caudate putamen, globus pallidus and substantia nigra with neuroleptic and cholinergic modification of locomotor activity. Neuropharmacology 11, 317–330 (1972)
Douglas, R. J., Isaacson, R. L.: Spontaneous alternation and scopolamine. Psychon. Sci. 4, 283–284 (1966)
Drew, W. G., Miller, L. L., Baugh, E. L.: Effects of Δ 9-THC, LSD-25, and scopolamine on continuous, spontaneous alternation in the Y-maze. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 32, 171–182 (1973)
Egger, G. J., Livesey, P. J., Dawson, R. G.: Ontogenetic aspects of central cholinergic involvement in spontaneous alternation behavior. Develop. Psychol. 6, 289–299 (1973)
Gellhorn, S.: Autonomic imbalance and the hypothalamus. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press 1957
Izquierdo, I.: Possible peripheral adrenergic and cholinergic mechanisms in pseudoconditioning. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 35, 189–193 (1974)
Janowsky, D. S., El-Yousef, M. K., Davis, J. M., Sekerke, H. J.: Cholinergic antagonism of methylphenidate-induced stereotyped behavior. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 27, 295–303 (1972)
Javoy, F., Agid, Y., Bouvet, D., Glowinski, J.: Changes in neostriatal DA metabolism after carbachol or atropine micro injections into the substantia nigra. Brain Res. 68, 253–260 (1974)
Jerussi, T. P., Glick, S. D.: Amphetamine-induced rotation in rats without lesions. Neuropharmacology 13, 283–286 (1974)
Jonsson, G., Einarsson, P., Fuxe, K., Hallman, H.: Microspectro-fluorometric studies on central 5-hydroxytryptamine neurons. In: Serotonin-New Vistas: Histochemistry and pharmacology, E. Costa, G. L. Gessa and M. Sandler, eds. New York: Raven Press 1974
Leaton, R. N., Utell, M. J.: Effects of scopolamine on spontaneous alternation following free and forced trials. Physiol. Behav. 5, 331–334 (1970)
Mennear, J. H.: Interactions between central cholinergic agents and amphetamine in mice. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 7, 107–114 (1965)
Meyers, B., Domino, E. F.: The effect of cholinergic blocking drugs on spontaneous alternation in rats. Arch. int. Pharmacodyn. 150, 525–529 (1964)
Proctor, C. D., Potts, J. L., Ashley, L. G., Denefield, B. A.: Pilocarpine reversal of d-amphetamine induced increase in mouse exploratory locomotor activity. Arch. int. Pharmacodyn. 167, 61–68 (1967)
Randrup, A., Munkvad, I.: Dopa and other naturally occurring substances as causes of stereotypy and rage in rats. Acta psychiat. scand. 42, Suppl. 191, 193–199(b) (1966)
Richardson, J. S.: Basic concepts of psychopharmacological research as applied to the psychopharmacological analysis of the amygdala. Acta neurobiol. exp. 34, 543–562 (1974)
Scheel-Krüger, J.: Central effects of anticholinergic drugs measured by the apomorphine gnawing test in mice. Acta pharmacol. T. (Kbh.) 28, 1–16 (1970)
Squire, R. L.: Effects of pretrial and posttrial administration of cholinergic and anticholinergic drugs on spontaneous alternation. J. comp. physiol. Psychol. 1, 69–75 (1969)
Stadler, H., Lloyd, K. G., Bartholini, G.: Dopaminergic inhibition of striatal cholinergic neurons: Synergistic blocking action of gamma-butyrolactone and neuroleptic drugs. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 283, 129–134 (1974)
Strömberg, U.: Dopa effects on motility in mice: Potentiation by MK485 and dexchlorpheniramine. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 18, 58–67 (1970)
Swonger, A. K., Rech, R. H.: Serotonergic and cholinergic involvement in habituation of activity and spontaneous alternation of rats in a Y-maze. J. comp. physiol. Psychol. 81, 509–522 (1972)
Ungerstedt, U.: Brain dopamine neurons and behavior. In: The Neurosciences: Third study program. F. O. Schmitt and F. G. Worden, eds., pp. 695–703. Cambridge: The MIT Press 1974
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kokkinidis, L., Anisman, H. Interaction between cholinergic and catecholaminergic agents in a spontaneous alternation task. Psychopharmacology 48, 261–270 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00496859
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00496859