Abstract
Radon-222 is a naturally occurring radioactive gas in the uranium-238 decay series that has traditionally been called, simply, radon. The lung cancer risks associated with the inhalation of radon decay products have been well documented by epidemiological studies on populations of uranium miners.
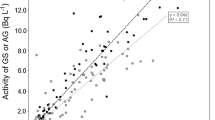
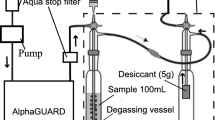
The realization that radon is a public health hazard has raised the need for sampling and analytical guidelines for field personnel. Several sampling and analytical methods are being used to document radon concentrations in ground water and surface water worldwide but no convenient, single set of guidelines is available. Three different sampling and analytical methods-bubbler, liquid scintillation, and field screening-are discussed in this paper. The bubbler and liquid scintillation methods have high accuracy and precision, and small analytical method detection limits of 0.2 and 10 pCi/l (picocuries per liter), respectively. The field screening method generally is used as a qualitative reconnaissance tool.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cothern, C. R.: 1987, ‘Estimating the health risk of radon in drinking water’, J. American Water Well Association, 70 (4), 153–158.
Cothern, C. R., Jarvis, A. N., Whittaker, E. L., and Battist, Lewis: 1984, ‘Radioactivity in environmental samples: Calibration standards, measurement methods, quality assurance, and data analysis’, environment International, 10, 109–116.
Durrance, E. M.: 1986, Radioactivity in Geology, Principles and Applications, John Wiley and Sons, Inc., New York, N.Y., 441 pp.
Gesell, T. F., and Prichard, H. M.: 1980, ‘The contribution of radon in tap water to indoor radon concentrations’, in Gesell, T. F., and Lowder, W. M. (Eds.), Natural Radiation Environment III, U.S. Department of Energy, CONF-780422, vol. 2, pp. 1347–1363.
Hiltebrand, D. J., Dyksen, J. E., and Raman, K.: 1987, ‘Radon in water supply wells: Treatment facility requirements and costs’, in Graves, Barbara (ed.), Radon, Radium and other Radioactivity in Ground Water, Chelsea, Michigan, Lewis Publishers Inc., pp. 521–534.
Inn, K. G. W., Mullen, P. A., and Hutchinson, J. M. R.: 1984, ‘Radioactivity standards for environmental monitoring II’, Environment International, 10, 91–97.
Lee, R. W., and Hollyday, E. F.: 1987, ‘Radon measurements in streams to determine location and magnitude of ground-water seepage’, in Graves, Barbara (ed.), Radon, Radium and other Radioactivity in Ground Water, Chelsea, Michigan, Lewis Publishers, Inc., pp. 241–249.
Lowry, J. D., and Brandon, J. E.: 1981, ‘Removal of radon from ground water supplies using granular activated carbon or diffused aeration’, University of Maine, Department of Civil Engineering, Orono, Maine.
Prichard, H. M., and Gesell, T. F.: 1977, ‘Rapid measurements of 222Rn concentrations in water with a commercial liquid scintillation counter’, Health Physics, 33, 577–581.
Prichard, H. M., and Gesell, T. F.: 1984, ‘Radon in the environment’, in Lett, J. T., Ehmann, U. K., and Cox, A. B. (Eds.), Advances in Radiotion Biology, Orlando, Florida, Academic Press, Inc., pp. 391–428.
Reid, G. W., Lassovszky, Peter, and Hathaway, Steven: 1985, ‘Treatment, waste management and cost for removal of radioactivity from drinking water’, Health Physics, 48, 671–694.
Reimer, G. M.: 1977, ‘Fixed-volume inlet system for an alpha-sensitive cell adapted for radon measurement’, U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 77-409, 3 pp.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: 1978, Radon in Water Sampling Program, EPA/EERF-Manual-78-1, 11 pp.
Wood, W. W.: 1981, ‘Guidelines for collection and field analysis of groundwater samples for selected unstable constituents’, Techniques of Water-Resources Investigations of the U.S. Geological Survey Book 1, Chapter D2, 24 pp.
Yang, I. C.: 1987, ‘Sampling and analysis of dissolved radon-222 in surface and ground water’, in Graves, Barbara (Ed.), Radon, Radium, and Other Radioactivity in Ground Water, Chelsea, Michigan, Lewis Publishers Inc., pp. 193–203.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cecil, L.D., Gesell, T.F. Sampling and analysis for radon-222 dissolved in ground water and surface water. Environ Monit Assess 20, 55–66 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00396521
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00396521