Abstract
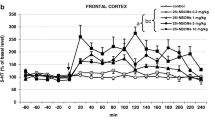
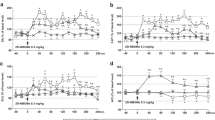
Rats were kept on a 12-h light-dark cycle. One hour after the light was switched on, physiological saline, (+)-amphetamine 1 mg/kg, and H 77/77 5 mg/kg were injected s.c.; the number of groomings was counted 1–2h after the treatments. (+)-Amphetamine and H 77/77 produced increased grooming which was antagonized by the tyrosine hydroxylase inhibitor H 44/68 (250 mg/kg), the dopamine-β-hydroxylase inhibitor FLA 63 (40), the neuroleptics haloperidol (0.1 and 0.5), and clozapine (1 and 5). The (+)-amphetamine-induced grooming was also antagonized by the NA-receptor blocker aceperone (10) but not by the sedative phenothiazines mepazine (10) and diphenhydramine (20) nor diazepam (1).
These results indicate that NA-release is involved in the mediation of (+)-amphetamine- and H 77/77-induced grooming. The inhibition of haloperidol and clozapine is presumably due to NA-receptor blockade.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andén, N.-E., Butcher, S. G., Corrodi, H., Fuxe, K., Ungerstedt, U.: Receptor activity and turnover of dopamine and noradrenaline after neuroleptics. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 11, 303–314 (1970)
Andén, N.-E., Corrodi, H., Fuxe, K.: Effect of neuroleptic drugs on central catecholamine turnover assessed using tyrosine- and dopamine-β-hydroxylase inhibitors. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 24, 177–182 (1972)
Angst, J., Jäenicke, U., Padrutt, A., Scharfetter, Ch.: Ergebnisse eines Doppelblindversuches von HF 1854[8-Chlor-11-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-5H-dibenzo(b,e)]1,4(diazepin) im Vergleich zu Levopromazin. Pharmakopsychiatr. 4, 192–200 (1971)
Angst, J., Bente, D., Berner, P., Heimann, H., Helmchen, H., Hippius, H.: Das klinische Wirkungsbild von Clozapin. Pharmakopsychiatr. 4, 201–211 (1971)
Berridge, T. L., Sharman, D. F.: The effect of tranquillizing drugs on the concentration of the sulphate ester of 4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenylethane-1,2-Diol in rat brain. Br. J. Pharmacol. 50, 156–158 (1974)
Bindra, D., Blond, J.: A time-sample method for measuring general activity and its components. Can. J. Psychol. 12, 74–76 (1958)
Bolles, R. C.: Grooming behavior in the rat. J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 53, 306–310 (1960)
Borbély, A. A., Huston, J. P., Waser, P. G.: Physiological and behavioral effects of parachlorophenylalanine in the rat. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 31, 131–142 (1973)
Bræstrup, C., Nielsen, M.: Regulation in the central norepinephrine neurotransmission induced in vivo by alpha adrenoceptor active drugs. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 198, 596–608 (1976)
Bürki, H. R., Eichenberger, E., Sayers, A. C., White, T. C.: Clozapine and the dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia, a critical appraisal. Pharmakopsychiatr. 8, 115–121 (1975)
Buus Lassen, J.: Evidence for a noradrenergic and dopaminergic mechanism in the hyperactivity produced by 4,α-dimethyl-m-tyramine (H 77/77) in rats. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 37, 331–340 (1974)
Carlsson, A., Lindqvist, M.: Effect of chlorpromazine or haloperidol on formation of 3-methoxytyramine and normetanephrine in mouse brain. Acta Pharmacol. (Kbh.) 20, 140–144 (1963)
Carlsson, A., Corrodi, H., Fuxe, K., Hökfelt, T.: Effects of some antidepressant drugs on the depletion of intraneuronal brain catecholamine stores caused by 4,α-dimethyl-meta-tyramine. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 5, 367–373 (1969)
Carlsson, A., Lindqvist, M., Wysokowski, J.: Substituted metatyramines as brain monoamine depletors. Acta Pharm. Suec. 7, 293–302 (1970)
Corrodi, H., Fuxe, K., Ljungdahl, Å., Ögren, S.-O.: Studies on the action of some psychoactive drugs on central noradrenaline neurones after inhibition of dopamine-β-hydroxylase. Brain Res. 24, 451–470 (1970)
Dingell, J. V., Owens, M. L., Norvich, M. R., Sulser, F.: On the role of norepinephrine biosynthesis in the central action of amphetamine. Life Sci. 6, 1155–1162 (1967)
Dominic, J. A., Moore, K. E.: Acute effects of α-methyl-tyrosine on brain catecholamine levels and on spontaneous and amphetamine-stimulated motor activity in mice. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. 178, 166–176 (1969)
von Gross, H., Langner, E.: Das Wirkungsprofil eines chemisch neuartigen Breitbandneuroleptikums der Dibenzodiazepingruppe. Wien. Med. Wochenschr. 40, 814–816 (1966)
von Gross, H., Langner, E.: Das Neuroleptikum 100-129/HF-1854 (Clozapin) in der Psychiatrie. Int. Pharmacopsychiatry 4, 220–230 (1970)
Hanselmann, G., Borbély, A. A.: Response of rat brain indoles and motor activity to short light dark cycles. J. Neurochem. 26, 951–955 (1976)
Hansson, L. C. F.: Evidence that the central action of (+)-amphetamine is mediated via catecholamines. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 10, 289–297 (1967)
Hyttel, J.: Effect of neuroleptics on the disappearance rate of (14C) labelled catecholamines formed from (14C) tyrosine in mouse brain. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 26, 588–596 (1974)
Janssen, P. A. J., Niemegeers, C. J. E., Schellekens, K. H. L.: Is it possible to predict the clinical effects of neuroleptic drugs (major tranquillizers) from animal data? Arzneim. Forsch. 15, 104–125 (1965)
Janssen, P. A. J., Niemegeers, C. J. E., Schellekens, K. H. L., Lenaerts, F. M.: Is it possible to predict the clinical effects of neuroleptic drugs (major tranquillizers) from animal data? Arzneim. Forsch. 17, 841–843 (1967)
Jonas, W., Scheel-Krüger, J.: Amphetamine induced stereotyped behavior correlated with the accumulation of O-methylated dopamine. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. 177, 379–389 (1969)
O'Keeffe, R., Sharman, O. F., Vogt, M.: Effects of drugs used in psychoses on cerebral dopamine metabolism. Br. J. Pharmacol. 38, 287–304 (1970)
Keller, H. H., Bartholini, G., Pletscher, A.: Increase of 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylethylene glycol in rat brain by neuroleptic drugs. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 23, 183–186 (1973)
Kurland, A.-A., Hanlon, T. E., Tatom, M. H., Ota, K. Y., Simopoulos, A. M.: The comparative effectiveness of six phenothiazine compounds, phenobarbital and inert placebo in the treatment of acutely ill patients: global measures of severity of illness. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 133, 1–18 (1961)
Leonard, B. E., Shallice, S. A.: Some neurochemical effects of amphetamine, methylamphetamine and p-bromomethylamphetamine in the rat. Br. J. Pharmacol. 41, 198–212 (1971)
DiMascio, A., Havens, L. L., Snell, J. E.: A comparison of four phenothiazine derivatives: a preliminary report on the assessment of chlorpromazine, promethazine, perphenazine, and trifluoperazine. In: Recent advances in biological psychiatry, Vol. III, J. Wortis, ed. New York: Grune and Stratton 1961
Meek, J. L., Neff, N. H.: The rate of formation of 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylethyleneglycol sulfate in brain as an estimate of the rate of formation of norepinephrine. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 184, 570–575 (1973)
Munkvad, I., Pakkenberg, H., Randrup, A.: Aminergic systems in basal ganglia associated with stereotyped hyperactivity behavior and catalepsy. Brain Behav. Evol. 1, 89–100 (1968)
Nielsen, M.: Estimation of noradrenaline and its major metabolites synthesized from (3H)tyrosine in the rat brain. J. Neurochem. 27, 493–500 (1976)
Nybäck, H.: Effects of neuroleptic drugs on brain catecholamine neurons. Stockholm: Karolinska Institutet (akad. avhandl.) (1971)
Peacock, I. J., Hodge, M. H., Thomas, R. K.: Ultrasonic measurement and automatic analysis of general activity in the rat. J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 62, 284–288 (1966)
Randrup, A., Munkvad, I., Udsen, P.: Adrenergic mechanisms and amphetamine induced abnormal behaviour. Acta Pharmacol. (Kbh.) 20, 145–157 (1963)
Randrup, A., Munkvad, J.: Role of catecholamines in the amphetamine excitatory response. Nature (Lond.) 211, 540 (1966)
Randrup, A., Munkvad, I.: Pharmacology and physiology of stereotyped behavior. J. Psychiatr. Res. 11, 1–10 (1974)
Scheel-Krüger, J.: Comparative studies of various amphetamine analogues demonstrating different interactions with the metabolism of the catecholamines in the brain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 14, 47–59 (1971)
Scheel-Krüger, J.: Studies on the accumulation of O-methylated dopamine and noradrenaline in the rat brain following various neuroleptics, thymoleptics and aceperone. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. 195, 372–378 (1972)
Schiørring, E.: Amphetamine induced selective stimulation of certain behaviour items with concurrent inhibition of others in an open-field test with rats. Behaviour 39, 1–17 (1971)
Sedvall, G., Nybäck, H.: Effect of clozapine and some other antipsychotic agents on synthesis and turnover of dopamine formed from 14C-tyrosine in mouse brain. Isr. J. Med. Sci. [Suppl.] 9, 24–30 (1973)
Sparber, S. B., Tilson, T. A.: The releasability of central norepinephrine and serotonin by peripherally administered d-amphetamine before and after tolerance. Life Sci. 11, Pt. 1, 1059–1067 (1972)
Stille, G., Lauener, H., Eichenberger, E.: The pharmacology of 8-chloro-11-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-5H-dibenzo(b.e.)(1,4)diazepine (clozapine) Farmaco [Part.] 26, 603–625 (1971)
Svensson, T. H., Waldeck, B.: On the significance of central noradrenaline for motor activity: experiments with a new dopamine β-hydroxylase inhibitor. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 7, 278–282 (1969)
Weissmann, A., Koe, B. K., Tenen, S.: Antiamphetamine effects following inhibition of tyrosine hydroxylase. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 151, 339–352 (1966)
Zucker, I.: Light-dark rhythms in rat eating and drinking behavior. Physiol. Behav. 6, 115–126 (1971)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buus Lassen, J. Evidence for a noradrenergic mechanism in the grooming produced by (+)-amphetamine and 4,α-dimethyl-m-tyramine (H 77/77) in rats. Psychopharmacology 54, 153–157 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00426772
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00426772