Summary
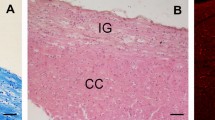
The presence of macrophages in the developing corpus callosum of fetal and neonatal rats is confirmed using ultrastructural, immunocytochemical and histochemical techniques. The macrophages are first seen in the corpus callosum at about the time the callosal axons cross the midline and penetrate the cerebral hemispheres and they persist until about 10 days postnatal. The cells are found in the corpus callosum dorsal to the lateral ventricle, in the sub-ventricular zone and in the forming cavum septi pellucidi. The macrophages were identified at the light and electron microscopic level, including labelling of the cells following an intracerebral injection of horseradish peroxidase. The cells were also positive for an esterase stain specific for blood monocytes and macrophages and were labelled with a monoclonal antibody directed against macrophage cell surface polypeptides (Springer et al. 1979). These observations confirm the non-neuroepithelial origin of certain forms of phagocytic cells during cerebral development.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JC (1977) Technical considerations on the use of horseradish peroxidase as a neuronal marker. Neurosci 2:141–145
Caley DW, Maxwell DS (1968) An electron microscopic study of the neuroglia during postnatal development of the cerebrum. J Comp Neurol 133:45–70
Carr I (1973) The macrophage. A review of ultrastructure and function. Academic Press, London New York
Choi BH (1981) Hematogenous cells in the central nervous system of developing human embryos and fetuses. J Comp Neurol 196:683–694
Das GD (1976) Resting and reactive macrophages in the developing cerebellum. An experimental ultrastructural study. Virchows Arch B 20:287–298
Del Rio Hortega P (1932) Microglia. In: W Penfield (ed) Cytology and cellular pathology of the nervous system, Vol II. Paul B Hoeber Inc, New York, pp 483–534
DeOlmos J, Hardy H, Heimer L (1978) The afferent connections of the main and the accessory olfactory bulb formations in the rat: An experimental HRP study. J Comp Neurol 181:213–244
Eng LF, Bigbee JW (1978) Immunohistochemistry of nervous system specific antigens. Adv Neurochem 3:43–98
Ghandour MS, Langley OK, Labourdette G, Vincedon B, Gombos G (1981) Specific and artefactual cellular localizations of S100 protein: An astrocyte marker in rat cerebellum. Dev Neurosci 4:68–78
Imamoto K, Leblond CP (1978) Radioautographic investigation of gliogenesis in the corpus callosum of young rats. II. Origin of microglial cells. J Comp Neurol 180:139–164
Ivy GO, Killackey H (1978) Transient populations of glial cells in developing rat telencephalon revealed by horseradish peroxidase. Brain Res 158:213–218
Konigsmark BW, Sidman RL (1963) Origin of brain macrophages in the mouse. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 22:643–676
Langford LA, Coggeshall RE (1980) The use of potassium ferricyanide in neural fixation. Anat Rec 197:297–303
LaVail JH, LaVail MM (1974) The retrograde intraaxonal transport of horseradish peroxidase in the chick visual system: A light and electron microscopic study. J Comp Neurol 157:303–357
Li CY, Lam KW, Yam LT (1973) Esterase in human leukocytes. J Histochem Cytochem 21:1–12
Ling EA (1976) Some aspects of ameboid microglia in the corpus callosum and neighboring regions of neonatal rats. J Anat 121:29–45
Ling EA, Tan CK (1974) Amoeboid microglial cells in the corpus callosum of neonatal rats. Arch Histol Jap 36:265–280
Ling EA, Penney D, Leblond CP (1980) Use of carbon labeling to demonstrate the role of blood monocytes as precursors of the “ameboid cells” present in corpus callosum of postnatal rats. J Comp Neurol 193:631–657
Mirsky R, Thompson EJ (1975) Thy-1 (theta) antigen on the surface of morphologically distinct brain cell types. Cell 4:95–101
Moore BW (1965) A soluble protein characteristic of the nervous system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 6:739–744
Reif AE, Allen JMV (1964) The AKR thymic antigen and its distribution in leukemias and nervous tissue. J Exp Med 120:413–433
Schmechel DE, Rakic R (1979) A Golgi study of radial glial cells in developing monkey telencephalon: Morphogenesis and transformation into astrocytes. Anat Embryol 156:115–152
Springer T, Galfre G, Secher DS, Milstein C (1979) Mac-1: A macrophage differentiation antigen identified by monoclonal antibody. Eur J Immunol 9:301–306
Stensaas LJ, Reichert WH (1971) Round and amoeboid microglial cells in the neonatal rabbit brain. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat 119:146–163
Sturrock RR (1976) Light microscopic identification of immature glial cells in semithin sections of the developing mouse corpus callosum. J Anat 122:521–537
Sturrock RR (1978) A developmental study of epiplexus cells and supraependymal cells and their possible relationship to microglia. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 4:307–322
Sutton JS (1967) Ultrastructural aspects of in vitro development of monocytes into macrophages, epithelioid cells, and multinucleated giant cells. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr 26:71–141
Valentino KL, Jones EG (1980) An electron microscopic study of the developing corpus callosum in fetal and neonatal rats. Neurosci Abstr 6:161–163
Vaughn JE, Peters A (1968) A third neuroglial cell type. An electron microscopic study. J Comp Neurol 133:267–288
Vaughn JE, Hinds PL, Skoff RP (1970) Electron microscopic studies of Wallerian degeneration in rat optic nerves. I. The multipotential glia. J Comp Neurol 140:175–206
Wise SP, Fleshman JW, Jones EG (1979) maturation of pyramidal cell form in relation to developing afferent and efferent connections of rat somatic sensory cortex. Neurosci 4:1275–1297
Yam LT, Li CY, Croty WH (1971) Cytochemical identification of monocytes and granulocytes. Am J Clin Pathol 55:283–290
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Valentino, K.L., Jones, E.G. Morphological and immunocytochemical identification of macrophages in the developing corpus callosum. Anat Embryol 163, 157–172 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00320673
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00320673