Abstract
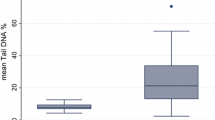
The genotoxic effect of occupational exposure to bitumen-based products was determined by the extent of DNA strand breaks and alkali-labile sites of the DNA of peripheral mononuclear blood cells from seven roofers, 18 road paving workers, and nine bitumen painters. In order to evaluate short-term genotoxic effect the workers were investigated on Fridays and on Mondays after a weekend free of occupational exposure. The roofers (all cigarette smokers) showed a significantly (P < 0.002) 43% higher mean level of alkaline DNA strand breaks on Friday than did the ten smoking controls included in this study. Also, comparison of the individual levels of alkaline strand breaks on Mondays and on Fridays revealed a significant increase (P < 0.05, Wilcoxon test) during the work week. In the road paving workers and the bitumen painters no statistically significant difference in the mean levels of alkaline strand breaks could be found compared to controls either for the measurement on Mondays or for that on Fridays. However, interesting tendencies were observed. As in the group of roofers, the mean level of alkaline DNA strand breaks as well as the majority of the individual levels of alkaline strand breaks of road paving workers was higher on Fridays than on Mondays. In contrast, bitumen painters exhibited a relatively high level of alkaline DNA strand breaks on Mondays and a decreased mean level of strand breaks on Fridays. DNA adducts could be detected at a low level (up to 2.9 adducts per 109 bases) in 10 of 14 road paving workers and bitumen painters using the 32p-postlabelling assay. The number of DNA adducts correlated with the years spent in the present job. Road paving workers and bitumen painters showed only suggestive evidence for a possible genotoxic effect due to their occupational exposure. Because we cannot exclude the formation of DNA cross-links in these workers, a more detailed investigation of the hazard is urgently needed. For roofers, substantial genotoxic damage in peripheral mononuclear blood cells was observed in this study.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bender MA, Awa AA, Brooks AL, Evans HJ, Groer PG, Little-field LG, Pereira C, Preston RJ, Wachholz BW (1988) Current status of cytogenetic procedures to detect and quantify previous exposures to radiation. Mutat Res 196:103–159
Bender AP, Parker DL, Johnson RA, Scharber WK, Williams AN, Marbury MC, Mandel JS (1989) Minnesota highway maintenance worker study: cancer mortality. Am J Ind Med 15:545–556
Boyum A (1964) Separation of white blood cells. Nature 204:793
Chiazze L, Watkins DK, Amsel J (1991) Asphalt and risk of cancer in man. Br J Ind Med 48:538–542
Fuchs J, Wullenweber U, Hengstler JG, Bienfait HG, Hiltl G, Oesch F (1994) Genotoxic risk for humans due to work place exposure to ethylene oxide: remarkable individual differences in susceptibility. Arch Toxicol 68:343–348
Hansen E (1989) Cancer incidence in an occupational cohort exposed to bitumen fumes. Scand J Work Environ Health 15:101–105
Hengstler JG, Fuchs J, Oesch F (1992) DNA strand breaks and DNA cross-links in peripheral mononuclear blood cells of ovarian cancer patients during chemotherapy with cyclophosphamide/carboplatin. Cancer Res 52:5622–5626
Herbert R, Marcus M, Wolff MS, Perera FP, Andrews L, Godbold JH, Rivera M, Stefanidis M, Lu XQ, Landrigan PJ, Santella RM (1990) Detection of adducts of deoxyribonucleic acid in white blood cells of roofers by 32P-postlabeling. Scand J Work Environ Health 16:135–143
Holmes GE, Bernstein C, Bernstein H (1992) Oxidative and other DNA damages as the basis of aging: a review. Mutat Res 275:305–315
IARC (1985) Monographs on the evaluation of the carcinogenic risk of chemicals to humans, vol 35. IARC, Lyon, France, pp 39–81
Jongeneelen FJ, Scheepers PLJ, Groenendijk A, van Aerts LAGJM, Anzion RBM, Bos RP, Veenstra SJ (1988) Airborne concentrations, skin contamination, and urinary metabolite excretion of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons among paving workers exposed to coal tar derived road tars. Am Ing Hyg Assoc J 49:600–607
Knecht U, Woitowitz HJ (1989) Risk of cancer from the use of tar bitumen in road workers. Br J Ind Med 46:24–30
Leadon SA, Cerutti PA (1982) A rapid and mild procedure for the isolation of DNA from mammalian cells. Anal Biochem 120:282–288
Machado ML, Beatty PW; Fetzer JC, Glickman AH, McGinnis EL (1993) Evaluation of the relationship between PAH content and mutagenic activity of fumes from roofing and paving asphalts and coal tar pitch. Fundam Appl Toxicol 21:492–499
Monarca S, Pasquini R, Scassellati-Sforzolini G, Savino A, Bauleo FA, Angeli G (1987) Environmental monitoring of mutagenic/carcinogenic hazards during road paving operations with bitumens. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 59:393–402
Oesch F, Hengstler JG, Fuchs J (1994) Cigarette smoking protects mononuclear blood cells of carcinogen exposed workers from additional work-exposure-induced DNA single strand breaks. Mutat Res 321:175–185
Ovrebo S, Haugen A, Phillips DA, Hewer A (1992) Detection of polycyclic hydrocarbon-DNA adducts in white blood cells from coke oven workers: correlation with job categories. Cancer Res 52:1510–1514
Partanen T, Boffetta P (1994) Cancer risk in asphalt workers and roofers: review and meta-analysis of epidemiological studies. Am J Ind Med 26:721–740
Phillips DH, Hemminki K, Alhonen A, Hewer A, Grover PL, Randerath K (1988) Monitoring occupational exposure to carcinogens: detection by 32P-postlabelling of aromatic DNA adducts in white blood cells of iron foundry workers. Mutat Res 204:531–541
Popp W, Vahrenholz C, Yaman S, Müller C, Müller G, Schmieding W, Norpoth K, Fahnert R (1992) Investigation of the frequency of DNA strand breakage and cross-linking and of sister chromatid exchange frequency in lymphocytes of female workers exposed to benzene and toluene. Carcinogenesis 13:57–61
Randerath E, Agrawal HP, Weaver JA, Bordelon CB, Randerrath K (1985) 32P-Postlabeling analysis of DNA adducts persisting for up to 42 weeks in the skin, epidermis and dermis of mice treated topically with 7,12-dimethylbenz[α]anthracene. Carcinogenesis 6:1117–1126
Randerath K, Putman KL, Osterburg HH, Johnson SA, Morgan DG, Finch CE (1993) Age-dependent increases of DNA adducts (I-compounds) in human and rat brain. Mutat Res 295: 11–18
Reddy MV, Randerath K (1986) Nuclease P1-mediated enhancement of sensitivity of 32P-postlabeling test for structurally diverse DNA adducts. Carcinogenesis 7:1543–1551
Walles SA, Edling C, Amundi H, Johanson G (1993) Exposure dependent increase in DNA single strand breaks in leucocytes from workers exposed to low concentrations of styrene. Br J Ind Med 50:570–574
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study contains parts of an M.D. thesis by G. Boettler
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fuchs, J., Hengstler, J.G. & Oesch, G.B.F. Primary DNA damage in peripheral mononuclear blood cells of workers exposed to bitumen-based products. Int. Arch Occup Environ Heath 68, 141–146 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00381622
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00381622