Abstract
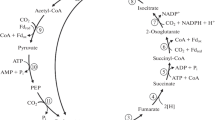
Chlorobium limicola has been proposed to assimilate CO2 autotrophically via a reductive tricarboxylic acid cycle rather than via the Calvin cycle. This proposal has been a matter of considerable controversy. In order to determine which pathway is operative, the bacterium was grown on a mineral salts medium with CO2 as the main carbon source supplemented with specifically labeled 14C-pyruvate, and the incorporation of 14C into alanine (≙intracellular pyruvate), aspartate (≙oxaloacetate), glutamate (≙α-ketoglutarate), and glucose (≙hexosephosphate) was measured in exponentially growing cells in long term labeling experiments. During growth in presence of pyruvate, 20% of the cell carbon were derived from pyruvate in the medium, 80% from CO2. Since pyruvate was not oxidized to CO2, only those compounds should become labeled which were synthesized from CO2 via pyruvate.
The three amino acids and glucose were found to be labeled. Alanine had one fifth the specific radioactivity of the extracellular pyruvate, indicating that 20% of the intracellular pyruvate pool were derived from pyruvate in the medium, 80% were synthesized from CO2. Glucose had twice the specific radioactivity of alanine, showing that hexosephosphate synthesis from CO2 proceeded via the pyruvate pool. The latter finding is not consistent with the operation of the Calvin cycle, in which pyruvate is not an intermediate. The specific radioactivities of aspartate (≙oxaloacetate) and of glutamate (≙α-ketoglutarate) were practically identical but considerably lower than that of alanine (≙ intracellular pyruvate). These findings are compatible with the operation of a reductive tricarboxylic acid cycle as mechanism of autotrophic CO2 fixation. Degradation studies of the cell components support this interpretation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergmeyer, H.-U., Bernt, E.: Bestimmung mit Glucose-Oxidase und Peroxidase. In: Methoden der enzymatischen Analyse, Vol. 2 (H.-U. Bergmeyer, ed.), pp. 1172–1181. Weinheim: Verlag Chemie 1970
Beuscher, N., Gottschalk, G.: Lack of citrate lyase — the key enzyme of the reductive carboxylic acid cycle — in Chlorobium thiosulfatophilum and Rhodospirillum rubrum. Z. Naturforsch. 27b, 967–973 (1972)
Buchanan, B. B.: Ferredoxin and carbon assimilation. In: Iron-sulfur proteins, Vol. 1 (W. Lowenberg, ed.), pp. 129–150, New York, London: Academic Press 1973
Buchanan, B. B., Evans, M. C. W.: The synthesis of α-ketoglutarate from succinate and carbon dioxide by subcellular preparation of a photosynthetic bacterium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 54, 1212–1218 (1965)
Buchanan, B. B., Schürmann, P., Shanmugam,K. T.: Role of the reductive carboxylic acid cycle in a photosynthetic bacterium lacking ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 283, 136–145 (1972)
Buchanan, B. B., Sirevåg, R.: Ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase and Chlorobium thiosulfatophilum. Arch. Microbiol. 109, 15–19 (1976)
Evans, M. C. W., Buchanan, B. B.: Photoreduction of ferredoxin and its use in carbon dioxide fixation by a subcellular system from a photosynthetic bacterium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 53, 1420–1425 (1965)
Evans, M. C. W., Buchanan, B. B., Arnon, D. I.: A new ferredoxin dependent carbon reduction cycle in a photosynthetic bacterium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 55, 928–934 (1966)
Fuchs, G., Stupperich, E., Thauer, R. K.: Acetate assimilation and the synthesis of alanine, aspartate and glutamate in Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Arch. Microbiol. 117, 61–66 (1978)
Fuchs, G., Stupperich, E., Eden, G.: Autotrophic CO2 fixation in Chlorobium limicola. Evidence for the operation of a reductive tricarboxylic acid cycle in growing cells. Arch. Microbiol. 128, 64–71 (1980)
Gottschalk, G.: The stereospecificity of the citrate synthase in sulfate-reducing and photosynthetic bacteria. Eur. J. Biochem. 5, 346–351 (1968)
Grassl, M.: Alaninbestimmung mit Glutamat-Pyruvat-Transaminase and Lactat-Dehydrogenase. In: Methoden der enzymatischen Analyse, Vol. 2 (H.-U. Bergmeyer, ed.), pp. 1637–1640, Weinheim: Verlag Chemie 1970
Hoare, D. S., Gibson, J.: Photoassimilation of acetate and the biosynthesis of amino acids by Chlorobium thiosulfatophilum. Biochem. J. 91, 546–559 (1964)
Hohorst, H.-J.: l-(+)-Lactat-Bestimmung mit Lactat-Dehydro-genase und NAD. In: Methoden der enzymatischen Analyse, Vol. 2 (H.-U. Bergmeyer, ed.), pp. 1425–1429. Weinheim: Verlag Chemie 1970
Larsen, H.: Photosynthesis of succinic acid by Chlorobium thiosulfatophilum. J. Biol. Chem. 193, 167–173 (1951)
Larsen, H.: On the culture and general physiology of the green sulfur bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 64, 187–196 (1952)
Pfennig, N., Trüper, H. G.: The phototrophic bacteria. In: Bergey's manual of determinative bacteriology, eighth edition (R. E. Buchanan, N. E. Gibbons, eds.), pp. 24–64. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins Co. 1974
Quandt, L.: Untersuchung der CO2-Fixierung und des Wasserstoff-Stoffwechsels in Chlorobium. Thesis, University of Göttingen (1978)
Quandt, L., Gottschalk, G., Ziegler, H., Stichler, W.: Isotope discrimination by photosynthetic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Letters 1, 125–128 (1977)
Quayle, J. R., Ferenci, T.: Evolutionary aspects of autotrophy. Microbiol. Rev. 42, 251–273 (1978)
Roberts, R. B., Abelson, P. H., Cowie, D. B., Bolton, E. T., Britton, R. J.: Studies of biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. Carnegie Institute, Washington 1957
Sadler, W. R., Stanier, R. Y.: The function of acetate in photosynthesis by green bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 46, 1328–1334 (1960)
Simon, H., Floss, H. G.: Anwendung von Isotopen in der organischen Chemie und Biochemie, Vol. 2, pp. 23ff., 50ff. Berlin. Heidelberg, New York: Springer 1967
Sirevåg, R.: Further studies on carbon dioxide fixation in Chlorobium. Arch. Microbiol. 98, 3–18 (1974)
Sirevåg, R.: Photoassimilation of acetate and metabolism of carbohydrate in Chlorobium thiosulfatophilum. Arch. Microbiol. 104, 105–111 (1975)
Sirevåg, R., Ormerod, J. G.: Carbon dioxide fixation in green sulfur bacteria. Biochem. J. 120, 399–408 (1970a)
Sirevåg, R., Ormerod, J. G.: Carbon dioxide fixation in photosynthetic green sulfur bacteria. Science 169, 186–188 (1970b)
Sirevåg, R., Buchanan, B. B., Berry, J. A., Troughton, J. H.: Mechanism of CO2 fixation in bacterial photosynthesis studied by the carbon isotope fractionation technique. Arch. Microbiol. 112, 35–38 (1977)
Smillie, R. M., Rigopoulos, N., Kelly, H.: Enzymes of the reductive pentose phosphate cycle in the purple and in the green photosynthetic sulphur bacteria. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 56, 612–614 (1962)
Srere, P. A.: The citrate enzymes: Their structures, mechanisms and biological functions. In: Current topics in cellular regulation, Vol. 5 (B. L. Horecker, E. R. Stadtman, eds.), pp. 229–283, New York: Academic Press 1972
Stegemann, H.: Bestimmung von Aminosäuren mit dithionitreduziertem Ninhydrin. Hoppe-Seylers Z. Physiol. Chem. 319, 102–109 (1960)
Tabita, F. R., McFadden, B. A., Pfennig, N.: d-Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase in Chlorobium thiosulfatophilum Tassajara. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 341, 187–194 (1974)
Van Niel, C. B.: On the morphology and physiology of the purple and green sulfur bacteria. Arch. Microbiol. 3, 1–112 (1931)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Offprint requests to: G. Fuchs
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fuchs, G., Stupperich, E. & Jaenchen, R. Autotrophic CO2 fixation in Chlorobium limicola. Evidence against the operation of the Calvin cycle in growing cells. Arch. Microbiol. 128, 56–63 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00422306
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00422306