Summary
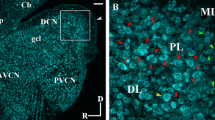
In 16 guinea pigs restricted lesions of the cochlea and the resulting degeneration in the cochlear nerve and in the cochlear nuclei were confirmed by Bodian and Schultze-Gros methods, to study the relationships of central projection of single cochlear turns with the cytoarchitectural areas of the cochlear nucleus complex. The ascending branches of the basal turn terminate in the medial part of the anteroventral cochlear nucleus (AVCN) including the globular cell area, the small spherical cell area and the caudal portion of the large spherical cell area. The descending branches of the basal turn project onto the dorsomedial two-thirds of the posteroventral nucleus (PVCN) with globular cell and octopus cell areas, and terminate in the dorsomedial portion of the central region of the dorsal cochlear nucleus (DCN). Terminals of the apical turn are associated with globular, small spherical and large spherical cells in the ventrolateral part of the AVCN, with globular cells, multipolar cells and a few octopus cells in the ventral PVCN, and with cells of the lateroventral extreme of the central region in the DCN. Lesions of the second and third turns result in degeneration in correspondingly intermediate regions of the cochlear nuclei. There is a predominance of the basal and second turn representation in the three major subdivisions of the cochlear nuclei except the anterior pole of the AVCN.
Zusammenfassung
An 16 Meerschweinchen wurden umschriebene Läsionen an der Cochlea gesetzt und die neurale Degeneration in der Cochlea, im Nervus cochlearis und im Cochleariskernkomplex mit Silberfärbungen nach Bodian und Schultze-Gros nachgewiesen. Dabei interessierten speziell die Projektion einzelner Windungen auf cytocarchitektonisch definierte Regionen der Cochleariskerne, wobei die Neuronenklassifikation nach Osen benutzt wurde. Die Rami ascendentes der Basalwindung enden im mediodoralen antero-ventralen Cochleariskern an Globular-Zellen, kleinen Rund-Zellen und im caudalen Teil der großen Rund-Zellregion. Die Rami descendentes der Basalwindung enden in den dorsalen zwei Dritteln des postero-ventralen Cochleariskerns an Globular- und Octopus-Zellen und im dorsomedialen Teil der Zentralregion des dorsalen Cochleariskerns. Fasern aus der Apexwindung enden im latero-ventralen Teil des AVCN an Globular-Zellen, kleinen und großen Rund-Zellen, und im ventralen Teil des PVCN an Globular-Zellen, multipolaren Zellen und einigen Octopus-Zellen sowie in der latero-ventralen Ecke der Zentralregion des DCN. Läsionen der zweiten und dritten Windungen führten zu Degenerationen in Regionen der Cochleariskerne, die zwischen den Endigungsstätten der Basis- und Apexwindung liegen. Die Dominanz der basalen und zweiten Windungen wurde in allen drei Unterabschnitten des Cochleariskernkomplexes mit Ausnahme des vordersten Poles des antero-ventralen Kerns beobachtet.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AVCN:
-
Anteroventral cochlear nucleus
- cr:
-
central region
- DCN:
-
dorsal cochlear nucleus
- g:
-
granular layer
- gl:
-
globular cell
- lsc:
-
large spherical cell
- mo:
-
molecular layer
- mp:
-
multipolar cell
- oc:
-
octopus cell
- PVCN:
-
posteroventral cochlear nucleus
- py:
-
pyramidal cell layer
- s:
-
section
- ssc:
-
small spherical cell
- VCN:
-
ventral cochlear nucleus
Literature
Anderson, H., Wedenberg, E.: A new method for hearing tests in the guinea pig. Acta oto-laryng. (Stockh.) 60, 375–393 (1965)
Bodian, D.: A new method for staining nerve fibers and nerve endings in mounted paraffin section. Anat. Rec. 65, 89–95 (1936)
Culler, E.: An experimental study of tonal localization in the cochlea of the guinea pig. Ann. Otol. (St. Louis) 44, 807–813 (1935)
Culler, E., Coakley, J. D., Lowy, K., Gross, N.: A revised frequency map of the guinea-pig cochlea. Amer. J. Psychol. 56, 476–500 (1943)
Fernandez, C. J.: Dimensions of the cochlea (guinea pig). J. Amer. Soc. Acoust. 24, 519–523 (1952)
Firbas, W., Wicke, W., Volavsek, Ch.: Über Zahl und Anordnung der Ganglienzellen im Ganglion spirale des Meerschweinchens. Mschr. Ohrenheilk. 104, 241–246 (1970)
Fujita, S., Elliott, D. N.: Thresholds of audition of three species of monkey. J. Amer. Soc. Acoust. 37, 139–144 (1965)
Fuse, G.: Das Ganglion ventrale und das Tuberculum acusticum bei einigen Säugern und beim Menschen. Arb. Hirnanat. Inst. Zürich 7, 1–210 (1913)
Guild, S. R.: A graphic reconstruction method for the study of the organ of Corti. Anat. Rec. 22, 141–157 (1921)
Harrison, J. M., Irving, R.: The anterior ventral cochlear nucleus. J. comp. Neurol. 124, 15–42 (1965)
Harrison, J. M., Irving, R.: The organization of the posterior ventral cochlear nucleus in the rat. J. comp. Neurol. 126, 391–402 (1966)
Kayser, D., Libouban, S.: Représentation au niveau de l'aire auditive du Cobaye des différentes spires de la cochlée. J. Physiol. (Paris) 55, 155–156 (1963)
Lewy, F. H., Kobrak, H.: The neural projection of the cochlear spirals on the primary acoustic centers. Arch. Neurol. Psychiat. (Chic.) 35, 839–852 (1936)
Moskowitz, N., Liu, J.: Central projections of the spiral ganglion of the squirrel monkey. J. comp. Neurol. 144, 335–344 (1972)
Moushegian, G., Rupert, A. L.: Response diversity of neurons in the ventral cochlear nucleus of kangaroo rat to low-frequency tones. J. Neurophysiol. 33, 351–364 (1970)
Osen, K. K.: Cytoarchitecture of the cochlear nuclei in the cat. J. comp. Neurol. 136, 453–483 (1969)
Pirsig, W.: Regionen, Zelltypen und Synapsen im ventralen Nucleus cochlearisdes Meerschweinchens. Arch. klin. exp. Ohr.-, Nas.- u. Kehlk.-Heilk. 192, 333–350 (1968)
Pirsig, W.: Tonotope Organisation der Hörbahn: morphologische und physiologische Befunde. HNO (Berl.) 22, (im Druck) (1974)
Pirsig, W., Noda, Y., Lehmann, I.: Tonotope Abbildung der Cochlea im Nucleus cochlearis ventralis des Meerschweinchens. Arch. klin. exp. Ohr.-, Nas.- u. Kehlk.-Heilk. 202, 494–500 (1972)
Pye, A.: The destructive effect of intense pure tones on the cochlea of mammals. In: Disorders of auditory function, ed. W. Taylor, pp. 89–96. London: Academic Press 1973
Rose, J. E., Galambos, R., Hughes, J. R.: Microelectrode studies of the cochlear nuclei of the cat. Bull. Johns Hopk. Hosp. 104, 211–251 (1959)
Sando, I.: The anatomical interrelationships, of the cochlear nerve fibers. Acta oto-laryng. (Stockh.) 59, 417–436 (1956)
Schultze-Gros: In: E. Fasske: Lehrbuch der histologischen Technik, pp. 71–72. München: Urban & Schwarzenberg 1964
Stebbins, W. C., Miller, J. M., Johnsson, L. G., Hawkins, J. E.: Ototoxic hearing loss and cochlear pathology in the monkey. Ann. Otol. (St. Louis) 78, 1007–1025 (1969)
Stevens, S. S., Davis, H., Lurie, M. H.: The localization of pitch perception on the basilar membrane. J. gen. Psychol. 13, 297–315 (1935)
Tasaki, I., Davis, H., Legouix, J. P.: The space-time pattern of the cochlear microphonics (guinea pig), as recorded by differential electrodes. J. Amer. Soc. Acoust. 24, 502–519 (1952)
Webster, D. B.: Projection of the cochlea to cochlear nuclei in Merriam's-Kangaroo rat. J. comp. Neurol. 143, 323–340 (1971)
Webster, D. B., Webster, M.: Kangaroo rat auditory thresholds before and after middle ear reduction. Brain, Behav. Evol. 5, 41–53 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Guest-assistent 1969–1972; now Ass. Professor, Univ. Okinawa, Japan.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noda, Y., Pirsig, W. Anatomical projection of the cochlea to the cochlear nuclei of the guinea pig. Arch Otorhinolaryngol 208, 107–120 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00453924
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00453924