Summary
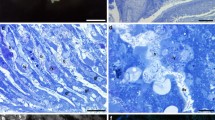
The gills of four lucinid bivalves from fine sediments in shallow reaches of Bermuda, Anodontia philippiana, Lucina multilineata, L. radians, and L. costata, were observed by electron microscope. They harbour intracellular bacterial endosymbionts similar to those in gills of clams from hydrothermal vents and other ‘sulphide biotopes’. The bacteria-containing bacteriocytes are found in distinct positions in the gill filaments, alternating with cells not invaded by the prokaryotes but with abundant mitochondria. Referring to the specific environment of the collected bivalves and to literature data from corresponding studies, the significance of this bacteria/animal association is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen JA (1958) On the basic form and adaptations to habitat in the Lucinacea (Eulamellibranchia). Phil Trans R Soc Lond B 241:421–484
Arp AJ, Childress JJ (1983) Sulfide binding by the blood of the hydrothermal vent tube worm Riftia pachyptila. Science 219:295–297
Berg CJ Jr, Alatalo P (1981) Laboratory culture of Bahamian bivalve molluscs: reproduction and general biology. Biol Bull 161:337–338
Berg CJ Jr, Alatalo P (1982) Reproductive strategies of bivalve mollusks from deep-sea hydrothermal vents and intertidal sulfide-rich environments. Biol Bull 163:397
Bretsky SS (1976) Evolution and classification of the Lucinidae (Mollusca; Bivalvia). Palaeontograph Am 8(50):215–337
Brown BE (1982) The form and function of metal-containing ‘granules’ in invertebrate tissues. Biol Rev 57:621–667
Cavanaugh CM (1983) Symbiotic chemoautotrophic bacteria in marine invertebrates from sulphide-rich habitats. Nature 302 (5903):58–61
Cavanaugh CM, Gardiner SL, Jones ML, Jannasch HW, Waterbury JB (1981) Prokaryotic cells in the hydrothermal vent tube worm Riftia pachyptila Jones: Possible chemoautotrophic symbionts. Science 213:340–342
Childress JJ, Mickel TJ (1982) Oxygen and sulfide consumption rates of the vent clam Calyptogena pacifica. Mar Biol Lett 3:73–80
Childress JJ, Arp AJ, Fisher CR Jr (1984) Metabolic and blood characteristics of the hydrothermal vent tube-worm Riftia pachyptila. Mar Biol 83:109–124
Doeller JE, Kraus DW, Colacino JM (1983) The presence of hemoglobin in Solemya velum (Bivalvia, Protobranchia). Am Zool 23:976
Felbeck H (1983) Sulfide oxidation and carbon fixation by the gutless clam Solemya reidi: an animal-bacteria symbiosis. J Comp Physiol 152:3–11
Felbeck H, Childress JJ, Somero GN (1981) Calvin-Benson cycle and sulphide oxidation enzymes in animals from sulphide-rich habitats. Nature 293:291–293
Felbeck H, Childress JJ, Somero GN (1983) Biochemical interactions between molluscs and their algal and bacterial symbionts. In: Hochachka PW (ed) The Mollusca, Vol 2: Environmental biochemistry and physiology. Academic Press, New York, pp 331–358
Fiala-Medioni A (1984) Mise en évidence par microscopie électronique à transmission de l'abondance de bactéries symbiotiques dans la branchie de Mollusques bivalves de sources hydrothermales profondes. C R Acad Sc Paris 298, sér 3, no 17:487–492
Fisher MR, Hand SC (1984) Chemoautotrophic symbionts in the bivalve Lucina floridana from seagrass beds. Biol Bull 167:445–459
George SG, Pirie BJS, Coombs TL (1975) Absorption, accumulation and excretion of iron complexes by Mytilus edulis (L). Proceedings of the International Conference on Heavy Metals in the Environment, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, Oct. 27–31, 1975, pp 887–900
Giere O (1981) The gutless marine oligochaete Phallodrilus leukodermatus. Structural studies on an aberrant tubificid associated with bacteria. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 5:353–357
Giere O (1985) The gutless marine tubificid Phallodrilus planus, a flattened oligochaete with symbiotic bacteria. Results from morphological and ecological studies. Zool Scr (in press)
Giere O, Liebezeit G, Dawson R (1982) Habitat conditions and distribution pattern of the gutless oligochaete Phallodrilus leukodermatus. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 8:291–299
Giere O, Felbeck H, Dawson R, Liebezeit G (1984) The gutless oligochaete Phallodrilus leukodermatus Giere, a tubificid of structural, ecological and physiological relevance. Hydrobiologia 115:83–89
Kuenen JG (1975) Colourless sulfur bacteria and their role in the sulfur cycle. Plant Soil 43:49–76
Powell MA, Somero GN (1983) Blood components prevent sulfide poisoning of respiration of the hydrothermal vent tube worm Riftia pachyptila. Science 219:297–299
Prentø P (1979) Metals and phosphate in the chloragosomes of Lumbricus terrestris and their possible physiological significance. Cell Tissue Res 196:123–134
Read KRH (1962) The hemoglobin of the bivalved mollusc Phacoides pectinatus Gmelin. Biol Bull 123:605–617
Reid RGB (1980) Aspects of the biology of a gutless species of Solemya (Bivalvia: Protobranchia). Can J Zool 58:386–393
Rona PA, Bostrom K, Laubier L, Smith KL Jr (eds) Hydrothermal processes at seafloor spreading centers. NATO Conference Series IV, Marine Sciences. Plenum Publishing Corporation, New York, pp 770
Schweimanns M, Felbeck H (1985) Significance of the occurrence of chemoautotrophic bacterial endosymbionts in lucinid clams from Bermuda. Mar Ecol Prog Ser (in press)
Shively JM, Ball F, Brown DH, Saunders RE (1973) Functional organelles in prokaryotes: Polyhedral inclusions (carboxysomes) of Thiobacillus neapolitanus. Science 182:584–586
Shively JM, Decker GL, Greenawalt JW (1970) Comparative ultrastructure of the Thiobacilli. J Bacteriol 101:618–627
Dando PR, Southward AJ, Southward EC, Terwilliger NB, Terwilliger RC (1985) Sulphur-oxidising bacteria and haemoglobin in gills of the bivalve mollusc Myrtea spinifera. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 23:85–98
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giere, O. Structure and position of bacterial endosymbionts in the gill filaments of lucinidae from bermuda (Mollusca, Bivalvia). Zoomorphology 105, 296–301 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00312060
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00312060