Summary
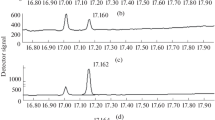
In order to reduce the health risks in solvent technology, produced by the largely used ethylene glycol ethers, these are getting more and more substituted by glycol ethers derived from propylene glycol. According to the current knowledge these also called 1-alkoxy-2-propanols are to a considerable amount excreted unmetabolized in urine; so these substances themselves might be used for the estimation of health risks. The sensitive analysis consists of a special extraction step using diatomaceous earth. The extract is then concentrated for further gas-chromatographic investigation (FID). Using this technique, 17 in part widely used glycol ethers in urine were determined.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miller RR, Hermann EA, Young JT, Landry TD, Calhoun LL (1984) Environ Health Pers 57:233–239
European Chemical Industry Ecology & Technology Centre (ECETOC) (1985) technical report No 17
Begerow E, Angerer J (1990) Fresenius J Anal Chem 366: 42–43
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hubner, B., Geibel, K. & Angerer, J. Gas-chromatographic determination of propylene- and diethylene glycol ethers in urine. Fresenius J Anal Chem 342, 746–748 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00321870
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00321870