Abstract
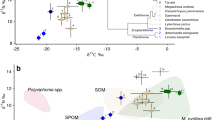
Stable carbon isotope measurements (δ13C) were used to assess the importance of kelp carbon (-13.6 to-16.5‰) versus phytoplankton carbon (-25.5 to-26.5‰) to resident fauna of an isolated kelp bed community on Alaska's north arctic coast from 1979 to 1983. The predominant kelp, Laminaria solidungula, showed some seasonal variation in δ13C which was correlated with changes in the carbon content of the tissue. Animals that showed the greatest assimilation of kelp carbon (>=50%) included macroalgal herbivores (gastropods and chitons,-16.9 to-18.2‰), a nonselective suspension feeder (an ascidian,-19.0‰) and a predatory gastropod (-17.6‰). Animals that showed the least incorporation of kelp carbon into body tissues (<=7%) included selective suspension-feeders (hydroids, soft corals and bryozoans,-22.8 to-25.1‰). Sponges, and polychaete, gastropod and crustacean omnivores exhibited an intermediate dependence on kelp carbon (15 to 40%). Within some taxonomic groups, species exhibited a broad range in isotopic composition which was related to differences in feeding strategies. In the polychaete group alone, δ13C values identified four major feeding habits: deposit-feeders (-18.0‰), omnivores (-20.4‰), predators (-22.2‰) and microalgal herbivores (-23.0‰). Distinct seasonal changes in the δ13C values of several animals indicated an increased dependence on kelp carbon during the dark winter period when phytoplankton were absent. Up to 50% of the body carbon of mysid crustaceans, which are key prey species for birds, fishes and marine mammals, was composed of carbon derived from kelp detritus during the ice-covered period.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Barnes, R. D.: Invertebrate zoology, 1089 pp. Philadelphia: Saunders College 1980
Barnes, P. W. and E. Reimnitz: Sedimentary processes on arctic shelves off the northern coast of Alaska. In: The coast and shelf of the Beaufort Sea, pp 439–476. Ed. by J. C. Reed and J. E. Slater. Arlington: Arctic Institute of North America 1974
Bedford, A. P. and P. G. Moore: Macrofaunal involvement in the sublittoral decay of kelp debris; the polychaete Platyneries dumerilii (Audouin and Milne-Edwards) (Annelida: Polychaeta). Estuar., cstl Shelf Sci. 20, 117–134 (1985)
Boutton, R. W., W. W. Wong, D. L. Hachey, L. S. Lee, M. P. Cabrera and P. D. Klein: Comparison of quartz and pyrex tubes for combustion of organic samples for stable carbon isotope analysis. Analyt. Chem. 55, 1832–1833 (1983)
Buchanan, D. L. and B. J. Corcoran: Sealed tube combustions for the determination of carbon-14 and total carbon. Analyt. Chem. 31, 1635–1638 (1959)
Chapman, A. R. O. and J. E. Lindley: Productivity of Laminaria solidungula J. Ag. in the Canadian High Arctic: a year round study. Proc. 10th int. Seaweed Symp. (Göteborg) 247–252 (1981). (Ed. by T. Levring. Berlin: Walter de Gruyter)
Clarke, W. D.: Mysids of the southern kelp region. Nova Hedwigia 32, 369–380 (1971)
Craig, H.: Isotopic standards for carbon and oxygen and correction factors for mass-spectrometric analysis of carbon dioxide. Geochim. cosmochim. Acta 12, 133–149 (1957)
Craig, P. C., W. B. Griffiths, S. R. Johnson and D. M. Schell: Trophic dynamics in an arctic lagoon. In: The Alaskan Beaufort Sea; ecosystems and environments, pp 347–380. Ed. by P. W. Barnes, D. Schell and E. Reimnitz. Orlando: Academic Press 1984
DeNiro, M. J. and S. Epstein: Influence of diet on the distribution of carbon isotopes in animals. Geochim. cosmochim. Acta 42, 495–506 (1978)
Des Marais, D. J. and J. M. Hayes: Tube cracker for opening glass-sealed ampules under vacuum. Analyt. Chem. 48, 1651–1652 (1976)
Dieckman, G. S.: Aspects of the ecology of Laminaria pallida (Grev.) J. Ag. off the Cape Peninsula (South Africa). I. Seasonal growth. Botanica mar. 23, 579–585 (1980)
Dunton, K. H.: An annual carbon budget for an arctic kelp community. In: The Alaskan Beaufort Sea; ecosystems and environments, pp 311–326. Ed. by P. W. Barnes, D. M. Schell and E. Reimnitz. Orlando: Academic Press 1984
Dunton, K. H.: Trophic dynamics in marine nearshore systems of the Alaskan High Arctic, 247 pp. PhD thesis, University of Alaska-Fairbanks 1985
Dunton, K. H., E. Reimnitz and S. Schonberg: An arctic kelp community in the Alaskan Beaufort Sea. Arctic 35, 465–484 (1982)
Dunton, K. H. and D. M. Schell: Seasonal carbon budget and growth of Laminaria solidungula in the Alaskan High Arctic. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. (In press) (1986)
Fauchald, K. and P. A. Jumars: The diet of worms; a study of polychaete feeding guilds. Oceanogr. mar. Biol. A. Rev. 17, 193–284 (1979)
Fretter, V. and A. Graham: British prosobranch molluses, 755 pp. London: The Ray Society 1962
Fry, B.: Fish and shrimp migrations in the northern Gulf of Mexico analyzed using stable C, N and S isotope ratios. Fish. Bull. U.S. 81, 789–801 (1984a)
Fry, B.: 13C/12C ratios and the trophic importance of algae in Florida Syringodium filiforme seagrass meadows. Mar. Biol. 79, 11–19 (1984b)
Fry, B., R. Lutes, M. Northam, P. L. Parker and J. Ogden: A 13C/12C comparison of food webs in Caribbean seagrass meadows and coral reefs. Aquat. Bot. 14, 389–398 (1982)
Fry, B. and P. L. Parker: Animal diet in Texas seagrass meadoss: δ13C evidence for the importance of benthic plants. Estuar. cstl mar. Sci. 8, 499–509 (1979)
Fry, B., R. S. Scalan and P. L. Parker: 13C/12C ratios in marine food webs of the Torres Strait, Queensland. Austr. J. mar. Freshwat. Res. 34, 707–716 (1983)
Fry, B. and E. B. Sherr: δ13C measurements as indicators of carbon flow in marine and freshwater ecosystems. Contr. mar. Sci. Univ. Tex. 27, 13–47 (1984)
Gibbs, R. J.: Effect of combustion temperature and time, and of the oxidation agent used in organic carbon and nitrogen analyses of sediments and dissolved organic material. J. sedim. Petrol. 47, 547–550 (1977)
Hackney, C. T. and E. B. Haines: Stable carbon isotope composition of fauna and organic matter collected in a Mississippi estuary. Estuar. cstl mar. Sci. 10, 703–708 (1980)
Haines, E. B.: Relation between the stable carbon isotope composition of fiddler crabs, plants and soils in a salt marsh. Limnol. Oceanogr. 21, 880–883 (1976a)
Haines, E. B.: Stable carbon isotope ratios in the biota, soils and tidal water of a Georgia salt marsh. Estuar. cstl mar. Sci. 4, 609–616 (1976b)
Haines, E. B.: The origins of detritus in Georgia salt marsh estuaries. Oikos 29, 254–260 (1977)
Haines, E. B. and C. L. Montague: Food sources of estuarine invertebrates analyzed using 13C/12C ratios. Ecology 60, 48–56 (1979)
Hughes, E. H. and E. B. Sherr: Subtidal food webs in a Georgia estuary; δ13C analysis. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 67, 227–242 (1983)
Incze, L. S., L. M. Mayer, E. B. Sherr and S. A. Macko: Carbon inputs to bivalve mollusks; a comparison of two estuaries. Can J. Fish. aquat. Sciences 39, 1348–1352 (1982)
Johnston, C. S., R. G. Jones and R. D. Hunt: A seasonal carbon budget for a laminarian population in a Scottish sea-loch. Helgoländer wiss. Meeresunters. 30, 527–545 (1977)
Kitting, C. L., B. Fry and M. D. Morgan: Detection of inconspicuous epiphytic algae supporting food webs in seagrass meadows. Oecologia (Berl.) 62, 145–149 (1984)
Lucas, M. I., R. C. Newell and B. Velimirov: Heterotrophic utilisation of mucilage released during fragmentation of kelp (Ecklonia maxima and Laminaria pallida). 2. Differential utilisation of dissolved organic components from kelp mucilage. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 4, 43–55 (1981)
Macko, S. A., M. L. F. Estep and W. Y. Lee: Stable hydrogen isotope analysis of foodwebs on laboratory and field populations of marine amphipods. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 72, 243–249 (1983)
Mann, K. H.: Seaweeds: their productivity and strategy for growth. Science, N.Y. 182, 975–981 (1973)
Mann, K. H.: Decomposition of marine macrophytes. In: The role of terrestrial and aquatic organisms in decomposition processes, pp 247–267. Ed. by J. M. Anderson and A. Macfadyen. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications 1975
McConnaughey, T. and C. P. McRoy: 13C label identifies eelgrass (Zostera marina) carbon in an Alaskan estuarine food web. Mar. Biol. 53, 263–269 (1979)
Minagawa, M., D. A. Winter and I. R. Kaplan: Comparison of Kjeldahl and combustion methods for measurement of nitrogen isotope ratios in organic matter. Analyt. Chem. 56, 1859–1861 (1984)
Mohr, J. L., N. J. Wilimovsky and E. Y. Dawson: An arctic Alaskan kelp bed. Arctic 10, 45–52 (1957)
Morris, R. H., D. P. Abbott and E. C. Haderlie: Intertidal invertebrates of California, 690 pp. Stanford: Stanford University Press 1980
Mullin, M. M., G. H. Rau and R. W. Eppley: Stable nitrogen isotopes in zooplankton; some geographic and temporal variations in the North Pacific. Limnol. Oceanogr. 29, 1267–1273 (1984)
Newell, R. C.: The biological role of detritus in the marine environment. In: Flows of energy and materials in marine ecosystems, pp 317–343. Ed by M. J. R. Fasham. New York: Plenum Press 1984
Newell, R. C. and J. G. Field: The contribution of bacteria and detritus to carbon and nitrogen flow in a benthic community. Mar. Biol. Lett. 4, 23–26 (1983)
Newell, R. C., J. G. Field and C. L. Griffiths: Energy balance and significance of micro-organisms in a kelp bed community. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 8, 103–113 (1982)
Newell, R. C., M. I. Lucas, B. Velimirov and L. J. Seiderer: Quantitative significance of dissolved organic losses following fragmentation of kelp (Ecklonia maxima and Laminaria pallida). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2, 45–59 (1980)
Pearce, J. B. and G. Thorson: The feeding and reproductive biology of the red whelk, Neptunea antiqua (L.). (Gastropoda, Prosobranchia). Ophelia 4, 277–314 (1967)
Peterson, B. J., R. W. Howarth and R. H. Garritt: Multiple stable isotopes used to trace the flow of organic matter in estuarine food webs. Science, N. Y. 227, 1361–1363 (1985)
Reiswig, H. M.: Particle feeding in natural populations of three marine demosponges. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 141, 568–591 (1971)
Robinson, J. D., K. H. Mann and J. A. Novisky: Conversion of the particulate fraction of seaweed detritus to bacterial biomass. Limnol. Oceanogr. 27, 1072–1079 (1982)
Schell, D. M.: Carbon-13 and carbon-14 abundances in Alaskan aquatic organisms; delayed production from peat in Arctic food webs. Science, N. Y. 219, 1068–1071 (1983)
Schell, D. M., P. J. Ziemann, D. M. Parrish, K. H. Dunton and E. J. Brown: Food web and nutrient dynamics in nearshore Alaska Beaufort Sea waters. In: Outer continental shelf environmental assessment program, final report, Vol 25, pp 327–499. Boulder, Colorado: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration 1984
Schwinghamer, P., F. C. Tan and D. C. Gordon, Jr.: Stable carbon isotope studies in Pecks Cove mudflat ecosystem in the Cumberland Basin, Bay of Fundy. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sciences 40 (Suppl. 1), 262–272 (1983)
Simenstad, C. A. and R. C. Wissmar: δ13C evidence of the origins and fates of organic carbon in estuarine and nearshore food webs. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 22, 141–152 (1985)
Sofer, Z.: Preparation of carbon dioxide for stable carbon isotope analysis of petroleum fractions. Analyt. Chem. 52, 1389–1391 (1980)
Stephenson, R. L. and R. L. Lyon: Carbon-13 depletion in an estuarine bivalve; detection of marine and terrestrial food sources. Oecologica (Berl.) 55, 110–113 (1982)
Stephenson, R. L., F. C. Tan and K. H. Mann: Stable carbon isotope variability in marine macrophytes and its implications for food web studies. Mar. Biol. 81, 223–230 (1984)
Stuart, V., J. G. Field and R. C. Newell: Evidence for the absorption of kelp detritus by the ribbed mussel Aulocomya ater using a new 51Cr-labelled microsphere technique. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 9, 263–271 (1982a)
Stuart, V., M. I. Lucas and R. C. Newell: Heterotrophic utilisation of particulate matter from the kelp Laminaria pallida. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 4, 337–348 (1981)
Stuart, V., R. C. Newell and M. I. Lucas: Conversion of kelp debris and faecal material from the mussel Aulocomya ater by marine microorganisms. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 7, 47–57 (1982b)
Suchanek, T. H., S. L. Williams, J. C. Ogden, D. K. Hubbard and I. P. Gill: Utilization of shallow-water seagrass detritus by Caribbean deep-sea macrofauna; δ13C evidence. Deep-Sea Res. 32, 201–214 (1985)
Tenore, K. R.: Utilization of aged detritus derived from different sources by the polychaete Capitella capitata. Mar. Biol. 44, 51–55 (1977a)
Tenore, K. R.: Growth of Capitella capitata cultured on various levels of detritus derived from different sources. Limnol. Oceanogr. 22, 936–941 (1977b)
Tenore, K. R.: Organic nitrogen and caloric content of detritus. Estuar., cstl Shelf Sci. 12, 39–47 (1981)
Toimil, L. J. and J. M. England: Environmental effects of gravel island construction, BF-37, Stefansson Sound, Alaska, 62 pp. Exxon Company, U.S.A., Final Report. Novato, Calif.: Harding-Lawson Associates 1982
Valentine, J. W.: Evolutionary paleoecology of the marine biosphere, 511 pp. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall 1973
Winston, J. E.: Feeding in marine bryozoans. In: Biology of bryozoans, pp 233–271. Ed. by R. M. Woollacott and R. L. Zimmer. New York: Academic Press 1977
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by R. S. Carney, Baton Rouge
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dunton, K.H., Schell, D.M. Dependence of consumers on macroalgal (Laminaria solidungula) carbon in an arctic kelp community: δ13C evidence. Mar. Biol. 93, 615–625 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00392799
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00392799