Abstract
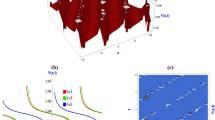
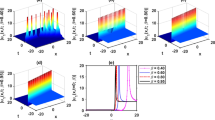
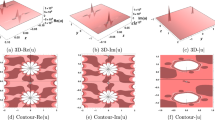
High-order finite element discretizations of the reduced wave equation have frequency bands where the solutions are harmonic decaying waves. In these so called “stopping” bands, the solutions are not purely propagating (real wavenumbers) but are attenuated (complex wavenumbers). In this paper we extend the standard dispersion analysis technique to include complex wavenumbers. We then use this complex Fourier analysis technique to examine the dispersion and attenuation characteristics of the p-version finite element method. Practical guidelines are reported for phase and amplitude accuracy in terms of the spectral order and the number of elements per wavelength.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AbboundN. N., PinskyP. M. (1992): Finite element dispersion analysis for the three-dimensional second-order scalar wave equation. Int. J. Number Meth. Eng. 35, 1183–1218
Alvin, K. F.; Park, K. C. (1991): Frequency-window tailoring of finite element models for vibration and acoustics analysis. In: Keltie, R. F. (ed): Structural acoustics. vol. NCA-vol. 12/AMD-vol. 128, pp. 117–128. ASME
BabuskaI.; CraigA.; MandelJ. (1991): Efficient preconditioning for the p-version finite element method in two-dimensions. SIAM J. Num. Anal. 28, 624–661
BauskaI.; SuriM. (1990): The p- and h-p versions of the finite element method,an overview. Comp. Meth. in Appl. Mech. Eng. 80, 5–26
BarragyE.; CareyG. F. (1991): Preconditioners for high degree elements. Comp. Meth. in Appl. Mech. Eng. 93, 97–110
BaylissA.; GoldsteinC. I.; TurkelE. (1985). On accuracy conditions for the numerical computation of waves. J. Comp. Phys. 59, 396–404
Bellanger, M. (1989): Digital Processing of Signals. John Wiley and Sons
BelytschkoT. B.; MindleW. L. (1980): Flexural wave propagation behaviour of lumped mass approximations. Comput. Struct. 12, 805–812
Belytschko, T. B.; Mullen, R. (1978): On dispersive properties of finite element solutions. In: Miklowitz, J. (ed.): Modern problems in elastic wave propagation, pp. 67–82
Brillouin, L. (1953): Wave propagation in periodic structures. Dover
Canuto, C.; Hussaini, M. Y.; Quarternoni, A.; Zang, T. A. (1988): Spectral methods in fluid dynamics. Springer-Verlag
Churchill, R. V.; Brown, J. W.; Verhey, R. F. (1976): Complex variables and applications. McGraw-Hill
DevilleM. O.; MundE. H. (1992): Fourier analysis of finite element preconditioned collocation schemes. SIAM J. Sci. Stat. Comp. 13, 596–610
Fischer, P. F.; Patera, A. T. (1991): Parallel spectral element methods for the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations. In: Supercomputing, pp. 71–143. ASME
FribergO.; MollerP. (1987): An adaptive procedure for eigenvalue problems using the hierarchical finite element method. Int. J. Num. Meth. Ing. 24, 319–335
Grosh, K.; Pinsky, P. M. (1992): Complex wavenumber finite element dispersion analysis: in vacuo and fluid-loaded plates. Submitted to: Comp. Meth. in Appl. Mech. Eng.
Harari, I.; Hughes, T. J. R. (1991a): Computational methods for problems of acoustics with particular reference to exterior domains. Tech. Report SUDAM No. 91-1, Stanford University
HarariI.; HughesT. J. R. (1991b): Finite element methods for the Helmholtz equation in an exterior domain: Model problems. Compl. Meth. in Appl. Mech. Eng. 87, 59–96
HughesT. J. R.; FrancaL. P.; HulbertG. M. (1989): A new finite element formulation for computational fluid dynamics: VIII. The galerkin least squares method for advective-diffusive equations. Comp. Meth. in Appl. Mech. Eng. 73, 173–189
Jasti, R. (1992): Mixed shell finite elements with applications in structural acoustics. Ph.D. Thesis, Stanford University
Maday, Y.; Patera, A. T. (1989): Spectral element methods for the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations. In: Noor, A. K.; Oden, J. T. (ed.): State-of-the-art surveys on computational mechanics, pp. 71–143, ASME
MindleW. L.; BelytschkoT. (1983): A study of shear factors in reduced-selective integration Mindlin beam elements. Comput. Struct. 17, 339–344
ParkK. C.; FlaggsD. L. (1984): A Fourier analysis of spurious mechanisms and locking in the finite element method. Comp. Meth. in Appl. Mech. Eng. 46, 65–81
ParkK. C.; FlaggsD. L. (1985): A symbolic Fourier synthesis of a one-point integrated quadrilateral plate element. Comp. Meth. in Appl. Mech. Eng. 48, 805–812
PateraA. T. (1984): A spectral element method for fluid dynamics: Laminar flow in a channel expansion. J. Comp. Phys. 54, 468–488
ShakibF.; HughesT. J. R. (1991): A new finite element formulation for computational fluid dynamics: IX Fourier analysis of space-time Galerkin/least-squares algorithms. Comp. Meth. in Appl. Mech. Eng. 87, 35–58
SilvaM. A. G. (1991): Study of pass and stop bands of some periodic composites. Acustica 75, 62–68
Szabo, B.; Babuska, I. (1991): Finite element analysis. Wiley
Thompson, L. L.; Pinsky, P. M. (1993): A Galerkin/least-squares finite element method for the two-dimensional Helmholtz equation. Submitted to: Int. J. Num. Meth. Eng.
UnderwoodP. (1974): Accuracy of finite difference representations for the transients response analysis of shells. Earthquake Eng. and Struc. Dynam. 2, 219–233
Voight, R. G.; Gottlieb, D.; Hussaini, M. Y. (1984): Spectral methods for partial differential equations. SIAM
Wolfram, S. (1991): Mathematica. Addison-Wesley
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by S. N. Atluri, March 30, 1993
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thompson, L.L., Pinsky, P.M. Complex wavenumber Fourier analysis of the p-version finite element method. Computational Mechanics 13, 255–275 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00350228
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00350228