Abstract
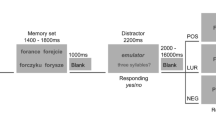
The effects of intramuscular injections of diazepam (0.3 mg/kg) and scopolamine (8 Μg/kg) on memory processes and subjective moods were studied in 36 volunteers. Subjects (Ss) were tested in groups of four in a double blind procedure with treatments distributed according to a Latin square design. Lists of words were presented to Ss who were then tested with an immediate free recall test prior to drug administration. Following injection delayed free recall and recognition tests were given. Subsequently two sets of lists were presented separately and tested in the same fashion. Two of the lists in the last set were composed of words falling into distinct categories. Memory was additionally analyzed by testing immediate recall of digit sequences and employing a visual recognition test. Subjective moods were evaluated with a rating questionnaire.
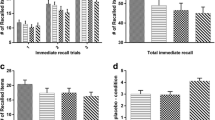
Both diazepam and scopolamine impaired memory functions although the action of the latter drug was more pronounced and prolonged. The deficit appeared to be in the storage process leaving retrieval processes unaffected. Scopolamine in addition interfered with organizational processes. Subjectively, scopolamine also produced a larger sedative effect than diazepam.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam, N.: Effects of general anesthetics on memory functions in man. J. comp. physiol. Psychol. 83, 294–305 (1973)
Atkinson, R. C., Shiffrin, R. M.: Human memory: A proposed system and its control processes. In: The psychology of learning and motivation, Vol. 2, K. W. Spence and J. T. Spence, eds., pp. 89–195. New York: Academic Press 1968
Atkinson, R. C., Shiffrin, R. M.: The control of short-term memory. Sci. Amer. 224, 82–90 (1971)
Baird, E. S., Hailey, D. M.: Plasma levels of diazepam and its major metabolite following intramuscular administration. Brit. J. Anaesth. 45, 546–547 (1973)
Battig, W. B., Montague, E. W.: Category norms for verbal items in 56 categories: A replication and extension of the Connecticut category norms. J. exp. Psychol. Mon. 80, 1–46 (1969)
Benton, A. L.: The revised visual retention test. Clinical and experimental applications. New York: The Psychological Corporation 1955
Bousfield, W. A.: The occurrence of clustering in recall of randomly arranged associates. J. gen. Psychol. 49, 229–240 (1953)
Calhoun, W. H., Smith, A. A.: Effects of scopolamine on acquisition of passive avoidance. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 13, 201–209 (1968)
Clarke, P. R. F., Eccersley, P. S., Frisby, J. P., Thornton, J. A.: The amnesic effect of diazepam (Valium). Brit. J. Anaesth. 42, 690–697 (1970)
Consolo, S., Ladinsky, H., Peri, G., Garattini, S.: Effect of diazepam on mouse whole brain and brain area acetylcholine and choline levels. Europ. J. Pharmacol. 27, 266–268 (1974)
Darley, C. F., Tinklenberg, J. R., Roth, W. T., Hollister, L. E., Atkinson, R. C.: Influence of marihuana on storage and retrieval processes in memory. Memory and Cognition 1, 196–200 (1973)
Darley, C. F., Tinklenberg, J. R., Roth, W. T., Atkinson, R. C.: The nature of storage deficits and state-dependent retrieval under marihuana. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 37, 139–149 (1974)
Drachman, D. A., Leavitt, J.: Human memory and the cholinergic system. Arch. Neurol. (Chic.) 30, 113–121 (1974)
Ghoneim, M. M., Mewaldt, S. P., Thatcher, J. W.: The effect of diazepam and fentanyl on mental, psychomotor and electroencephalographic functions and their rate of recovery. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) (in press)
Greenblatt, D. J., Shader, R. I.: Anticholinergics. New Engl. J. Med. 288, 1215–1219 (1973)
Greenblatt, D. J., Shader, R. I.: Benzodiazepines. New Engl. J. Med. 291, 1011–1015 (1974)
Hardy, T. K., Wakely, D.: The amnesic properties of hyoscine and atropine in pre-anesthetic medication. Anaesthesia 17, 331–336 (1962)
JÄÄttelÄ, A., MÄnnistö, P., Paatero, H., Tuomisto, J.: The effects of diazepam or diphenhydramine on healthy human subjects. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 21, 202–211 (1971)
James, F. M.: The effects of cyclopropane anesthesia without surgical operation on mental functions of normal man. Anesthesiology 30, 264–272 (1969)
Leaton, R. N.: The limbic system and its pharmacological aspects. In: An introduction to psychopharmacology, R. H. Rech and K. E. Moore, eds., pp. 137–174. New York: Raven Press 1971
Mandler, G.: Organization and memory. In: The psychology of learning and motivation, Vol. 1, K. W. Spence and J. T. Spence, eds., pp. 327–372. New York: Academic Press 1967
McCaughey, W., Dundee, J. W.: Comparison of the sedative effects of diazepam given by oral and intramuscular routes. Brit. J. Anaesth. 44, 901–902 (1972)
Norris, H.: The action of sedatives on brain stem oculomotor systems in man. Neuropharmacology 10, 181–191 (1971)
Ostfeld, A. M., Aruguete, A.: Central nervous system effects of hyoscine in man. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 137, 133–139 (1962)
Penfield, W., Mathieson, G.: Memory. Arch. Neurol. (Chic.) 31, 145–154 (1974)
Safer, D. J., Allen, R. P.: The central effects of scopolamine in man. Biol. Psychiat. 3, 347–355 (1971)
Thorndike, E. L., Lorge, L.: The teacher's word book of 30,000 words. New York: Columbia University Press 1944
Underwood, B. J.: Degree of learning and measurement of forgetting. J. Verb. Learn. Verb. Behav. 3, 112–129 (1964)
Wiener, N. I., Messer, J.: Scopolamine-induced impairment of long-term retention in rats. Behav. Biol. 9, 227–234 (1973)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghoneim, M.M., Mewaldt, S.P. Effects of diazepam and scopolamine on storage, retrieval and organizational processes in memory. Psychopharmacologia 44, 257–262 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00428903
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00428903